一、重载运算符的目的:实现复数类对象之间直接进行运算,像基本数据类型一样。
二、运算符重载实质:编写以运算符作为名称的函数。
三、如何写:
返回值类型 operator运算符(形参表)
{
具体实现代码
}
注:运算符可以被多次重载。运算符可以重载为全局函数,也可以重载为类的成员函数。重载为成员函数时,运算符左边通常是一个对象,this指针指向该对象。
四、复数类加减代码。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//目的:实现对象之间的加减运算
class Complex{
private:
double real ,imag;
public:
Complex(double r=0.0, double i=0.0):real(r),imag(i){}
Complex operator-(const Complex& b); //减号左边对象的成员函数,两个复数对象相减
Complex operator-(double r); //减号左边对象的成员函数,复数-实数
friend Complex operator-(double r, const Complex& a); //实数-复试
friend Complex operator+(const Complex& a,const Complex& b);//两个复数对象相加
Complex operator+(const Complex& b); //多次重载 复数+复数
Complex operator+(double r); //加号左边的对象的成员函数,复数+实数
friend Complex operator+(double r, const Complex& a); //实数+复数
Complex& operator=(const Complex& a); //左值对象的成员函数,重载赋值运算符
void myPrint();
};
//1.用类的成员函数实现运算符重载时,一个对象作为this实现调用成员函数,另一个对象作为参数
Complex Complex::operator-(const Complex& b){
return Complex(this->real-b.real,this->imag-b.imag); //创建临时对象返回
}
Complex Complex::operator-(double r){
return Complex(real-r,imag);
}
//实数-复数
//减号左边是一个实数,无法重载为成员函数,用友元重载为全局函数
Complex operator-(double r, const Complex& a){
return Complex(r-a.real,a.imag);
}
//2.用全局函数实现运算符重载时,两个对象对应两个参数
Complex operator+(const Complex& a,const Complex& b){
return Complex(a.real+b.real,a.imag+b.imag);
}
Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex& b){
return Complex(real+b.real,imag+b.imag);
}
Complex Complex::operator+(double r){
return Complex(real+r,imag);
}
Complex operator+(double r, const Complex& a){
return Complex(r+a.real,a.imag);
}
void Complex::myPrint(){
cout << this->real << "+" << imag << "i" << endl;
}
Complex& Complex::operator=(const Complex& a){
this->real = a.real;
imag = a.imag;
return *this;
}
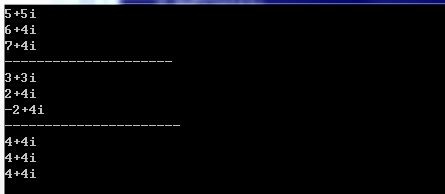
void testAdd(){
Complex a(4,4), b(1,1), c;
c = a+b; //两个复数相加,等价于a.operator+(b)
c.myPrint();
Complex d = a + 2; //复数+实数,a.operator+(2)
d.myPrint();
Complex e = 3 + a; //实数+复数,operator(3,a)
e.myPrint();
}
void testSub(){
Complex a(4,4), b(1,1);
Complex c = a-b;
c.myPrint();
Complex d = a - 2;
d.myPrint();
Complex e = 2- a;
e.myPrint();
}
void testAss(){
Complex a(4,4);
Complex b, c;
c = b = a;
a.myPrint();
b.myPrint();
c.myPrint();
}
int main(){
testAdd();
cout << "---------------------" << endl;
testSub();
cout << "----------------------" << endl;
testAss();
return 0;
}
五、输出结果:
六、总结:
1.赋值运算符只能重载为类的成员函数。
2.重载为全局函数时,函数参数个数等于运算符的操作数个数;重载为成员函数时,函数参数个数等于运算符的操作数个数减一。
3.对于全局函数,访问类的私有成员函数必须使用声明为类的友元函数。
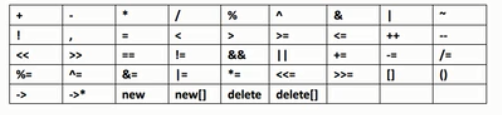
4、可以被重载的运算符如下:








 本文详细介绍了在C++中如何通过运算符重载实现复数类对象间的加减运算,包括重载为成员函数和全局函数的方法,以及如何处理复数与实数之间的运算。
本文详细介绍了在C++中如何通过运算符重载实现复数类对象间的加减运算,包括重载为成员函数和全局函数的方法,以及如何处理复数与实数之间的运算。
















 3050
3050

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








