目录:
- 面试中常见的动态规划类型
- 坐标型动态规划
1.1 题目 - 最小路径和(求最大最小值)
1.2 题目 - 不同的路径(统计方案个数)
1.3 题目 - 爬楼梯 (统计方案个数、一维坐标上的dp)
1.4 题目 - jump game (是否可行、一维坐标上的dp - follow up:求最小值)
1.5 题目 - 最长上升子序列 (最大最小值) - 序列型动态规划
2.1 题目 - word break (可行性)
2.2 题目 - 切割回文串 palindrome-partitioning-ii (最大最小值)- 判断回文串(区间型动态规划) - 双序列型动态规划
3.1 题目 - 最长公共子序列(求Max)
3.2 题目 - Edit Distance (求Min)
3.3 题目 - Distinct Subsequence (求方案总数)
3.4 题目 - Interleaving String (求是否可行) - 其他类型的动态规划
0.面试中常见的动态规划类型

1.坐标型动态规划
初始化一个二维的动态规划的时候,首先初始化起点,紧接着初始化第0行和第0列。

1.1最小路径和
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/minimum-path-sum/
给定一个只含非负整数的m*n网格,找到一条从左上角到右下角的可以使数字和最小的路径。
2)思路
如果是上下左右四个方向都可以走,则不能用dp,因为四个方向的话存在环,这样就不能定义远近关系,也就是不能定义大状态和小状态,就没法定义递推方程。但也存在例外,比如说滑雪的题目,按照数值降低定义远近关系。


class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param grid: a list of lists of integers
* @return: An integer, minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path
*/
int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
// write your code here
int n = grid.size();
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
int m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(m,INT_MAX));
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[i][0] = grid[i][0] + dp[i-1][0];
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
dp[0][i] = grid[0][i] + dp[0][i-1];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<m;++j){
dp[i][j] = grid[i][j] + min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[n-1][m-1];
}
};
1.2 题目 - 不同的路径(统计方案个数)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/unique-paths/
有一个机器人的位于一个 m × n 个网格左上角。
机器人每一时刻只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角。
问有多少条不同的路径?
follow up:
中间某些格子有障碍物。
2)思路
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param m: positive integer (1 <= m <= 100)
* @param n: positive integer (1 <= n <= 100)
* @return: An integer
*/
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// write your code here
vector<vector<int>> dp(m,vector<int>(n,0));
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
dp[0][i] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for(int i=1;i<m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<n;++j){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param obstacleGrid: A list of lists of integers
* @return: An integer
*/
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>> &obstacleGrid) {
// write your code here
if(obstacleGrid.size()==0 || obstacleGrid[0].size() == 0){
return 0;
}
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m,vector<int>(n,0));
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
if(obstacleGrid[0][i]==0){
dp[0][i] = 1;
}
else{
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
if(obstacleGrid[i][0]==0){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
else{
break;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<n;++j){
if(obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1){
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
};
1.3题目 - 爬楼梯 (统计方案个数)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/climbing-stairs/
假设你正在爬楼梯,需要n步你才能到达顶部。但每次你只能爬一步或者两步,你能有多少种不同的方法爬到楼顶部?
follow up:
一个小孩爬一个 n 层台阶的楼梯。他可以每次跳 1 步, 2 步 或者 3 步。实现一个方法来统计总共有多少种不同的方式爬到最顶层的台阶。
2)思路
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] 斐波那契数列
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param n: An integer
* @return: An integer
*/
int climbStairs(int n) {
// write your code here
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
if(n==1){
return 1;
}
vector<int> dp(n,0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 2;
for(int i=2;i<n;++i){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param n: An integer
* @return: An integer
*/
int climbStairs2(int n) {
// write your code here
if(n==0){
return 1;
}
if(n==1){
return 1;
}
if(n==2){
return 2;
}
vector<int> dp(n,0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 2;
dp[2] = 4;
for(int i=3;i<n;++i){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2] + dp[i-3];
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
1.4 题目 - jump game (是否可行、一维坐标上的dp)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/jump-game/

follow up:- (求最小值)


2)思路

动态规划:
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param A: A list of integers
* @return: A boolean
*/
bool canJump(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code here
int n = A.size();
vector<bool> dp(n,false);
dp[0] = true;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
for(int j=0;j<i;++j){
if(dp[j] && A[j] + j >= i){
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
贪心法:
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param A: A list of integers
* @return: A boolean
*/
bool canJump(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code here
int n = A.size();
if(n==0){
return true;
}
int far = A[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
if(i <= far && A[i] + i > far){
far = A[i] + i;
}
}
return far >= n-1;
}
};
follow up - 求最小值:动态规划求解
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param A: A list of integers
* @return: An integer
*/
int jump(vector<int> &A) {
// write your code here
int n = A.size();
vector<int> dp(n, INT_MAX);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
int minstep = INT_MAX;
for(int j=0;j<i;++j){
if(dp[j]!=INT_MAX && A[j] + j >= i){
minstep = min(minstep, dp[j]+1);
}
}
dp[i] = minstep;
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
follow up - 求最小值:贪心法求解
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param A: A list of integers
* @return: An integer
*/
int jump(vector<int> &A) {
int n = A.size();
if(n==0){
return -1;
}
int start=0,end=0,jumps = 0;
while(end < n-1){
jumps++;
int far = end;
for(int i=start;i<=end;++i){
if(A[i] + i > far){
far = A[i] + i;
}
}
start = end + 1;
end = far;
}
return jumps;
}
};
1.5 题目 - 最长上升子序列 (最大最小值)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-increasing-subsequence/
subarray:必须是连续的。 subsequence:不一定连续
2)思路
A. 动规
B. 二分法
暴力求解复杂度是O(2^n),每个元素选或者不选, 所以可能采用dp

class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param nums: An integer array
* @return: The length of LIS (longest increasing subsequence)
*/
int longestIncreasingSubsequence(vector<int> &nums) {
// write your code here
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> dp(n, 1);
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
for(int j=0;j<i;++j){
if(nums[i] > nums[j]){
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
int LIC = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
LIC = max(LIC, dp[i]);
}
return LIC;
}
};
二分法:(理解了)
下面介绍一种O(nlogn)的LIS算法:
- 记数组为a[0…n-1];
- 状态定义:
dp[i]代表LIS的第i项最小值, dpLen代表当前dp数组的长度; - 状态转移:
dp初始为空数组, 我们按a数组元素的下标顺序进行扫描, 假设现在扫描到a[i], 先找到dp数组中第一项大于或等于a[i]的元素, 记为dp[j]; 将dp[j]更新成a[i]即可; 如果dp数组中没有元素比a[i]大的话, 那么直接将a[i]插入到dp数组的尾部,再更新dp数组长度; - 整个数组的LIS结果就是dpLen.
- 需要注意的是, 虽然dp数组最终长度就是LIS, 但是里边的元素并不是真正的子序列, 如果要求输出这个序列, 加上一些反向追踪变量就能得到了. 但是如何求LIS的数量呢?
- 刚开始dp数组为空,显然是单调递增数组, 而后面的每一步替换或者尾部插入执行都不影响其单调递增的特性, 所以每次定位到dp[j]可以用二分法, 复杂度是 O(logn)
- 整体算法复杂度:
状态转移次数为n, 每次状态转移代码都是logn, 所以总复杂度为O(nlogn).
算法步骤示例:
假设a = [4, 2, 6, 3, 1, 5], 初始dp=[], 具体算法运行步骤如下:
- a[0]=4 => dp=[4];
- a[1]=2 => dp=[2];
- a[2]=6 => dp=[2, 6];
- a[3]=3 => dp=[2, 3];
- a[4]=1 => dp=[1, 3];
- a[5]=1 => dp=[1, 3, 5];
所以这个a数组的LIS就是len(dp)=3. 从运行步骤里可以看出, 如果一个数很小, 可以作为LIS的头部或者中部, 让后面的数字更容易接到它后面, 以此增大LIS长度; 而一个数非常大, 则可以很容易接到LIS的尾部, 也一样能增大LIS长度; 所以让它们找准自己的定位还是非常重要的.
2.单序列型动态规划
给定数字数组或者字符数组(字符串),求最优或者其他。这里是前i个位置,而坐标型是第i个位置

2.1 题目 - word break(切割问题、可行性)
1)题目
切割问题
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/word-break/


2)思路

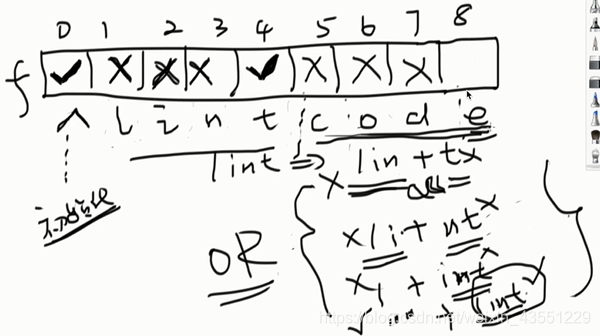
为什么申请n+1个空间?


单词的平均长度:5点几
简单dp: - O(n^3)
优化1:
因为单词的最长长度也就20多,所以从后往前割,当割到单词词典中单词的最长长度后,便不需要再切割下去。
最外层循环用时是n,从后往前找单词时间是L,判断单词是否在字典中,时间是L,
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param s: A string
* @param dict: A dictionary of words dict
* @return: A boolean
*/
bool wordBreak(string &s, unordered_set<string> &dict) {
// write your code here
int maxlen = getMaxLen(dict);
bool *dp = new bool[s.size()+1];
dp[0] = true;
for(int i=1;i<=s.size();++i){
dp[i] = false;
for(int j=1;j<=maxlen && j<=i;j++){
if(!dp[i-j]){
continue;
}
string w = s.substr(i-j,j);
if(dict.find(w)!=dict.end()){
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.size()];
}
int getMaxLen(unordered_set<string> &dict){
int maxlen = 0;
for(unordered_set<string>::iterator it=dict.begin();it!=dict.end();++it){
int l = (*it).size();
maxlen = max(maxlen, l);
}
return maxlen;
}
};
2.2 题目 - 切割回文串 palindrome-partitioning-ii (最大最小值)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/palindrome-partitioning-ii/


2)思路

区间型动态规划


如果简单判断回文串的话时间复杂度是O(n^3),会超时,所以将判断回文串加速,提升到O(1)
总的时间复杂度:O(n^2)
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param s a string
* @return an integer
*/
int minCut(string s) {
// write your code here
int n = s.size();
int dp[n+1];
bool isPali[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
isPali[i][i] = true;
if(i+1<n){
isPali[i][i+1] = (s[i]==s[i+1]);
}
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;--i){ //i必须从n-1出发,不能从0开始
for(int j=i+2;j<n;j++){
isPali[i][j] = isPali[i+1][j-1] && (s[i] == s[j]);
}
}
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
dp[i] = i;
for(int j=0;j<i;++j){
if(isPali[j][i-1]){
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[n]-1;
}
};
3. 双序列型动态规划
给了两个串,研究两个串之间的关系

3.1 题目 - 最长公共子序列(最大最小值)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/longest-common-subsequence/


2)思路
暴力:两个序列的子序列(相当于子集)比较。

class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param A: A string
* @param B: A string
* @return: The length of longest common subsequence of A and B
*/
int longestCommonSubsequence(string &A, string &B) {
// write your code here
int m = A.size(), n = B.size();
int dp[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;++i){
dp[i][0] = 0;
}
for(int j=0;j<=n;++j){
dp[0][j] = 0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){
if(A[i-1] == B[j-1]){ //
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] +1;
}
else{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
3.2 题目 - Edit Distance (求Min)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/edit-distance/

2)思路

class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param word1: A string
* @param word2: A string
* @return: The minimum number of steps.
*/
int minDistance(string &word1, string &word2) {
// write your code here
int m = word1.size(), n = word2.size();
int dp[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;++i){
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j=0;j<=n;++j){
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){
if(word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1]+1); // 匹配、插入
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j]+1); //删除
}
else{
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1]+1, dp[i-1][j]+1);//替换、删除
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i][j-1]+1);//插入
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
类似题:

3.3 题目 - Distinct Subsequence (求方案总数)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/distinct-subsequences/
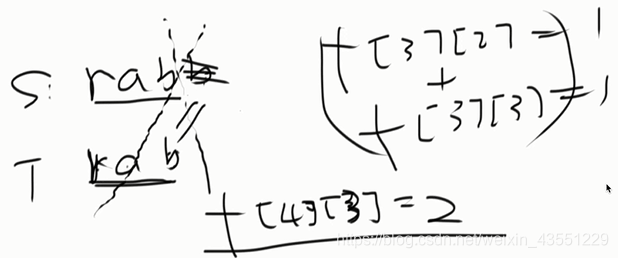
2)思路

class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param : A string
* @param : A string
* @return: Count the number of distinct subsequences
*/
int numDistinct(string S, string T) {
// write your code here
int m=S.size(), n = T.size();
int dp[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;++i){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){ //注意j从1开始
dp[0][j] = 0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){
if(S[i-1] == T[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j];
}
else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
3.4 题目 - Interleaving String (求是否可行)
1)题目
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/interleaving-string/
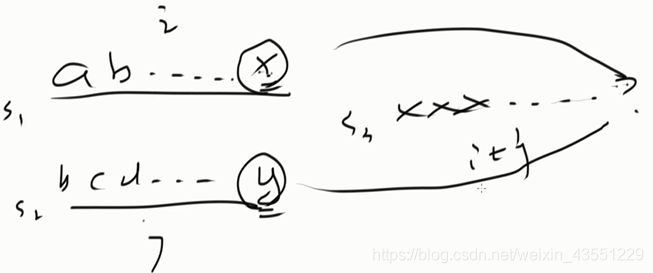
2)思路

class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param s1: A string
* @param s2: A string
* @param s3: A string
* @return: Determine whether s3 is formed by interleaving of s1 and s2
*/
bool isInterleave(string &s1, string &s2, string &s3) {
// write your code here
int m = s1.size(), n = s2.size(), r = s3.size();
if(r!=m+n){
return false;
}
bool dp[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;++i){
dp[i][0] = (s1.substr(0,i) == s3.substr(0,i));
}
for(int j=0;j<=n;++j){
dp[0][j] = (s2.substr(0,j) == s3.substr(0,j));
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){
dp[i][j] = (s1[i-1]==s3[i+j-1] && dp[i-1][j] || s2[j-1] == s3[i+j-1] && dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};
4. 其他类型的动态规划:
背包类:
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/backpack/
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/backpack-ii/
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/minimum-adjustment-cost/
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/k-sum/
• 区间类:
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/coins-in-a-line-iii/
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/scramble-string/
• 划分类:
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iv/
• http://www.lintcode.com/problem/maximum-subarray-iii/
513. 完美平方
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/perfect-squares/
正整数 n, 找到若干个完全平方数(比如1, 4, 9, … )使得他们的和等于 n。你需要让平方数的个数最少。
超时代码如下:
等差数列法判断一个数是否是平方数:
bool isSqure(int n){
for(int i=1;n>0;i+=2){
n-=i;
}
if(n==0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
代码:
class Solution {
public:
/*
* @param n: a positive integer
* @return: An integer
*/
int numSquares(int n) {
// write your code here
int dp[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=n;++i){
dp[i] = INT_MAX;
}
for(int i=0;i*i<=n;++i){
dp[i*i] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<=n;++i){
for(int j=1;j*j<=i;++j){
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i-j*j]+1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
数学求解算法:
首先有一个四平方和定理Lagrange’s four-square theorem,这个定理说明每个正整数都能表示为4个整数的平方和,用到这个题目上,就是说可能的最少次数只有1,2,3,4四种可能。
然后还有一个定理Legendre’s three-square theorem ,该定理说明满足n = 4^k(8m + 7)的n,最少只能表示为4个整数的平方和。
剩下只需要对可能次数为1和2再作判断即可,以下是纯数学方法的代码:

603. 最大整除子集
// 倍数关系是可以传递的,接龙的要求是后面一个数是前面一个数的倍数 public class Solution { public List largestDivisibleSubset(int[] nums) { // 必须先排序 Arrays.sort(nums); // f[i]表示第i个数结尾的最长龙有多长 int[] f = new int[nums.length]; // pre[i]记录当前i的上一个接龙数的位置 // 建立pre数组目的是为了后面将具体方案添加入队列的需要 int[] pre = new int[nums.length]; // 两重for循环,从头开始计算f[i]的值 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 先将f[i]初始化为1 f[i] = 1; // pre[i] = i或者pre[i] = -1代表前面没有值了 pre[i] = i; // 动态规划方程,从所有j < i 的f[j]中找出最大的 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { if (nums[i] % nums[j] == 0 && f[i] < f[j] + 1) { f[i] = f[j] + 1; pre[i] = j; } } } List ans = new ArrayList(); // 特殊情况 if (nums.length == 0) { return ans; } // 从头到尾找到f[i]数组中的最大值和它的下标i // 从i开始往开头方向找出具体接龙的所有位置,加入数组 int max = 0; int max_i = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (f[i] > max) { max = f[i]; max_i = i; } } ans.add(nums[max_i]); // 若pre[i] = i 证明到头了,pre[i] != i时继续往前找 while (max_i != pre[max_i]) { max_i = pre[max_i]; ans.add(nums[max_i]); } Collections.reverse(ans); return ans; } }





 本文详细介绍了动态规划在面试中常见的几种类型,包括坐标型、单序列型和双序列型,并通过具体题目如最小路径和、爬楼梯、word break、最长公共子序列等,讲解了各类动态规划问题的解决思路和方法。动态规划的核心在于状态定义和状态转移,通过这些经典题目,读者可以深入理解动态规划的应用。
本文详细介绍了动态规划在面试中常见的几种类型,包括坐标型、单序列型和双序列型,并通过具体题目如最小路径和、爬楼梯、word break、最长公共子序列等,讲解了各类动态规划问题的解决思路和方法。动态规划的核心在于状态定义和状态转移,通过这些经典题目,读者可以深入理解动态规划的应用。
















 6332
6332

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








