CPU 的 cache 往往是分多级的金字塔模型,L1 最靠近 CPU,访问延迟最小,但 cache 的容量也最小。本文介绍如何测试多级 cache 的访存延迟,以及背后蕴含的计算机原理。
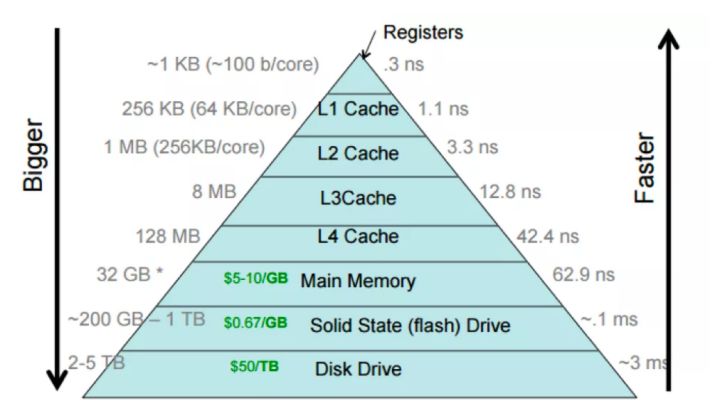
图源:https://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1310/2020/assign/labs/lab4.html
Cache Latency
Wikichip[1] 提供了不同 CPU 型号的 cache 延迟,单位一般为 cycle,通过简单的运算,转换为 ns。以 skylake 为例,CPU 各级 cache 延迟的基准值为:
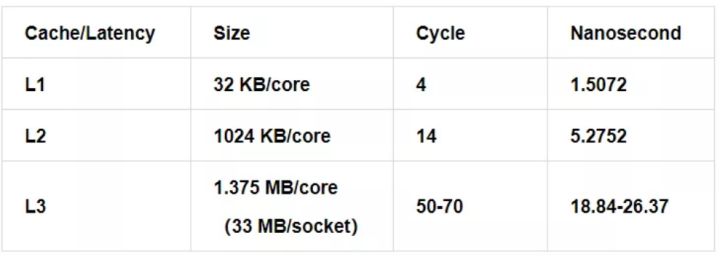
CPU Frequency:2654MHz (0.3768 nanosec/clock)
设计实验
1. naive thinking
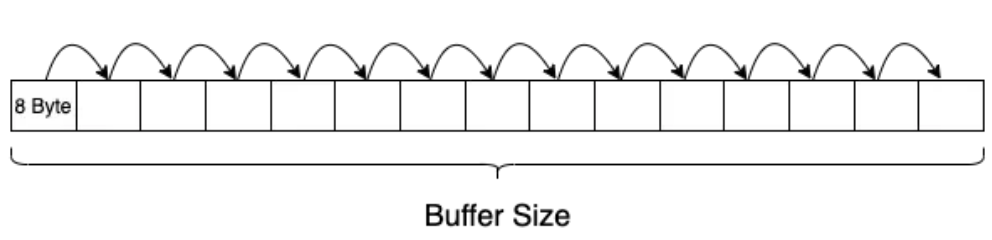
申请一个 buffer,buffer size 为 cache 对应的大小,第一次遍历进行预热,将数据全部加载到 cache 中。第二次遍历统计耗时,计算每次 read 的延迟平均值。
代码实现 mem-lat.c 如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define ONE p = (char **)*p;
#define FIVE ONE ONE ONE ONE ONE
#define TEN FIVE FIVE
#define FIFTY TEN TEN TEN TEN TEN
#define HUNDRED FIFTY FIFTY
static void usage()
{
printf("Usage: ./mem-lat -b xxx -n xxx -s xxx\n");
printf(" -b buffer size in KB\n");
printf(" -n number of read\n\n");
printf(" -s stride skipped before the next access\n\n");
printf("Please don't use non-decimal based number\n");
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned long i, j, size, tmp;
unsigned long memsize = 0x800000; /* 1/4 LLC size of skylake, 1/5 of broadwell */
unsigned long count = 1048576; /* memsize / 64 * 8 */
unsigned int stride = 64; /* skipped amount of memory before the next access */
unsigned long sec, usec;
struct timeval tv1, tv2;
struct timezone tz;
unsigned int *indices;
while (argc-- > 0) {
if ((*argv)[0] == '-') { /* look at first char of next */
switch ((*argv)[1]) { /* look at second */
case 'b':
argv++;
argc--;
memsize = atoi(*argv) * 1024;
break;
case 'n':
argv++;
argc--;
count = atoi(*argv);
break;
case 's':
argv++;
argc--;
stride = atoi(*argv);
break;
default:
usage();
exit(1);
break;
}
}
argv++;
}
char* mem = mmap(NULL, memsize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANON, -1, 0);
// trick3: init pointer chasing, per stride=8 byte
size = memsize / stride;
indices = malloc(size * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
indices[i] = i;
// trick 2: fill mem with pointer references
for (i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
*(char **)&mem[indices[i]*stride]= (char*)&mem[indices[i+1]*stride];
*(char **)&mem[indices[size-1]*stride]= (char*)&mem[indices[0]*stride];
char **p = (char **) mem;
tmp = count / 100;
gettimeofday (&tv1, &tz);
for (i = 0; i < tmp; ++i) {
HUNDRED; //trick 1
}
gettimeofday (&tv2, &tz);
if (tv2.tv_usec < tv1.tv_usec) {
usec = 1000




 本文探讨了CPU Cache访问延迟的测试方法和背后原理,通过设计实验揭示了预取、编译器优化等因素如何影响延迟。通过调整实验参数,如stride和使用register关键字,最终得到了更接近预期的L1、L2和L3延迟结果。
本文探讨了CPU Cache访问延迟的测试方法和背后原理,通过设计实验揭示了预取、编译器优化等因素如何影响延迟。通过调整实验参数,如stride和使用register关键字,最终得到了更接近预期的L1、L2和L3延迟结果。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 43
43

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








