ThreadLocal
基本用法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MThread("stringThreadLocal1").start();
new MThread("stringThreadLocal2").start();
/* out:
stringThreadLocal20
stringThreadLocal21
stringThreadLocal10
stringThreadLocal11
*/
}
}
class MThread extends Thread{
static ThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
static ThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<>();
String s;
public MThread(String s) {
this.s= s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
stringThreadLocal.set(s+"0");
stringThreadLocal1.set(s+"1");
System.out.println( stringThreadLocal.get());
System.out.println( stringThreadLocal1.get());
}
}
原理
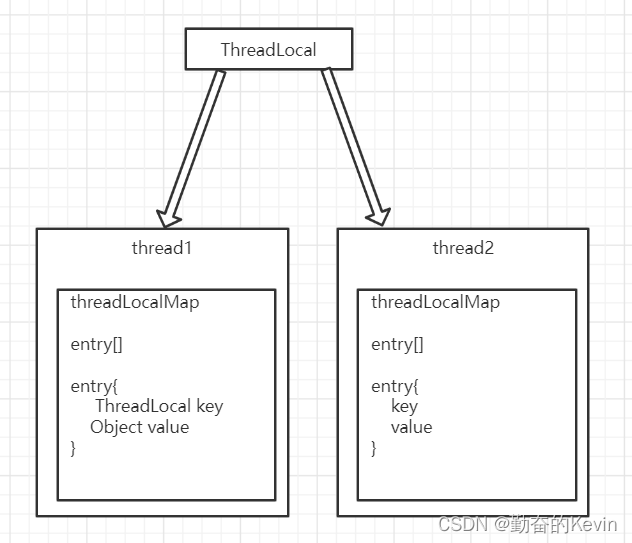
Thread类的定义中有ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
说明每个线程自己保存一个 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap 类
每次使用ThreadLocal的get()或set(), 都是用ThreadLocal作为key获取或存放map的value
ThreadLocal可以避免在一个线程类中的方法中重复传递参数
public static final ThreadLocal<T> THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
void test(){
THREAD_LOCAL.set("wupx");
String v = THREAD_LOCAL.get();
}
Set()
ThreadLocal 的 set ()
先获取当前线程
获取线程的ThreadLocalMap
map为null 就 createMap(t, value);
不为null就map.set(this, value);
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
map.set(this, value);
} else {
createMap(t, value);
}
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
get()
同样是去找当前thread的ThreadLocalMap, 对map进行getEntry()
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
底层实现是Entry[], 下面是entry的定义
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
ThreadLocal作为key, 并且是弱引用, 可以通过WeakReference的父类REference的get()来获取
用ThreadLocal的nextHashCode作为下标, Object类作为value, 放入entry中
这意味着每个ThreadLocal类在每个线程中都能找到对应的value
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
// ...
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
// ...
// 新建一个16位的Entry[]
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// 计算firstkey的hash值
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
// 将entry放入数组中
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
// 设置table中已放入entry的数量
size = 1;
// 设置哈希表扩容的阈值
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
ThreadLocal 内存泄漏
threadLocalMap 中保存的 key 值是弱引用, GC时被回收
但是 Entry 被 threadLocalMap 对象引用,threadLocalMap 对象又被 Thread 对象所引用
当 Thread 一直不终结的话,value 对象就会一直存在于内存中,也就导致了内存泄漏
在使用完 ThreadLocal 变量后,需要我们手动 remove 掉
源码 :
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null) {
m.remove(this);
}
}








 本文详细介绍了Java中的ThreadLocal,包括其基本用法、内部原理,如Set()、get()操作,以及ThreadLocalMap的实现。重点讨论了ThreadLocal可能导致的内存泄漏问题,解释了弱引用在防止内存泄漏中的角色,并提醒在使用完毕后需要手动调用remove()以避免内存问题。
本文详细介绍了Java中的ThreadLocal,包括其基本用法、内部原理,如Set()、get()操作,以及ThreadLocalMap的实现。重点讨论了ThreadLocal可能导致的内存泄漏问题,解释了弱引用在防止内存泄漏中的角色,并提醒在使用完毕后需要手动调用remove()以避免内存问题。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








