Deadlock
Deadlock
- (一) Def : Deadlock 意思是系統中存在一組 process 陷入互相等待對方所擁有的資源的情況(Circular Waiting),造成所有的 process 無法往下執行,使得 CPU 利用度大幅降低,thoughput下降。
- (二) Deadlock 發生須符合以下 4 項充要條件
- (1) Mutual exclusion:某些資源在同一個時間點最多只能被一個 process 使用
- 例:大部分的 Resource 都是互斥使用 e.g. CPU,memory,I/O-device…
- 例:Read-only File 不受互斥影響
- (2) Hold and wait:某 process 持有部分資源,並等待其他 process 正在持有的資源
- (3) No preemption:process 不可以任意強奪其他 process 所持有的資源
- (4) Circular waiting:系統中存在一組 processes P=P0,P1,…,Pn,其中 P0 等待 P1 所持有的資源 … Pn 等待 P0 所持有的資源,形成循環式等待。(因此,deadlock不會存在於single process環境中)
- (1) Mutual exclusion:某些資源在同一個時間點最多只能被一個 process 使用
- (三) 例子
- I. 系統面
- II. 日常生活面
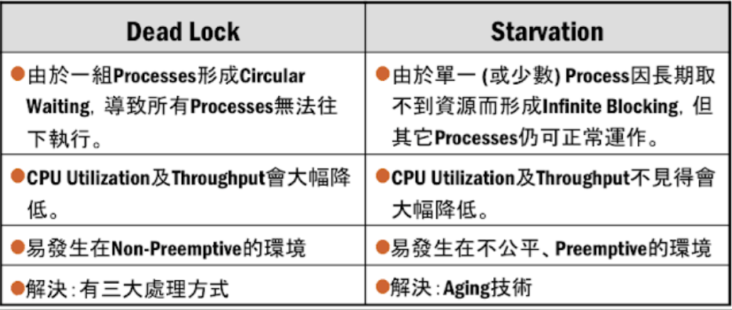
- (四) Deadlock v.s Starvation
Deadlock 處理方法
Deadlock 三種處理方法:
- Deadlock prevention
- Deadlock avoidance
- Deadlock detection & recovery
prevention 和 avoidance
- 優點 : 保證系統不會進入 Deadlock
- 缺點 : 資源利用度低,且可能有 Starvation 問題
detection & recovery
- 優點 : 資源利用度較高
- 缺點 : recovery cost 極高,且可能進入 Deadlock State
1.Deadlock prevention
打破必要條件四項之一,即可保證 Deadlock 永不發生。
- 打破 Mutual exclusion:為資源與生俱來之性質,無法打破。
- 打破 Hold and wait:系統產能低。
- [法一] 規定 : 除非 proces 可以一次取得所有工作所需的資源,才允許持有資源。
- [法二] 規定 : process 執行之初可持有部分資源,但要再申請資源前,要先釋放手中所有資源。
- 打破 No Preemption : 改成 “Preemption” 即可,but 讓高優先 process 搶低優先 process 的資源,會造成 starvation。
- 打破 Circular waiting:Process須按照資源編號(unique resource ID)遞增(Ascending)方式申請資源。
2.Deadlock avoidance
當 process 提出資源申請時,OS 會執行Banker algorithm 來判斷系統在「假設核准該申請後」是否處於 Safe state,是則核准,否則請 process 等待。
- safe state : 至少存在 ≧1組 safe sequence , O.S 按照 order 分配 Resource
- unsafe state : 可能有 deadlock
- Time Complexity : O(n^2*m) -> 耗時,耗成本
//假設有 n 個 process , m 種 resource
int Request[m] //Process申請量
int Available[m] //系統目前各類資源的可用數量。(Available = 資源總量 - Allocation)
int Max[n,m] //各 process 需要多少資源才可以完成工作。
int Allocation[n,m] //目前各 process 持有的資源量。
int Need[n,m] //還要多少資源才可以完成工作。 (Need = Max - Allocation)
void Banker_Algo()
{
if(Request_i <= Need_i)//檢查需求之合理性 O(m)
{
if(Request_i < Available)//檢察系統可否負擔 O(m)
{
Allocation_i = Allocation_i + Request_i; // O(m)
Need_i = Need_i -Request_i;
Available = Available - Request_i;
if(Safe()=="Safe")
return "核准申請";
else if(Safe()=="Unsafe")
return "否決申請";
}
else
Process_i wait until 系統資源足夠;
}
else
終止 Process_i;
}
int Work[m] //系統目前可用的資源累計數量
bool Finish[n] //True:表Pi完工 ; False:Pi尚未完工
void Safe()
{
while( Finish is not all TRUE )
{
Work = Available; //初始設定 O(m)
foreach(bool initial in Finish) //初始設定
{
initial = false; // O(n)
}
foreach (i in process set P) //check finish O(n)
{
//最多檢查 process 數目 = n + (n-1) + ...+ 1 = n(n+1)/2
if(Finish[i] == false && Need_i <= Work[i]) // O(m)
{
Finish[i] == true;
Work = Work + Allocation; // O(m)
P = P - {i};
}
}
if (!Finish) return Unsafe;
}
return Safe;
}
3. Deadlock Detection & Recovery
Allow system to enter deadlock state
Recovery 方法
- 1.kill processes in Deadlock
- kill “all” 全部刪除
⇒ Cost 高 : processes 先前的工作成果全做白工 or process 數目太多 - kill “one” then detect again 一次刪一個 process,直到打破 deadlock
⇒ Cost 高 : loop 次數高 x detect cost
- kill “all” 全部刪除
- 2.Resource Preemption 資源搶奪
- 挑選 victim process -> 剝奪其資源(可能造成 starvation) -> 恢復無該資源前狀態(cost 高)
Detection algorithm
- Single instance : topological sort (using wait-for graph)
- 使用 adjcent matrix : O(n2)
- 使用 adjcent list : O(V+E)
- Several instance : 用 Banker algorithm 判斷系統是否已經在 unsafe state
Resource allocation graph
Some facts about RAG :
- If graph contains no cycles ⇒ no deadlock.
- If graph contains a cycle
- one instance ⇔ deadlock.
- several instances, possibility of deadlock. ( deadlock ⇒ cycle )





















 221
221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








