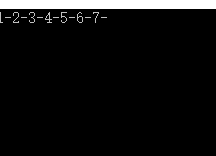
案例一:随机获取0-100之间7个不重复的数(如10,27,18,36,15,5,33)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 随机获取0_100之间7个不重复的数
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//先定义一个随机函数
Random r = new Random();
//定义一个数组来装这7个数
int[] array=new int[7];
//定义一个i 表示索引值
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
//Random对象有一个“Next”无参随机正整数,取值范围是 0-2147483647,返回值为int类型 可以取到0但是取不到101
array[i] = r.Next(0,101);
//当索引值大于0的时候
//定义一个k用来和第一次循环作比较
for (int k = 0; k < i; k++)
{
//如果两次循环的数值相等的话
if (array[i]==array[k])
{
//我们让它重新随机
i--;
}
}
}
//我们把符合上面条件的数字写在控制台上
for (int h = 0; h <array.Length; h++)
{
Console.WriteLine(array[h]+"-");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}

案例2:随机获取0-9之间6个数,并保证两两相同(如:1,2,3,2,1,3)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//先定义一个随机函数
Random r = new Random();
//定义一个数组Basse 为我们所需要的6个数
int[] basse = new int[6];
//定义一个数组array 为6个数中的三个不同的数(3对)
int[] array = new int[3];
//先获取到三个不同的数的索引
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
// if (i>0)
// {
//这6个数的取值范围是0-9 表示方法.next(0,10)能取到0但是不能取到10
array[i] = r.Next(0, 10);
//在定义一个j表示另外一个数的索引
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
//假如第一个数和第二个数相等 则重新获取数
if (array[i] == array[j])
{
i--;
}
}
// }
}
//先获取到六个不同的数的索引
for (int i = 0; i < basse.Length; i++)
{
//我们让他在3个数中随机 用index来接收下
int index = r.Next(array.Length);
basse[i] = array[index];
//定义一个变量count
int count = 0;
//在定义一个j表示另外一个数的索引
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (i>0)
{
// 我们用第一个数和第二个数作比较 如果第一个数和第二个数一样 则储存下来
if (basse[i] == basse[j])
{
count++;
//假如储存了两个数的话 那就说明有三个数相同 此时我们就需要重新在三个数中重新获取
if (count == 2)
// 第一种条件
//if (count > 2)//第二种条件
{
i--;
}
}
}
}
}
//把我们所得到的6个数便利出来写在控制台上
for (int i = 0; i < basse.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(basse[i]+"-");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
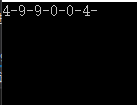
案例三:随机获取0-100之间的(n^2)个数,并保证数字是n个相同(如:1,4,5,5,1,4,4,5,1)
我们这里举的是9个数三三相同(如:1,2,3,1,2,3,1,2,3)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 随机获取0_100之间的_n_2_个数_并保证数字是n个相同_1_4_5_5_1_4_4_5_1_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//先定义一个随机函数
Random r = new Random();
//定义一个数组Basse 为我们所需要的9个数
int n;
int[] basse = new int[9];
//定义一个数组array 为9个数中的三个不同的数(3对)
int[] array = new int[3];
//先获取到三个不同的数的索引
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
// if (i>0)
// {
//这6个数的取值范围是0-100 表示方法.next(0,101)能取到0但是不能取到101
array[i] = r.Next(0, 101);
//在定义一个j表示另外一个数的索引
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
//假如第一个数和第二个数相等 则重新获取数
if (array[i] == array[j])
{
i--;
}
}
// }
}
//先获取到9个不同的数的索引
for (int i = 0; i < basse.Length; i++)
{
// if (i>0)
//我们让他在3个数中随机 用index来接收下
int index = r.Next(array.Length);
basse[i] = array[index];
//定义一个变量count
int count = 0;
//在定义一个j表示另外一个数的索引
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (i > 0)
{
//把第一次个数和第二个数作比较
if (basse[i] == basse[j])
{
//如果相同 我们把他们储存下来
count++;
//假如储存了三个数的话 那就说明有四个数相同 此时我们就需要重新在三个数中重新获取
// 第一种条件if(count==3)
if (count >2)//第二种条件
{
i--;
}
}
}
}
// }
}
//把我们所得到的9个数便利出来写在控制台上
for (int i = 0; i < basse.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(basse[i]+"-");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
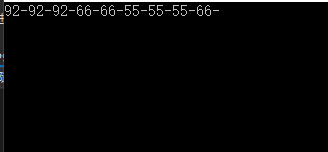
案例四:针对一个数组进行去重
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] list = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5, 6, 3, 4, 6, 7, 1 };
int[] res;
string str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < list.Length; j++)
{
//将出现的重复的索引获取到
if (list[i]==list[j])
{
str += j.ToString() + ",";
}
}
}
string[] index = str.Split(new char[] { ','});
string liststr = "";
for (int i = 0; i < list.Length; i++)
{
bool istrue = false;
for (int j = 0; j < index.Length; j++)
{
if (index[j]!=""&&i == int.Parse(index[j]))
{
istrue = true;
}
}
if (!istrue)
{
liststr += list[i] + ",";
}
}
string[] num = liststr.Split(new char[] { ',' });
res = new int[num.Length-1];
for (int i = 0; i < num.Length-1; i++)
{
res[i] = int.Parse(num[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < res.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(res[i]+"-");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
案例五:输入一个身份证号,判断是否是合法身份证号(长度),如果是合法身份证号则返回出生年月日
这里我们只是按照长度来判断
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 输入一个身份证号_判断是否是合法身份证号_长度__如果是合法身份证号则返回出生年月日
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入身份证号码:");
//设置在控制台中随机输入一组数字
string str=Console.ReadLine();
//假如这组数字的长度是18个字符
if (str.Length==18)
{
//我们从索引值为6开始截取,截取后面4个数
string a = str.Substring(6,4);
//我们从索引值为10开始截取,截取后面2个数
string b = str.Substring(10, 2);
//我们从索引值为12开始截取,截取后面2个数
string c = str.Substring(12, 2);
Console.Write("您的出生年月日为:"+a+"年");
Console.Write(b + "月");
Console.Write(c + "日");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入正确的身份证格式");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}

案例六:随便输入一个ID号(英文字母+数字)将ID号中的所有字母大写,并将"O"(ou)和“I”换成“0”和“1”
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 随便输入一个ID号将ID号中的所有字母大写_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//先随意输入一个字符串
Console.WriteLine("请输入ID:");
string s = Console.ReadLine();
//我们让这个字符串变成大写
string arr =s.ToUpper();
//把大写的内容显示在控制台上
Console.WriteLine("大写之后为:"+arr);
//然后把大写的o和i替换成0和1.再定义一个str来接收
string str = arr.Replace("O", "0").Replace("I", "1");
//然后写在控制台上
Console.WriteLine("替换之后为:" + str);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
























 16
16

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








