- open函数
参数说明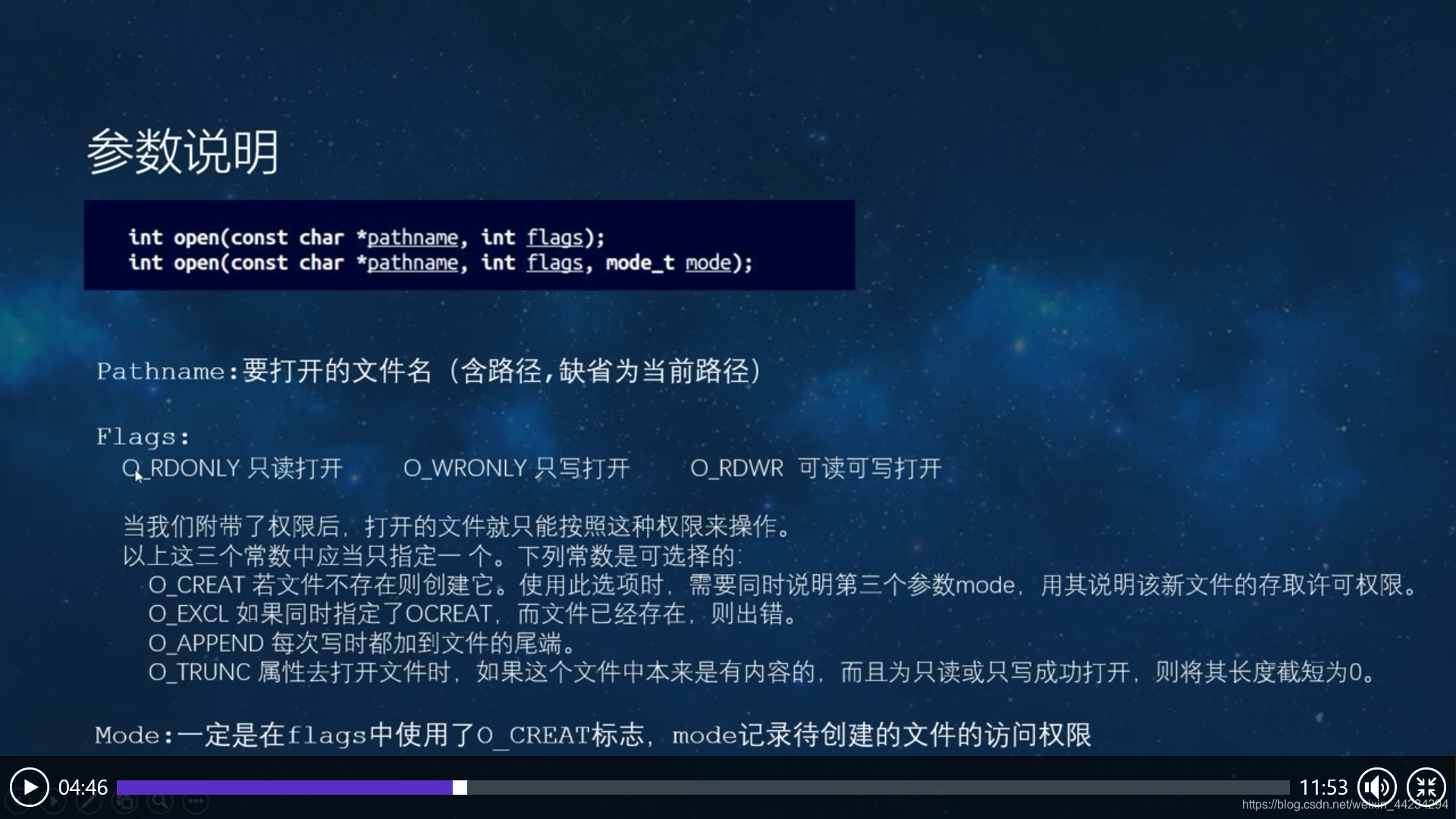
- demo1代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
//int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
fd=open("./file1",O_RDWR);//可读可写
printf("fd=%d\n",fd);
return 0;
}
如果事先创好文件file1(touch file1),则fd =3(我这里是3),如果之前没有创建file1,则fd=-1.
优化过后的代码(如果之前没有创建则创建)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
//int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
fd=open("./file1",O_RDWR);//可读可写
if(fd == -1){
printf("创建失败\n");
//int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
fd=open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600);//如果没有file1则创建,0600:权限是可读可写
if(fd > 0){
printf("创建成功,fd=%d\n",fd);
}
}
return 0;
}
补充:可读 4.可写 2.执行1,6=4+2,可读可写。
— -> 0 (no excute , no write ,no read)
–x -> 1 excute, (no write, no read)
-w- -> 2 write
-wx -> 3 write, excute
r-- -> 4 read
r-x -> 5 read, excute
rw- -> 6 read, write ,
rwx -> 7 read, write , excute
**
- O_EXCL(判断文件是否存在)
如果同时指定CREAT,而文件已经存在,则出错。
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
//int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
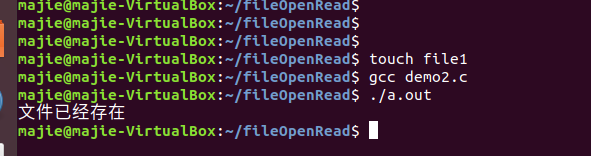
fd=open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_EXCL,0600);//如果没有file1则创建,0600:权限是可读可写
if(fd ==-1){
printf("文件已经存在\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
O_APPEND
每次写的时候加到文件的尾端
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
int n_open;
int n_write;
int n_read;
char *Buf="hello ubuntu";
fd=open("./file7",O_RDWR);
n_write=write(fd,Buf,strlen(Buf));
if(n_write != -1){
printf("写入成功,写了%d个字节\n",n_write);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
没有加O_APPEND
运行前的file7

运行后
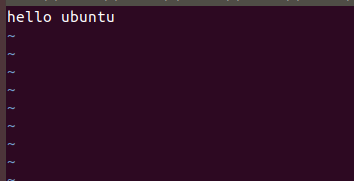
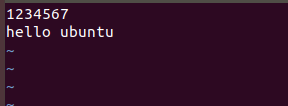
相当于覆盖了之前写的东西(hello ubuntu 覆盖掉了1234567)
加了O_APPEND
运行前

运行后
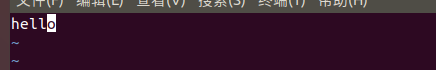
O_TRUNC
去打开文件时,如果这个文件夹本来是有内容的,而且为只读或者只写成功打开,则见其长度截短为0。(相当于把原来的存在的直接干掉)
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
int n_open;
int n_write;
int n_read;
char *Buf="hello";
fd=open("./file7",O_RDWR|O_TRUNC);
n_write=write(fd,Buf,strlen(Buf));
if(n_write != -1){
printf("写入成功,写了%d个字节\n",n_write);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
运行前
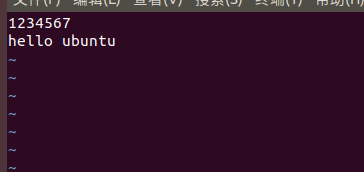
运行后
O_CREAT
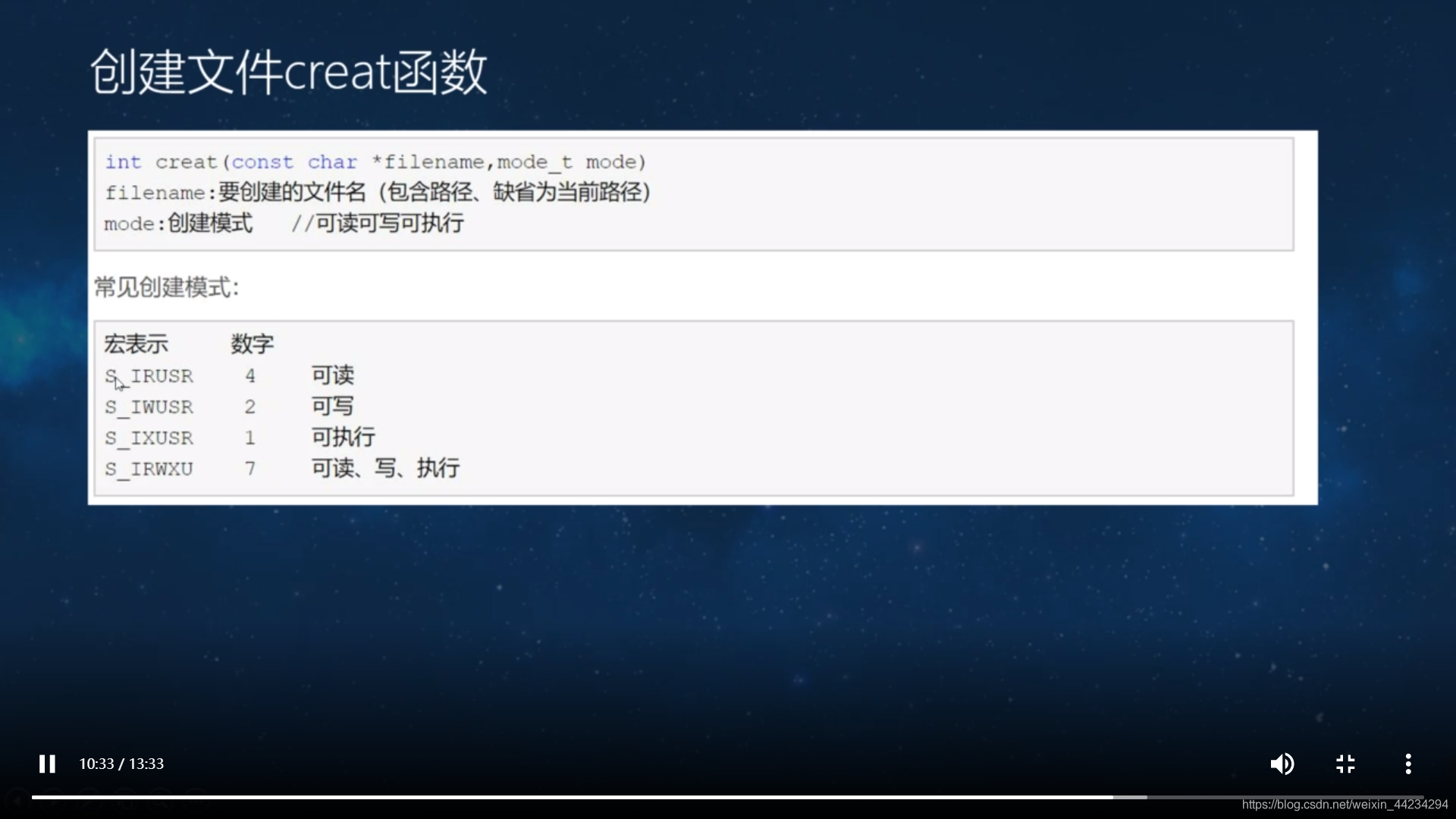
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
//int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
creat("./file9", S_IRWXU);//可读可写可执行
close(fd);
return 0;
}
结果






 本文详细解析了Linux系统中open函数的使用方法及其各种标志位的功能,包括O_RDWR、O_CREAT、O_EXCL、O_APPEND、O_TRUNC等,并通过实例代码展示了如何创建、读写和控制文件。
本文详细解析了Linux系统中open函数的使用方法及其各种标志位的功能,包括O_RDWR、O_CREAT、O_EXCL、O_APPEND、O_TRUNC等,并通过实例代码展示了如何创建、读写和控制文件。
















 193
193

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








