1.Collection接口实现类的特点
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
- collection实现子类可以存放多个元素,每个元素可以是Object
- 有些Collection的实现类,可以存放重复的元素,有些不可以
- 有些Collection的实现类,有些是有序的(List),有些不是有序(Set)
- Collection接口没有直接的实现子类,是通过它的子接口Set 和 List来实现的
2.Collection接口常用方法
常用方法
- 以实现子类ArrayList来演示.CollectionMethod.java
- add:添加单个元素
- remove:删除指定元素
- contains:查找元素是否存在
- size:获取元素个数
- isEmpty:判断是否为空
- clear:清空
- addAll:添加多个元素
- containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在
- removeAll:删除多个元素
- 说明:以ArrayList实现类来演示.
代码示例
package com.Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
//add:添加单个元素
list.add("jack");
list.add(10); //list.add(new Integer(10));
list.add(true);
System.out.println("list=" + list);//list=[jack, 10, true]
//remove:删除指定元素
list.remove(0); //删除第一个元素
list.remove(true); //删除指定元素
System.out.println("list=" + list);//list=[10]
//contains:查找元素是否存在
System.out.println(list.contains("jack"));//false
//size:获取元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());//1
//isEmpty:判断是否为空
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());//false
//clear:清空
list.clear();
System.out.println("list=" + list);//list=[]
//addAll添加多个元素
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add("tom");
list2.add("jack");
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);//list=[tom, jack]
//containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在
System.out.println(list.containsAll(list));//true
//removeAll:删除多个元素
list.removeAll(list);
System.out.println("list=" + list);//list=[]
}
}
Collection方法——接口遍历元素方式
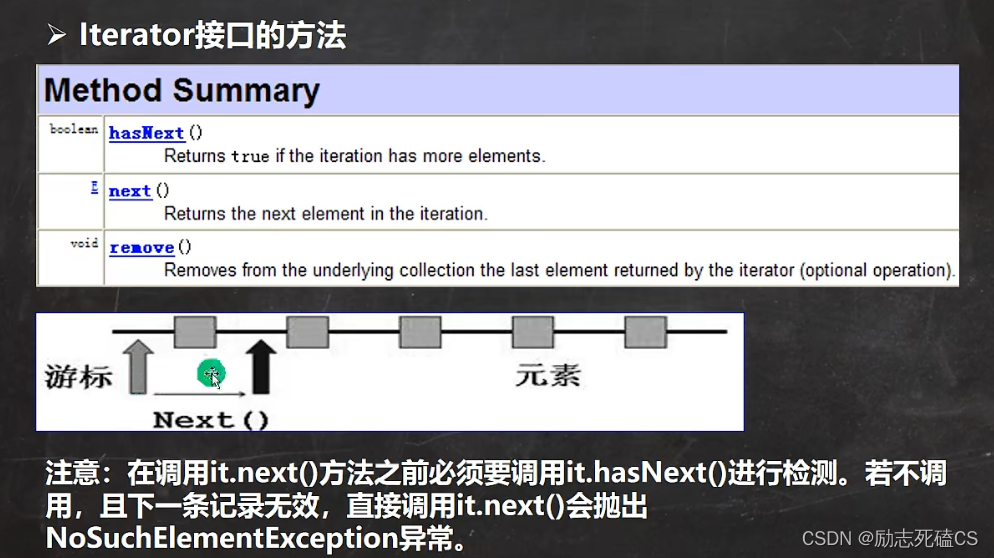
- 方式一—使用lterator(迭代器)
- Iterator对象称为迭代器,主要用于遍历Collection 集合中的元素。
- 所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了lterator接口的对象,即可以返回一个迭代器。
- Iterator的结构.[看一张图]
- Iterator仅用于遍历集合lterator本身并不存放对象。
迭代器执行原理

Iterator接口方法
代码示例
package com.Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 10));
col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 5));
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 34));
// System.out.println("col=" + col);
//遍历col集合
//1.先得到col对应的迭代器
Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
//2.使用while循环遍历
while (iterator.hasNext()) { //判断是否还有数据
Object obj = iterator.next(); //返回下一个元素,类型是Object
System.out.println("obj=" + obj);
}
//3.当退出while循环后,这时的iterator迭代器,指向最后的元素
//iterator.next();//NoSuchElementException
//4.如果需要再次遍历,则需要重置迭代器
iterator = col.iterator(); //重置迭代器
System.out.println("---------第二次遍历--------");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj=" + obj);
}
System.out.println("---------第三次遍历--------");
//使用foreach
col.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
- 方式二—for循环增强
增强for循环,可以代替iterator迭代器,特点:增强for就是简化版的iterator,本质一样。只能用于遍历集合或数组。
基本语法
for(元素类型 元素名 : 集合名或数组名) {
访问元素
}
package com.Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 10));
col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 5));
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 34));
//使用增强for
//1.使用增强for,在Collection集合
//2.增强for的底层仍然是迭代器
//3.增强for就是简化版的迭代器
//4.快捷键 I
for (Object book : col) {
System.out.println("book=" + book);
}
//增强for也可以直接在数组中使用
// int[] nums = {1, 8, 10, 90};
// for (int i : nums) {
// System.out.println("i" + i);
// }
}
}





 本文详细解读了Collection接口在Java中的核心概念,包括其子接口Set和List的区别,以及ArrayList等常见实现类的特性。涵盖了添加、删除、查找、大小判断和遍历方法的实例演示。
本文详细解读了Collection接口在Java中的核心概念,包括其子接口Set和List的区别,以及ArrayList等常见实现类的特性。涵盖了添加、删除、查找、大小判断和遍历方法的实例演示。
















 616
616

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








