其实少了一个排序算法,但我们假设从小到大排好了。
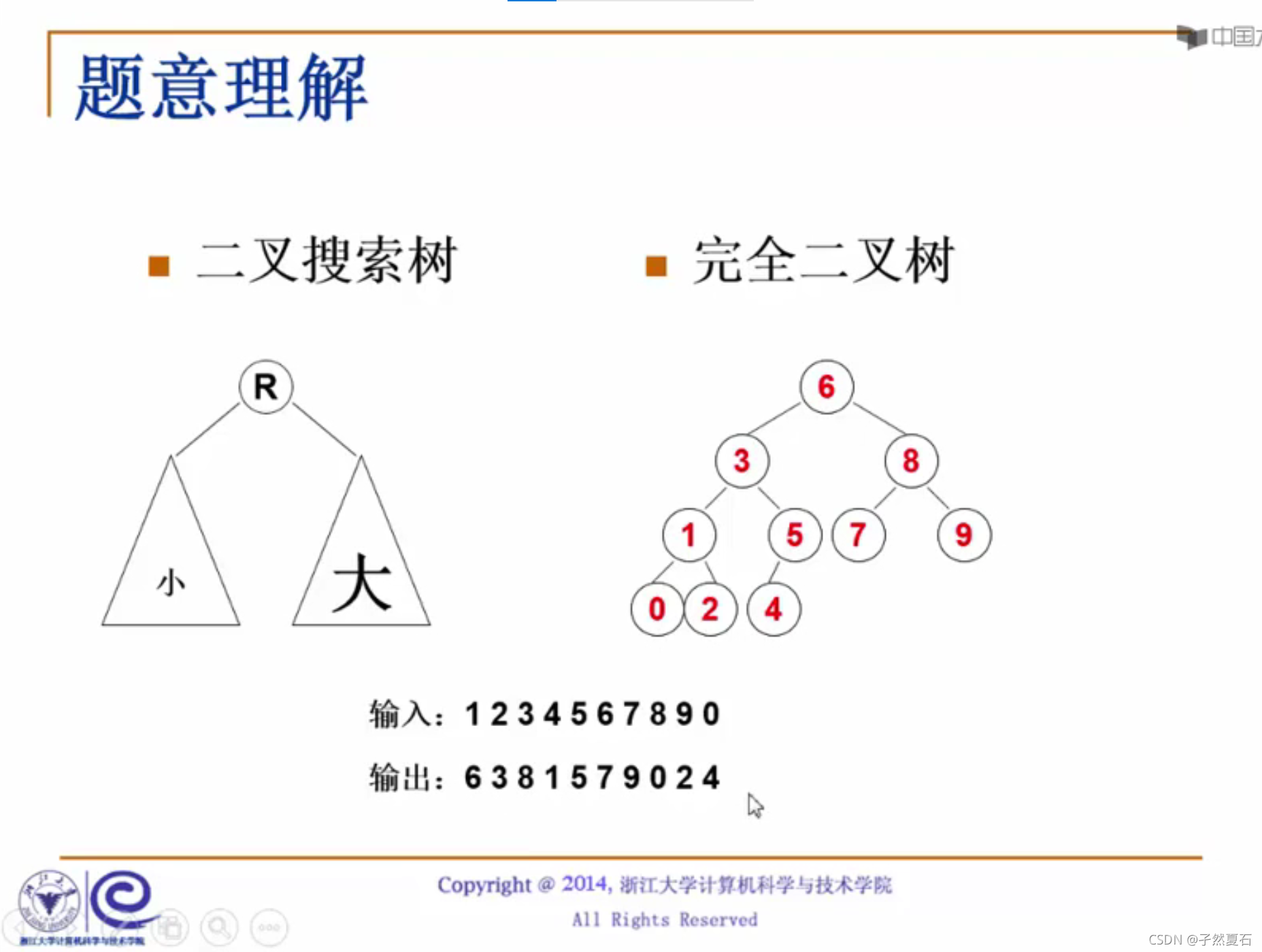

/*完全二叉搜索树,假设0用上了,注意弄清下标和个数之间的关系*/
#include <math.h>
int GetLeftLen(int num)
{
int left, temp = 1;
while (temp < num)
temp *= 2;
/*虽然多了,但恰好是层数*/
int k = (pow(2, temp) - 1) - pow(2, temp - 2);
/*k代表了左子树最后一个下标,有t层至多有2^t-1个*/
/*pow(2,temp)-2是有0时,全都有的完美最后一个下标。*/
/*pow(2,temp-2)-2是有0时,第n层有的个数数量的一半*/
if (num >= k)
left = pow(2, temp - 1) - 1;
else
left = pow(2, temp - 2) + num - (pow(2, temp - 1) - 1);
/*左子树除最后一层时规律的,再加上最后几个*/
return left;
}
/*假设已经有一列排好的数组,从小到大往里面放*/
void compelete_binary_search_tree(int head, int num, int root)
{
int origin[10], new[10];
if (num == 0) return;
int left, right;
left = GetLeftLen(num);
right = num - left - 1;
new[root] = origin[head + left];
/*有0就稍微有点不一样*/
int left_child, right_child;
left_child = 2 * root + 1;
right_child = left_child + 1;
compelete_binary_search_tree(head, left, new[left_child]);
compelete_binary_search_tree(left+head, right, new[right_child]);
}








 本文详细介绍了如何使用递归实现完全二叉搜索树的构建,通过GetLeftLen函数确定节点插入位置,并演示了如何根据已排序数组填充树结构。重点在于理解递归调用和二叉树特性在插入过程中的应用。
本文详细介绍了如何使用递归实现完全二叉搜索树的构建,通过GetLeftLen函数确定节点插入位置,并演示了如何根据已排序数组填充树结构。重点在于理解递归调用和二叉树特性在插入过程中的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








