import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_date = np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)[:,np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_date.shape)
y_date = x_date*0.1+0.2+noise
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
L1 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(x,w)+b)
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1]))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
L2 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(L1,w2)+b2)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-L2))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for _ in range(1000):
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:x_date,y:y_date})
producton_value = sess.run(L2,feed_dict={x:x_date})
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(x_date,y_date)
plt.plot(x_date,producton_value,‘r-’,lw=5)
plt.show()
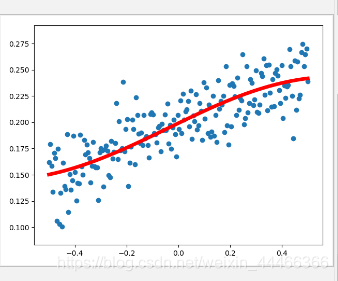
将代码L2 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(L1,w2)+b2)改为L2 = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(L1,w2)+b2为什么结果就变成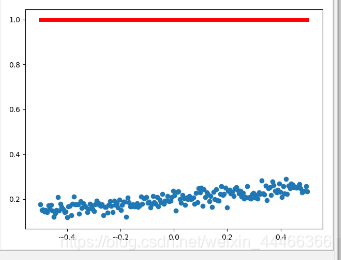







 本文通过使用TensorFlow和NumPy库,展示了如何构建并训练一个具有两层的神经网络来拟合一组带有噪声的数据。首先,生成了线性的数据并添加了随机噪声。然后,定义了占位符、变量和计算图,包括使用tanh激活函数的隐藏层和输出层。在会话中初始化所有变量后,进行了1000次迭代训练,每次迭代都更新权重和偏置以最小化损失函数。最后,绘制了预测值与实际值的对比图。
本文通过使用TensorFlow和NumPy库,展示了如何构建并训练一个具有两层的神经网络来拟合一组带有噪声的数据。首先,生成了线性的数据并添加了随机噪声。然后,定义了占位符、变量和计算图,包括使用tanh激活函数的隐藏层和输出层。在会话中初始化所有变量后,进行了1000次迭代训练,每次迭代都更新权重和偏置以最小化损失函数。最后,绘制了预测值与实际值的对比图。
















 411
411

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








