角色组成
工厂类:根据逻辑不同,产生具体的工厂产品。 抽象产品:一般是具体产品继承的父类或者实现的接口。 具体产品: 工厂类所创建的对象。
public interface Operation {
public double compute ( double numberA, double numberB) ;
}
public class AddOperation implements Operation {
@Override
public double compute ( double numberA, double numberB) {
return numberA + numberB;
}
}
public class SubOperation implements Operation {
@Override
public double compute ( double numberA, double numberB) {
return numberA - numberB;
}
}
public class MultiplyOperation implements Operation {
@Override
public double compute ( double numberA, double numberB) {
return numberA * numberB;
}
}
public class DivideOperation implements Operation {
@Override
public double compute ( double numberA, double numberB) {
if ( numberB== 0 )
throw new IllegalArgumentException ( "numberB must not be 0" ) ;
return numberA / numberB;
}
}
public enum OperationEnum {
ADD,
SUB,
MULTIPLY,
DIVIDE;
private OperationEnum ( ) { }
}
public class SimpleOperationFactory {
public static Operation createOperation ( OperationEnum type) {
Assert. notNull ( type, "type must not be null" ) ;
Operation operation = null;
switch ( type)
{
case ADD:
operation = new AddOperation ( ) ;
break ;
case SUB:
operation = new SubOperation ( ) ;
break ;
case MULTIPLY:
operation = new MultiplyOperation ( ) ;
break ;
case DIVIDE:
operation = new DivideOperation ( ) ;
break ;
}
return operation;
}
}
public class SimpleFactoryTest {
public static void main ( String[ ] args) {
Operation operation = SimpleOperationFactory. createOperation ( OperationEnum. ADD) ;
double compute = operation. compute ( 1 , 22 ) ;
System. out. println ( "compute = " + compute) ;
Operation o2 = SimpleOperationFactory. createOperation ( OperationEnum. SUB) ;
double compute1 = o2. compute ( 55 , 12 ) ;
System. out. println ( "compute1 = " + compute1) ;
Operation o3 = SimpleOperationFactory. createOperation ( OperationEnum. MULTIPLY) ;
double compute2 = o3. compute ( 12 , 3 ) ;
System. out. println ( "compute2 = " + compute2) ;
Operation o4 = SimpleOperationFactory. createOperation ( OperationEnum. DIVIDE) ;
double compute3 = o4. compute ( 25 , 0 ) ;
System. out. println ( "compute3 = " + compute3) ;
}
}
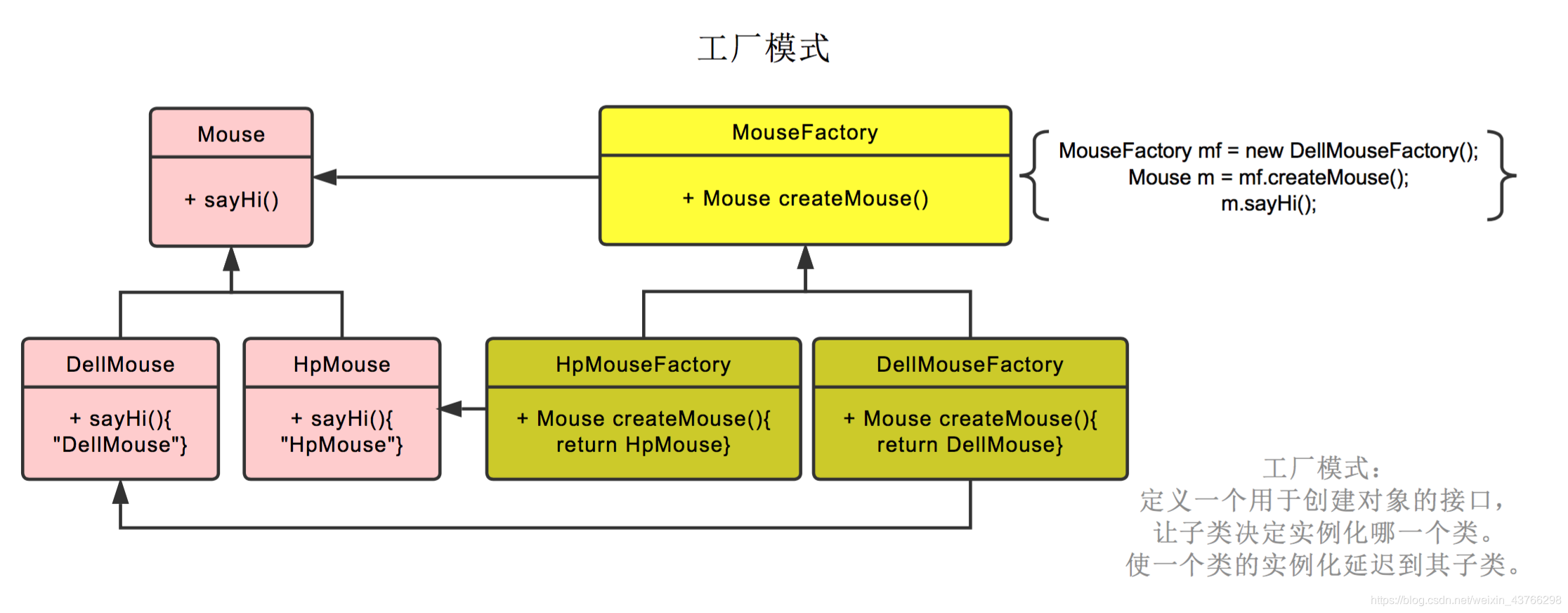
角色组成
抽象工厂:是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。 具体工厂:每个具体工厂只负责一个具体产品。 抽象产品:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口。 具体产品:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。
public interface Mouse {
void sayHi ( ) ;
}
public class HpMouse implements Mouse {
@Override
public void sayHi ( ) {
System. out. println ( "HpMouse..." ) ;
}
}
public class DellMouse implements Mouse {
@Override
public void sayHi ( ) {
System. out. println ( "DellMouse..." ) ;
}
}
public interface MouseFactory {
Mouse createMouse ( ) ;
}
public class HpMouseFactory implements MouseFactory {
@Override
public Mouse createMouse ( ) {
return new HpMouse ( ) ;
}
}
public class DellMouseFactory implements MouseFactory {
@Override
public Mouse createMouse ( ) {
return new DellMouse ( ) ;
}
}
角色组成
抽象工厂:是具体工厂角色必须实现的接口或者必须继承的父类。 具体工厂:每个具体工厂负责一个系列产品的生产(产品族)。 抽象产品:它是具体产品继承的父类或者是实现的接口,抽象工厂模式有多个抽象产品。 具体产品:具体工厂角色所创建的对象就是此角色的实例。
public interface BenzCar {
void makeBenzCar ( ) ;
}
public interface BmwCar {
void makeBmwCar ( ) ;
}
public class BenzSportCar implements BenzCar {
@Override
public void makeBenzCar ( ) {
System. out. println ( " make BenzSportCar..." ) ;
}
}
public class BenzBusinessCar implements BenzCar {
@Override
public void makeBenzCar ( ) {
System. out. println ( " make BenzBusinessCar..." ) ;
}
}
public class BmwSportCar implements BmwCar {
@Override
public void makeBmwCar ( ) {
System. out. println ( " make BmwSportCar..." ) ;
}
}
public class BmwBusinessCar implements BmwCar {
@Override
public void makeBmwCar ( ) {
System. out. println ( " make BmwBusinessCar..." ) ;
}
}
public abstract class CarFactory {
public abstract BenzCar createBenzCar ( ) ;
public abstract BmwCar createBmwCar ( ) ;
}
public class SportCarFactory extends CarFactory {
public BenzCar createBenzCar ( ) {
return new BenzSportCar ( ) ;
}
public BmwCar createBmwCar ( ) {
return new BmwSportCar ( ) ;
}
}
public class BusinessCarFactory extends CarFactory {
public BenzCar createBenzCar ( ) {
return new BenzBusinessCar ( ) ;
}
public BmwCar createBmwCar ( ) {
return new BmwBusinessCar ( ) ;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main ( String[ ] args) {
SportCarFactory sportCarFactory = new SportCarFactory ( ) ;
BenzCar benzCar = sportCarFactory. createBenzCar ( ) ;
benzCar. makeBenzCar ( ) ;
BmwCar bmwCar = sportCarFactory. createBmwCar ( ) ;
bmwCar. makeBmwCar ( ) ;
BusinessCarFactory businessCarFactory = new BusinessCarFactory ( ) ;
BenzCar benzCar2 = businessCarFactory. createBenzCar ( ) ;
benzCar2. makeBenzCar ( ) ;
BmwCar bmwCar2 = businessCarFactory. createBmwCar ( ) ;
bmwCar2. makeBmwCar ( ) ;
}
}
控制台输出结果:
make BenzSportCar. . .
make BmwSportCar. . .
make BenzBusinessCar. . .
make BmwBusinessCar. . .
① 抽象产品:工厂方法模式只有一个抽象产品类,而抽象工厂模式有多个。 ② 具体工厂类能创建的具体产品类型:工厂方法模式的具体工厂类只能创建一种具体产品类的实例, 而抽象工厂模式可以创建多种具体产品类的实例。
public interface SubjectFactory {
Subject createSubject ( SubjectContext context) ;
}
具体工厂DefaultSubjectFactory public class DefaultSubjectFactory implements SubjectFactory {
public DefaultSubjectFactory ( ) {
}
public Subject createSubject ( SubjectContext context) {
SecurityManager securityManager = context. resolveSecurityManager ( ) ;
Session session = context. resolveSession ( ) ;
boolean sessionCreationEnabled = context. isSessionCreationEnabled ( ) ;
PrincipalCollection principals = context. resolvePrincipals ( ) ;
boolean authenticated = context. resolveAuthenticated ( ) ;
String host = context. resolveHost ( ) ;
return new DelegatingSubject ( principals, authenticated, host, session, sessionCreationEnabled, securityManager) ;
}
}
具体工厂DefaultWebSubjectFactory,扩展了DefaultSubjectFactory public class DefaultWebSubjectFactory extends DefaultSubjectFactory {
public DefaultWebSubjectFactory ( ) {
}
public Subject createSubject ( SubjectContext context) {
if ( ! ( context instanceof WebSubjectContext ) ) {
return super . createSubject ( context) ;
} else {
WebSubjectContext wsc = ( WebSubjectContext) context;
SecurityManager securityManager = wsc. resolveSecurityManager ( ) ;
Session session = wsc. resolveSession ( ) ;
boolean sessionEnabled = wsc. isSessionCreationEnabled ( ) ;
PrincipalCollection principals = wsc. resolvePrincipals ( ) ;
boolean authenticated = wsc. resolveAuthenticated ( ) ;
String host = wsc. resolveHost ( ) ;
ServletRequest request = wsc. resolveServletRequest ( ) ;
ServletResponse response = wsc. resolveServletResponse ( ) ;
return new WebDelegatingSubject ( principals, authenticated, host, session, sessionEnabled, request, response, securityManager) ;
}
}
}
public interface Subject {
Object getPrincipal ( ) ;
PrincipalCollection getPrincipals ( ) ;
boolean isPermitted ( String var1) ;
}
具体产品DelegatingSubject和WebDelegatingSubject












 本文深入解析了工厂模式的三种形态:简单工厂模式、工厂方法模式和抽象工厂模式,通过实例展示了每种模式的角色组成和实现方式,并对比了它们之间的区别。
本文深入解析了工厂模式的三种形态:简单工厂模式、工厂方法模式和抽象工厂模式,通过实例展示了每种模式的角色组成和实现方式,并对比了它们之间的区别。
















 366
366

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








