一、前后缀分解
42. 接雨水
前后缀分解
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
int[] suf = new int[n];
// 两端不用算
for (int i = n - 2; i > 0; i--) {
suf[i] = Math.max(suf[i + 1], height[i + 1]);
}
int res = 0, pre = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
pre = Math.max(pre, height[i - 1]);
res += Math.max(0, Math.min(pre, suf[i]) - height[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
双指针
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1;
int res = 0, left = 0, right = 0;
// 按小的一边计算柱子的贡献值
while (i < j) {
int x = height[i], y = height[j];
left = Math.max(left, x);
right = Math.max(right, y);
if (x < y) {
res += left - x;
i++;
} else {
res += right - y;
j--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
单调栈
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
Deque<Integer> q = new LinkedList();
int res = 0, n = height.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = height[i];
// 单调递减栈
while (!q.isEmpty() && x > height[q.peek()]) {
int j = q.pop();
if (q.isEmpty()) break;
int high = Math.min(x, height[q.peek()]) - height[j];
// 分层计算
res += high * (i - q.peek() - 1);
}
q.push(i);
}
return res;
}
}
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n];
int suf = 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res[i] = suf;
suf *= nums[i];
}
int pre = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] *= pre;
pre *= nums[i];
}
return res;
}
}
2906. 构造乘积矩阵
class Solution {
public int[][] constructProductMatrix(int[][] grid) {
final int MOD = 12345;
int n = grid.length, m = grid[0].length;
int[][] p = new int[n][m];
long suf = 1; // 后缀乘积
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
p[i][j] = (int) suf; // p[i][j] 先初始化成后缀乘积
suf = suf * grid[i][j] % MOD;
}
}
long pre = 1; // 前缀乘积
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
p[i][j] = (int) (p[i][j] * pre % MOD); // 然后再乘上前缀乘积
pre = pre * grid[i][j] % MOD;
}
}
return p;
}
}
2256. 最小平均差
class Solution {
public int minimumAverageDifference(int[] nums) {
long suf = 0, pre = 0;
for(int x : nums) suf += x;
int ans = -1, n = nums.length;
long average = suf + 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
pre += nums[i];
suf -= nums[i];
long d = i == n - 1 ? pre / n: Math.abs(pre / (i + 1) - suf / (n - i - 1));
if(d < average){
ans = i;
average = d;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
670. 最大交换
class Solution {
public int maximumSwap(int num) {
char[] cs = Integer.toString(num).toCharArray();
int n = cs.length;
int[] a = new int[n];
Arrays.setAll(a, i -> i);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0 ; i--) {
if (cs[i] <= cs[a[i + 1]]) {
a[i] = a[i + 1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (cs[i] != cs[a[i]]) {
char temp = cs[i];
cs[i] = cs[a[i]];
cs[a[i]] = temp;
break;
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(new String(cs));
}
}
class Solution {
public int maximumSwap(int num) {
char[] cs = Integer.toString(num).toCharArray();
int n = cs.length;
int maxIndex = n - 1, p = -1, rmax = 0;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0 ; i--) {
if (cs[i] > cs[maxIndex]) { // s[i] 是目前最大数字
maxIndex = i;
} if (cs[i] < cs[maxIndex]) { // s[i] 右边有比它大的
p = i;
rmax = maxIndex;
}
}
if (p == -1) return num; // 说明 cs 降序
char temp = cs[p];
cs[p] = cs[rmax];
cs[rmax] = temp;
return Integer.parseInt(new String(cs));
}
}
2483. 商店的最少代价
class Solution {
public int bestClosingTime(String customers) {
char[] s = customers.toCharArray();
int n = s.length;
int res = 0, cost = 0;
for (char c : s) if (c == 'Y') cost++;
// 0 点关代价为 cost
int mn = cost;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// i 点不关
if (s[i] == 'N') ++cost;
else {
--cost;
// 代价更小了,下一时问考虑关
if (cost < mn) {
res = i + 1;
mn = cost;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int bestClosingTime(String customers) {
char[] s = customers.toCharArray();
int n = s.length;
int res = 0;
int balance = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (s[i] == 'N') ++balance;
else {
--balance;
if (balance < 0) {
res = i + 1;
balance = 0; // 清零, 再次 < 0,说明更小了。
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
★2420. 找到所有好下标
先倒着遍历,得到从每个位置向后的最长连续非降序列的长度,然后正着遍历,得到每个位置向前的最长连续非增序列的长度,同时统计答案。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> goodIndices(int[] nums, int k) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int n = nums.length;
int[] dec = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dec, 1); // ? dec[n - 1] = 1;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= k; i--)
if (nums[i] <= nums[i + 1])
dec[i] = dec[i + 1] + 1;
int inc = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n - k; i++) {
if (inc >= k && dec[i + 1] >= k) res.add(i);
if (nums[i - 1] >= nums[i]) inc++;
else inc = 1;
}
return res;
}
}
2167. 移除所有载有违禁货物车厢所需的最少时间
class Solution {
public int minimumTime(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int[] suf = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i)
suf[i] = s.charAt(i) == '0' ? suf[i + 1] : Math.min(suf[i + 1] + 2, n - i);
int ans = suf[0];
int pre = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (s.charAt(i) == '1') {
pre = Math.min(pre + 2, i + 1);
ans = Math.min(ans, pre + suf[i + 1]);
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minimumTime(String s) {
// 左侧:只用考虑两种情况,一按 2 算,二整体移除前缀,选最优。
int n = s.length(), res = n, cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n;) {
// 计算左侧
// 先按 2 算
cnt += (s.charAt(i) - '0') * 2;
// 如果大于长度,则按长度计算
if (cnt > ++i) cnt = i;
// 左侧 + 后缀,右侧先接最大值,即后缀计算,逐步更新。
res = Math.min(res, cnt + n - i);
}
return res;
}
}
1930. 长度为 3 的不同回文子序列
class Solution {
public int countPalindromicSubsequence(String s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0;
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
int[] suf = new int[26];
boolean[] pre = new boolean[26];
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[26][26];
for (char c : cs) suf[c - 'a']++;
for (char c : cs) {
int i = c - 'a';
suf[i]--;
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)
if (!vis[i][j] && suf[j] > 0 && pre[j]) {
vis[i][j] = true;
ans++;
}
pre[i] = true;
}
return ans;
}
}
2484. 统计回文子序列数目
首先倒着遍历 s,统计每个字符的出现次数 suf[a] 和两个字符的组合个数 suf2[a][b]。
class Solution {
long MOD = (long) 1e9 + 7;
public int countPalindromes(String s) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
int n = cs.length;
int[] pre = new int[10], suf = new int[10];
int[][] pre2 = new int[10][10], suf2 = new int[10][10];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
int d = cs[i] - '0';
for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
suf2[d][j] += suf[j];
++suf[d];
}
long ans = 0L;
for (int d : cs) {
d -= '0';
--suf[d];
for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
suf2[d][j] -= suf[j]; // 撤销
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
ans += (long) pre2[i][j] * suf2[i][j]; // 枚举所有字符组合
for (var j = 0; j < 10; ++j)
pre2[d][j] += pre[j];
++pre[d];
}
return (int) (ans % MOD);
}
}
2565. 最少得分子序列
class Solution {
public int minimumScore(String s, String t) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray(), ct = t.toCharArray();
int n = cs.length, m = ct.length;
var suf = new int[n + 1];
suf[n] = m;
for (int i = n - 1, j = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (j >= 0 && cs[i] == ct[j]) --j;
suf[i] = j + 1;
}
int ans = suf[0]; // 删除 t[:suf[0]]
if (ans == 0) return 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (cs[i] == ct[j]) // 注意 j 不会等于 m,因为上面 suf[0] > 0 表示 t 不是 s 的子序列
ans = Math.min(ans, suf[i + 1] - ++j); // ++j 后,删除 t[j:suf[i+1]]
return ans;
}
}
2552. 统计上升四元组
class Solution {
public long countQuadruplets(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[][] great = new int[n][n + 1];
for (int k = n - 2; k > 0; k--) {
great[k] = great[k + 1].clone();
for (int x = nums[k + 1] - 1; x > 0; x--)
great[k][x]++;
}
long ans = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < n - 2; j++)
for (int k = j + 1; k < n - 1; k++) {
int x = nums[k];
if (nums[j] > x)
ans += (x - n + 1 + j + great[j][x]) * great[k][nums[j]];
}
return ans;
}
}
2680. 最大或值
1、选最高位 1 的数更优 ;
2、最高位 1 可能有多个数,此时不管选谁,只要操作一次以后,变成结论1,因此,只需将 k 次操作都交给同一个数,且一定是最高位 1 的那几个数之一。
class Solution {
public long maximumOr(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
// 前后缀和 n + 1
var suf = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
suf[i] = suf[i + 1] | nums[i];
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0, pre = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 左移可能会溢出
ans = Math.max(ans, pre | (long) nums[i] << k | suf[i + 1]);
pre |= nums[i];
}
return ans;
}
}
1653. 使字符串平衡的最少删除次数
灵茶山艾府
问:为什么把 if - else 写成 (c - ‘a’) * 2 - 1 就会快很多?
答:CPU 在遇到分支(条件跳转指令)时会预测代码要执行哪个分支,如果预测正确,CPU 就会继续按照预测的路径执行程序。但如果预测失败,CPU 就需要回滚之前的指令并加载正确的指令,以确保程序执行的正确性。
对于本题的数据,字符 ‘a’ 和 ‘b’ 可以认为是随机出现的,在这种情况下分支预测就会有 50% 的概率失败。失败导致的回滚和加载操作需要消耗额外的 CPU 周期,如果能用较小的代价去掉分支,对于本题的情况必然可以带来效率上的提升。
注意:这种优化方法往往会降低可读性,最好不要在业务代码中使用。
class Solution {
public int minimumDeletions(String S) {
var s = S.toCharArray();
int del = 0;
for (var c : s)
del += 'b' - c; // 统计 'a' 的个数
int ans = del;
for (var c : s) {
// 'a' -> -1 'b' -> 1
del += (c - 'a') * 2 - 1;
ans = Math.min(ans, del);
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minimumDeletions(String s) {
// 当前是 'a',若有 'b', 则删除一个,其它情况长度增一
int b = 0, res = 0, n = s.length();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == 'b') b++;
// else if (b > 0) {
// b--;
// res++;
//}
else {
res += (b + n - 1) / n;
b = Math.max(0, --b);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2909. 元素和最小的山形三元组 II
class Solution {
public int minimumSum(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, res = Integer.MAX_VALUE, INF = res;
int[] suf = new int[n]; // 后缀最小值
suf[n-1] = nums[n-1];
for (int i = n - 2; i > 0; i--)
suf[i] = Math.min(nums[i], suf[i + 1]);
int pre = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
int x = nums[i]; // 前缀最小值
if (x > pre && x > suf[i+1])
res = Math.min(res, pre + x + suf[i + 1]);
pre = Math.min(pre, x);
}
return res == INF ? -1 : res;
}
}
2865. 美丽塔 I
枚举计算每一座山作为“山顶”时的山状数组的总高度和。
class Solution {
public long maximumSumOfHeights(List<Integer> maxHeights) {
long res = 0;
int n = maxHeights.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 假设 i 是山顶
long ans = 0;
int t = maxHeights.get(i);
// 计算以i为山顶所能形成的山状数组的元素总和
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
t = Math.min(maxHeights.get(j), t);
ans += t;
}
t = maxHeights.get(i);
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
t = Math.min(maxHeights.get(j), t);
ans += t;
}
res = Math.max(res, ans);
}
return res;
}
}
2866. 美丽塔 II
用例范围由 103 增大至 105,不能暴力枚举,无法通过记忆背包解决,数值范围超内存;维护一个单调栈,分两次单向获取某个节点左边和右边的总量,最后加起来实现 O(n) 算法。
前后缀分解 + 单调栈
class Solution {
public long maximumSumOfHeights(List<Integer> maxHeights) {
// int[] a = maxHeights.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
Integer[] a = maxHeights.toArray(Integer[]::new);
int n = a.length;
long[] suf = new long[n + 1];
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.push(n); // 哨兵 方便计算区间长度
long sum = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int x = a[i];
while (q.size() > 1 && x <= a[q.peek()]) {
int j = q.pop();
// 撤销之前加到 sum 中的
sum -= (long) a[j] * (q.peek() - j);
}
// 从 i 到 q.peek() - 1 都是 x
sum += (long) x * (q.peek() - i);
suf[i] = sum;
q.push(i);
}
long ans = sum;
q.clear();
q.push(-1); // 哨兵
long pre = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = a[i];
while (q.size() > 1 && x <= a[q.peek()]) {
int j = q.pop();
pre -= (long) a[j] * (j - q.peek()); // 撤销之前加到 pre 中的
}
pre += (long) x * (i - q.peek()); // 从 q.peek()+1 到 i 都是 x
ans = Math.max(ans, pre + suf[i + 1]);
q.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
★1671. 得到山形数组的最少删除次数
class Solution {
public int minimumMountainRemovals(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// pre[i] 表示以下标 i 结尾 LIS 长度。
int[] pre = new int[n];
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// int j = Collections.binarySearch(arr, nums[i]);
// if (j < 0) j = ~j;
int j = binarySearch(arr, nums[i]);
if (j == arr.size()) arr.add(nums[i]);
else arr.set(j, nums[i]);
pre[i] = j + 1;
}
arr.clear();
int res = 0;
// suf
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int j = binarySearch(arr, nums[i]);
if (j == arr.size()) arr.add(nums[i]);
else arr.set(j, nums[i]);
int suf = j + 1;
if (pre[i] > 1 && suf > 1)
res = Math.max(res, pre[i] + suf - 1);
}
return n - res;
}
public static int binarySearch(List<Integer> arr, int target) {
int left = 0, right = arr.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + right >> 1;
if (arr.get(mid) < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
return left;
}
}
10038. 执行操作后的最大分割数量
枚举+前后缀
枚举位置 i,如何修改 i 使得 B + s[i] + D 的能够拆分的段数最多。
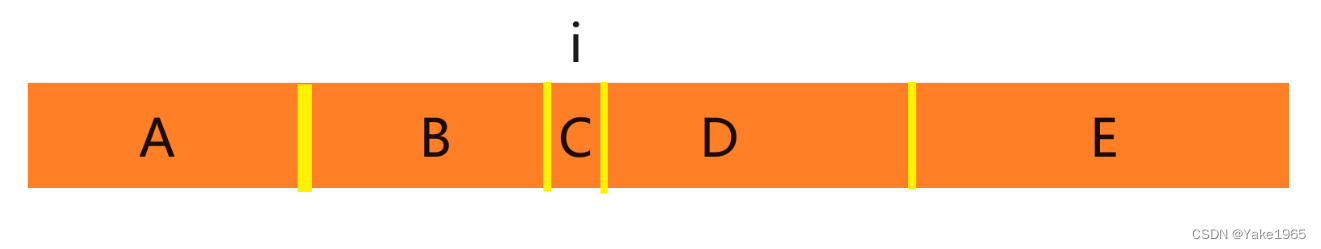
L[i][1] 表示 B 中不同字符的数量, R[i][1] 表示 D 中不同字符的数量。
count 表示 B + D 中不同字符的数量。
分情况讨论:
情况 1:最多能分成 1 段。
如果满足 min(count + 1, 26) ≤ k ,则表示 i 修改为任何数字,不同字符数量都小于 k,所以最多能分成 1 段。
情况 2:最多能分成 3 段。
如果满足 L[i][1] == k && R[i][1] == k && count < 26,则表示 B 中不同字符的数量等于 k,D 中不同字符的数量等于 k
且 i 能修改为不同于 B D 中的字符,所以能够分成 3 段。
情况 3 :最多能分成 2 段。
除了情况 1 和 2 的其余情况,最多能分成 2 段。
class Solution {
char[] cs;
int k, n;
public int maxPartitionsAfterOperations(String s, int k) {
cs = s.toCharArray();
this.k = k;
n = cs.length;
var pre = pre();
var suf = suf();
int res = 0, MX = 26;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int ops = pre[i][2] + 2 + suf[i][2] ;
int count = Integer.bitCount(pre[i][0] | suf[i][0]);
if (pre[i][1] == k && suf[i][1] == k && count < MX) ops++;
else if (Math.min(count + 1, MX) <= k) ops--;
res = Math.max(res, ops);
}
return res;
}
private int[][] pre() {
var pre = new int[n][3];
int mask = 0, cnt = 0, id = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int bit = 1 << cs[i] - 'a';
if ((mask & bit) == 0) {
if (++cnt > k) {
cnt = 1;
mask = bit;
id++;
} else mask |= bit;
}
pre[i + 1][0] = mask;
pre[i + 1][1] = cnt;
pre[i + 1][2] = id;
}
return pre;
}
private int[][] suf() {
var suf = new int[n][3];
int mask = 0, cnt = 0, id = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int bit = 1 << cs[i] - 'a';
if ((mask & bit) == 0) {
if (++cnt > k) {
cnt = 1;
mask = bit;
id++;
} else mask |= bit;
}
suf[i - 1][0] = mask;
suf[i - 1][1] = cnt;
suf[i - 1][2] = id;
}
return suf;
}
}
二、枚举「中间」点
447. 回旋镖的数量
class Solution {
public int numberOfBoomerangs(int[][] points) {
int res = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap();
for (int[] p : points) {
map.clear();
for (int[] q : points) {
int d = (p[0] - q[0]) * (p[0] - q[0]) + (p[1] - q[1]) * (p[1] - q[1]);
int c = map.getOrDefault(d, 0);
res += c * 2;
map.put(d, c + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2874. 有序三元组中的最大值 II
枚举 j
class Solution {
public long maximumTripletValue(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] sufMax = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i > 1; i--) {
sufMax[i] = Math.max(sufMax[i + 1], nums[i]);
}
long res = 0;
int preMax = nums[0];
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
if (nums[j] < preMax) res = Math.max(res, (long) (preMax - nums[j]) * sufMax[j + 1]);
else preMax = nums[j];
}
return res;
}
}
枚举 k
class Solution {
public long maximumTripletValue(int[] nums) {
long res = 0;
int preMax = 0, maxDiff = 0;
for (int x : nums) {
res = Math.max(res, (long)maxDiff * x);
maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, preMax - x);
preMax = Math.max(preMax, x);
}
return res;
}
}
2242. 节点序列的最大得分
枚举边作为中间边,边的两端各自延伸出去找尽量大的邻居。
预处理:查找每一个节点,其所有邻居节点中,分数值最大的三个节点。
规避形成自环和三角形:查找最大的三个节点。
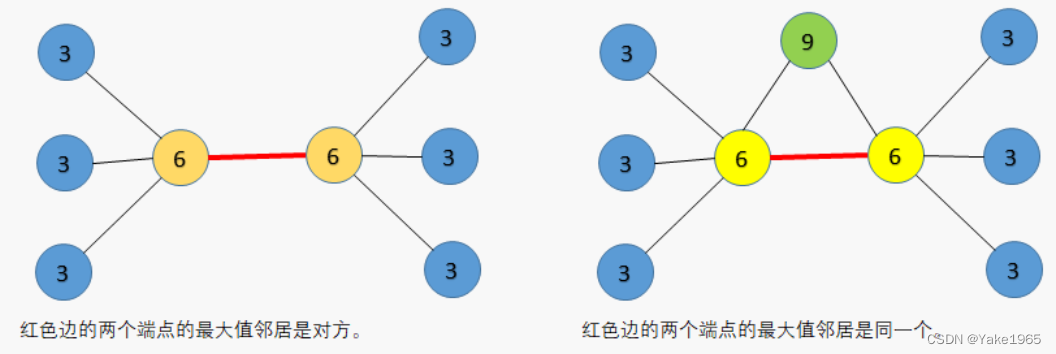
class Solution {
public int maximumScore(int[] scores, int[][] edges) {
var n = scores.length;
List<int[]>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].add(new int[]{scores[y], y});
g[y].add(new int[]{scores[x], x});
}
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (g[i].size() > 3) {
g[i].sort((a, b) -> (scores[b[1]] - scores[a[1]])); // ? 改成离线排序 73/75 过不了
g[i] = new ArrayList<>(g[i].subList(0, 3)); // subList 是 g[i] 的一个视图
}
var ans = -1;
for (var e : edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
for (var p : g[x]) {
for (var q : g[y]) {
int a = p[1], b = q[1];
if (a != y && b != x && a != b)
ans = Math.max(ans, p[0] + scores[x] + scores[y] + q[0]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
2867. 统计树中的合法路径数目
这题本质上是求一种类似于「非质数-质数-非质数」的路径个数。和题目 2242 的共同点在于「枚举中间」。
枚举每个质数结点 x:
分别统计与 x 连通的每一个连通块的非质数结点数,为避免反复 DFS 同一个非质数连通块,可以把每个非质数所处的连通块的大小记录下来(类似记忆化搜索)。如果之前计算过,就无需再次 DFS。
class Solution {
private final static int MX = (int) 1e5;
private final static boolean[] np = new boolean[MX + 1]; // 质数 = false 非质数 = true
static {
np[1] = true;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= MX; i++)
if (!np[i])
for (int j = i * i; j <= MX; j += i)
np[j] = true;
}
List<Integer>[] g;
List<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
public long countPaths(int n, int[][] edges) {
g = new ArrayList[n + 1];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1];
g[x].add(y);
g[y].add(x);
}
long res = 0;
int[] size = new int[n + 1];
// 遍历质数
for (int x = 2; x <= n; x++) {
if (np[x]) continue; // 跳过非质数
int sum = 0; // 连通质数 x 的非质数总数
for (int y : g[x]) { // 质数 x 把这棵树分成了若干个连通块
if (!np[y]) continue;
if (size[y] == 0) { // 尚未计算过
nodes.clear(); // 最后有多少个结点就有多少条合法路径数目(从 x 出发的)
dfs(y, -1); // 遍历 y 所在连通块,在不经过质数的前提下,统计有多少个非质数
for (int z : nodes) // 连通块的所有结点统一赋值
size[z] = nodes.size();
}
// 这 size[y] 个非质数与之前遍历到的 sum 个非质数,两两之间的路径只包含质数 x
res += (long) size[y] * sum;
sum += size[y];
}
res += sum; // 从 x 出发的路径
}
return res;
}
// 统计连通块的非质数
private void dfs(int x, int fa) {
nodes.add(x);
for (int y : g[x])
if (y != fa && np[y]) dfs(y, x);
}
}
字典序最小
316. 去除重复字母
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int[] cnt = new int[26];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[26];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
char[] t = s.toCharArray();
for(char c : t) cnt[c - 'a']++;
for(char c : t){
if(!vis[c - 'a']){
int i = sb.length() - 1;
while(i > -1 && c < sb.charAt(i) && cnt[sb.charAt(i) - 'a'] > 0){
vis[sb.charAt(i) - 'a'] = false;
sb.deleteCharAt(i--);
}
vis[c - 'a'] = true;
sb.append(c);
}
cnt[c - 'a']--;
}
return sb.toString();
// boolean[] vis = new boolean[26];
// int[] num = new int[26]; // 模拟哈希表统计字符个数
// char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
// for (char ch : arr){num[ch - 'a']++;}
// StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // 模拟栈
// for (char ch : arr){
// if (!vis[ch - 'a']){
// int i = sb.length() - 1;
// // 栈顶字母还有剩余,并且比较大,删除,也就是说在后面可以再出现。
// while (i > -1 && sb.charAt(i) > ch && num[sb.charAt(i) - 'a'] > 0){
// vis[sb.charAt(i) - 'a'] = false;
// sb.deleteCharAt(i--);
// }
// vis[ch - 'a'] = true;
// sb.append(ch);
// }
// num[ch - 'a'] -= 1;
// }
// return sb.toString();
}
}
316 扩展:重复个数不超过 limit
402. 移掉 K 位数字
class Solution {
public String removeKdigits(String num, int k) {
// int n = num.length(), remain = n - k, top = -1; // 栈顶索引
// if (n == k) return "0";
// 1、StringBuilder 模拟栈
// StringBuilder q = new StringBuilder();
// for(char c : num.toCharArray()){
// while (top != -1 && k > 0 && q.charAt(top) > c){
// q.deleteCharAt(top); top--; k--;
// }
// q.append(c);
// top++;
// }
// int i = 0;
// while (i < top && q.charAt(i) == '0') i++;
// return i >= remain ? "0" : q.substring(i, remain);
// 2、array 模拟栈
// char[] q = new char[n];
// for(char c : num.toCharArray()){
// while (k > 0 && top != -1 && q[top] > c){
// top--; k--;
// }
// q[++top] = c;
// }
// StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// for (int i = 0; i < remain; i++){
// if(sb.isEmpty() && q[i] == '0') continue;
// sb.append(q[i]);
// }
// return sb.isEmpty() ? "0" : sb.toString();
// 3、Deque 单调栈
// Deque<Character> q = new LinkedList<>();
// for (char c : num.toCharArray()) {
// while (!q.isEmpty() && k > 0 && q.peek() > c) {
// q.pop(); k--;
// }
// q.push(c);
// }
// for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) q.pop(); // 继续删除
// while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peekLast() == '0') q.pollLast(); // 前导 0
// StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// while (!q.isEmpty()) sb.append(q.pollLast()); // 倒装车
// return sb.length() == 0 ? "0" : sb.toString();
Deque<Character> q = new LinkedList<>();
for(char c : num.toCharArray()){
while(!q.isEmpty() && k > 0 && c < q.peek()){
q.pop(); k --;
}
q.push(c);
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++) q.pop();
while(!q.isEmpty() && q.peekLast() == '0') q.pollLast();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(!q.isEmpty()) sb.append(q.pollLast());
return sb.length() == 0 ? "0" : sb.toString();
}
}
321. 拼接最大数
class Solution:
def maxNumber(self, nums1, nums2, k):
def pick(nums, k):
q, drop = [], len(nums) - k
for num in nums:
while drop > 0 and q and q[-1] < num:
q.pop()
drop -= 1
q.append(num)
return q[:k]
def merge(A, B):
ans = []
while A or B:
bigger = A if A > B else B
ans.append(bigger.pop(0))
#bigger.pop(0)
return ans
return max(merge(pick(nums1, i), pick(nums2, k-i)) for i in range(k+1) if i <= len(nums1) and k-i <= len(nums2))
部分题目也可以用状态机 DP 解决。








 这篇博客主要介绍了前后缀分解和枚举中间点这两种技术在解决算法问题中的应用,涉及多种算法题目的解题思路,如接雨水问题、回旋镖的数量、有序三元组的最大值等。通过这些例子,阐述了如何利用前后缀分解和枚举中间点优化解题过程,并提供了解题策略和关键技巧。
这篇博客主要介绍了前后缀分解和枚举中间点这两种技术在解决算法问题中的应用,涉及多种算法题目的解题思路,如接雨水问题、回旋镖的数量、有序三元组的最大值等。通过这些例子,阐述了如何利用前后缀分解和枚举中间点优化解题过程,并提供了解题策略和关键技巧。
















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








