1. Unix可用的五种 I/O 模型:
- 堵塞式I/O
- 非堵塞式 I/O
- I/O 复用
- 信号驱动式 I/O
- 异步 I/O
1-4 都是同步 I/O。
2. 什么是同步与异步?
同步:发出一个功能调用,然后一直等待调用返回 。
异步:发出一个功能调用,不会马上知道结果,调用方也不会一直等待,而是继续往下执行,等有结果了通过回调通知 我 。
3. 什么是堵塞式 I/O?

应用进程调用系统调用 recvfrom,进入内核态,等待数据准备好。
性调用 recvfrom开始到它返回整段时间内是被堵塞的,recvfrom返回后,应用程序处理数据报。
4. 什么是非堵塞式 I/O?

非堵塞模式就是系统不断轮询,调用 recvfrom 不会堵塞,通过不断的重复调用查询,知道内核中有数据。
通过系统函数fcntl(fd, F_SRTFL, flag | 0_NONBLOCK);设置为非堵塞模式。
5. 什么是I/O复用模型?
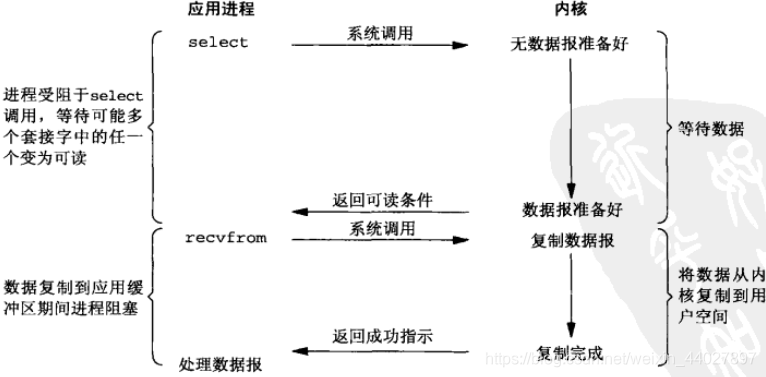
I/O 复用模型还是堵塞模型,只不过 堵塞 不是发生在 recvfrom 而是发生在 select。
6. 信号驱动I/O模型

先建立 SIGIO信号的处理函数,当数据报准备好后,内核会为该进程产生一个 SIGIO 信号。
7. 异步I/O模型

异步I/O 与信号驱动的不同之处在于, 异步IO是由内核通知我们I/O操作何时完成。而信号驱动是内核通知我们何时启动一个 I/O。
8.Select 事例
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
9. select 描述符何时就绪?

10 select 回射 client 端实现
下面的事例使用 select 同时管理 stdin,和 client connection 两个 描述符。
相互不会影响。
但是 也遇见一个 小问题:
如果 把 下面三行挪到 while 循环外面,则 select 只能监控 stdin,不能监控 client connection。不知为啥…
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
ssize_t readn(int fd, void *buf, size_t count)
{
int n_left = count;
int n_read;
char * readbuf = (char *)buf;
while (n_left > 0)
{
if ((n_read = read(fd, readbuf, n_left)) < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
return -1;
}
else if (n_read == 0)
{
printf ("client has closed\n");
break;
}
printf ("1. receive data is %s, length is %d,lef data:%d\n", readbuf, n_read, n_left - n_read);
readbuf += n_read;
n_left -= n_read;
printf("left data is %d", n_left);
}
return count - n_left;
}
ssize_t writen(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count)
{
int n_left = count;
int n_written;
char * writebuf = (char *)buf;
while (n_left > 0)
{
if ((n_written = write(fd, writebuf, n_left)) < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
return -1;
}
else if (n_written == 0)
{
continue;
}
writebuf += n_written;
n_left -= n_written;
}
return count - n_left;
}
int max(int compare1, int compare2)
{
return (compare1 >= compare2) ? compare1 : compare2;
}
void echo_string_select(int confd)
{
fd_set read_set;
FD_ZERO(&read_set);
int nfds = 0;
int numfd;
char sendbuf[50] = {0};
char recbuf[50] = {0};
int readnum = 0;
FD_SET(fileno(stdin), &read_set);
FD_SET(confd, &read_set);
nfds = max(fileno(stdin), confd) + 1;
while (1)
{
FD_SET(fileno(stdin), &read_set);
FD_SET(confd, &read_set);
nfds = max(fileno(stdin), confd) + 1;
numfd = select(nfds, &read_set, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (FD_ISSET(fileno(stdin), &read_set))
{
if (fgets(sendbuf, sizeof(sendbuf), stdin) != NULL)
{
writen(confd, sendbuf, strlen(sendbuf));
memset(sendbuf, 0 , sizeof(sendbuf));
}
}
if (FD_ISSET(confd, &read_set))
{
if ((readnum = read(confd, recbuf, sizeof(recbuf))) < 0)
{
perror("read errr");
exit(0);
}
else if (readnum == 0)
{
close(confd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
printf ("receive data:%s\n", recbuf);
memset(recbuf, 0, sizeof(recbuf));
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int confd = 0;
if((confd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1)
{
perror("socket error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("create socket success\n");
struct sockaddr_in seraddr;
memset(&seraddr, 0, sizeof(seraddr));
seraddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
seraddr.sin_port = htons(51888);
seraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
if (connect(confd, (struct sockaddr *)&seraddr, sizeof(seraddr)) < 0)
{
perror("connect error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf ("connect to server success\n");
echo_string_select(confd);
#if 0
char sendbuf[50] = {0};
char recbuf[50] = {0};
while (fgets(sendbuf, sizeof(sendbuf), stdin) != NULL)
{
writen(confd, sendbuf, strlen(sendbuf));
read(confd, recbuf, sizeof(recbuf));
printf ("receive data:%s\n", recbuf);
memset(sendbuf, 0, sizeof(sendbuf));
memset(recbuf, 0, sizeof(recbuf));
}
close(confd);
#endif
return 0;
}








 本文介绍了Unix可用的五种I/O模型,包括阻塞式、非阻塞式、I/O复用、信号驱动式和异步I/O,其中前四种为同步I/O。还解释了同步与异步的概念,详细阐述了各I/O模型的工作原理。此外,给出了Select函数示例及描述符就绪条件,最后展示了Select回射client端实现并提出一个小问题。
本文介绍了Unix可用的五种I/O模型,包括阻塞式、非阻塞式、I/O复用、信号驱动式和异步I/O,其中前四种为同步I/O。还解释了同步与异步的概念,详细阐述了各I/O模型的工作原理。此外,给出了Select函数示例及描述符就绪条件,最后展示了Select回射client端实现并提出一个小问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








