Map
map是以键值对(key-value)来存储的接口
键不重复(重复的键值对覆盖原来的值(value))
map接口如下,比较常用的实现类是Hashmap和TreeMap
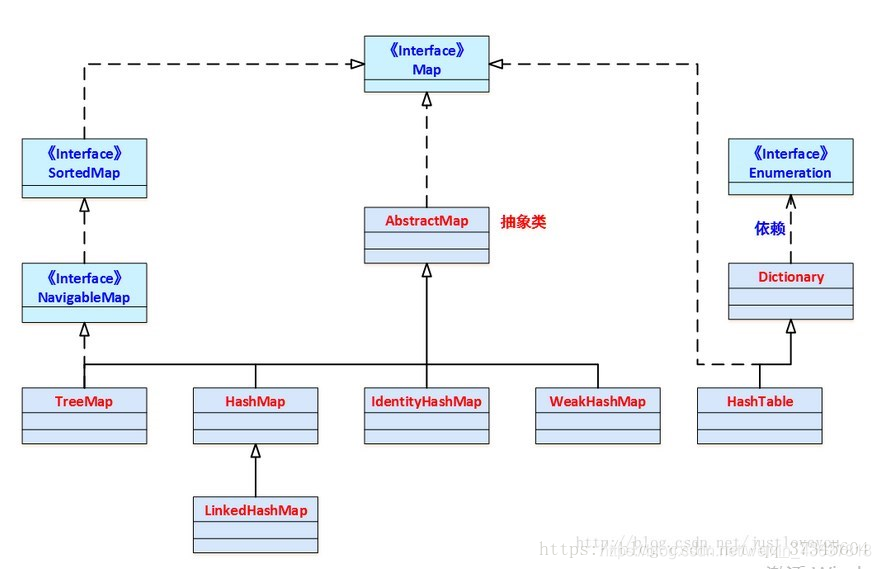
map的初始化
//泛型<k,v> 可以是任意对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map的方法
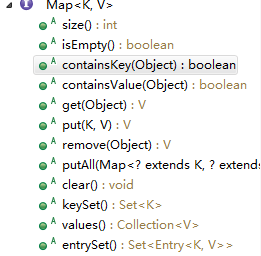
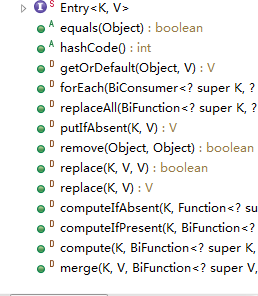
//部分方法测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"test01");
map.put(2, "test02");
map.put(3, "test03");
System.out.println(map.get(1));
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println(map.size());
map.remove(2);
System.out.println(map);
}
运行结果
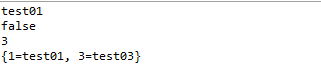
底层基本分析
HashMap
hashmap是通过散列表的形式来存储的。核心是由一个存储链表的数组来实现的,通过key的hashcode来计算对应的数组下标值,最后实现存储对应的链表区域。
java中由于每个类都继承了基类Object,hashcode属于Object
故所有不同类都有不同的hashcode,再通过hashcode由散列算法计算出对应的hash值来得出存储位置。
code(链表基本元素)
code属性和方法
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
哈希算法
jdk1.8
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
存储
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
TreeMap
实现了排序(按照key递增),依靠comparable,定义的类需要实现comparable接口来实现排序(返回值为负数小于,整数大于,o等于)
通过红黑二叉树来实现
set接口
底层实现的hashset和treeset
HashSet实际上是使用了HashMap<k,v>来代替,其中v用一个不变的量来代替。
TreeSet则是使用了TreeMap<k,v>
























 1419
1419

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








