一、结论
1. 目标结论
refresh方法是初始化Spring容器的核心代码,共分为12个步骤
2. 其他结论
设计思想:
- 抽象思维锻炼
代码风格:
- 代码应该有个好名字。起不了好名字,有可能是违反了单一职责
- javadoc文档。
- Spring源码的习惯utils使用abstract class,虽然平时大家都不会去new,但谁知道呢,“可能会/一定不会”
- …
二、找线索
官方文档线索
官方文档摘录
The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. The BeanFactory interface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object. ApplicationContext is a sub-interface of BeanFactory.
The org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext interface represents the Spring IoC container and is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling the beans.
Several implementations of the ApplicationContext interface are supplied with Spring. In stand-alone applications, it is common to create an instance of ClassPathXmlApplicationContext or FileSystemXmlApplicationContext.
这里说明我们应该关注org.springframework.beans 和org.springframework.context两个包,核心接口BeanFactory和ApplicationContext。
可以初步确定研究对象 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext这两个实现类。
源码层线索
org.springframework.context包下ApplicationContext的实现
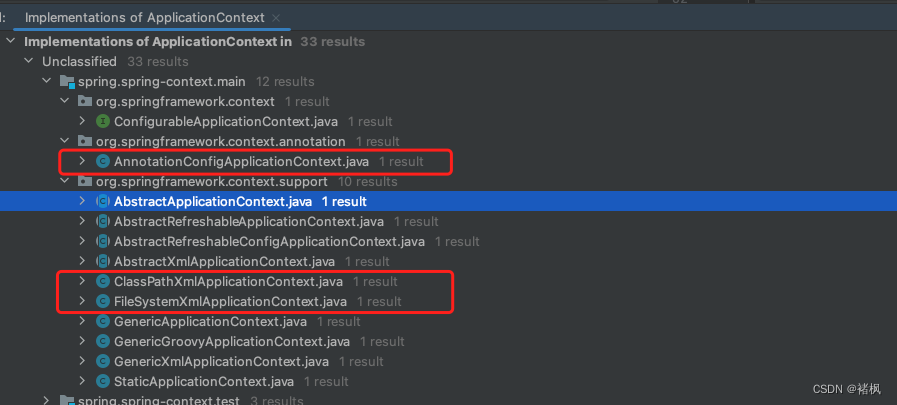
在org.springframework.context包下创建IOC容器的方式:
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从classpath中加载配置文件;
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从磁盘中加载配置文件;
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:使用注解配置容器对象时,使用此类进行注解读取,创建容器;
三、源码分析
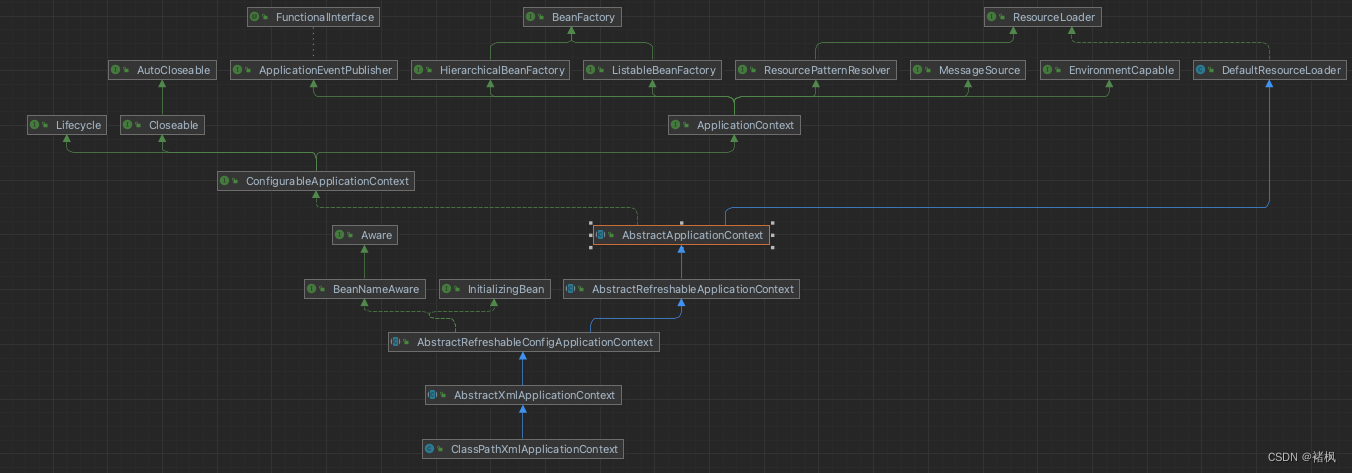
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 类图
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext源码
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
// ApplictionContext继承了HierarchicalBeanFactory,可以竖向竖向扩展
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 刷新IoC容器,这里调用的父类AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh实现
refresh();
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext源码
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 容器刷新准备工作
// 1. 设置启动时间、激活/关闭标识位
// 2. 执行属性资源的初始化验证必须的属性
// 3. 进行监听器和监听事件集合初始化
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 告知AbstractApplicationContext的实现类刷新beanFactory
// 1. 创建DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 2. 解析配置文件
// 3. 加载BeanDefinition
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 初始化beanFactory
// 设置容器的根ClassLoader,初始化SpEL表达功能,内置后置处理器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// BeanFactory的后置处理,子类根据实际情况来定
// 这个时候BeanDefinition已经被加载了,但还没有实例化,可以在这里做些特殊的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用已注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessors
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化MessageSource(例如处理国际化i18n)
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化ApplicationEvent广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 初始化一些特殊的bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 在所有注册的Bean中找到ApplicationListener Bean,注册到消息广播器中
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化所有非懒加载的单例对象
// 注意这里只是初始化了非懒加载的单例对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 完成初始化
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// 重制Spring‘s core 的缓存
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
四、附言
验证finishBeanFactoryInitialization只是加载非懒加载的单里对象
spring-beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.example.spring.LazySingleton" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true"/>
<bean class="com.example.spring.Singleton" scope="singleton"/>
<bean class="com.example.spring.Prototype" scope="prototype"/>
</beans>
public class LazySingleton {
public LazySingleton() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " init");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " destroy");
}
}
public class Prototype {
public Prototype() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " init");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " destroy");
}
}
public class Singleton {
public Singleton() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " init");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " destroy");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/spring-beans.xml");
System.out.println("========");
getBean(context);
context.close();
}
public static void getBean(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.getBean(Prototype.class);
context.getBean(LazySingleton.class);
}
输出
Singleton init
========
Prototype init
LazySingleton init
LazySingleton destroy
Singleton destroy





 本文详细分析了Spring Framework的初始化过程,重点探讨了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AbstractApplicationContext的源码,揭示了IoC容器的核心操作,包括refresh方法的12个步骤。文章通过官方文档和源码线索,引导读者理解Spring的IoC设计思想,并验证了finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法的作用。
本文详细分析了Spring Framework的初始化过程,重点探讨了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AbstractApplicationContext的源码,揭示了IoC容器的核心操作,包括refresh方法的12个步骤。文章通过官方文档和源码线索,引导读者理解Spring的IoC设计思想,并验证了finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法的作用。
















 849
849

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








