DBUtils 介绍
DBUtils工具类完成 DAO 的封装 ,简化DAO层代码编写

核心类和接口是QueryRunner && ResultSetHandler,一起使用,完成数据表增删改查
QueryRunner 框架核心类 ,所有数据库操作都是必须通过 QueryRunner 进行的
ResultSetHandler 结果集封装接口,完成将ResultSet 结果集 封装为一个Java对象
封装前案例
@Test
public void query() throws SQLException, PropertyVetoException {
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getDataSource().getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password =? ";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "ww");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 789);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
User user = null;
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
String password = resultSet.getString("password");
String email = resultSet.getString("email");
user = new User(id, username, password, email);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
封装后代码,大大简化了代码
@Test
public void query() throws SQLException, PropertyVetoException {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password =? ";
Object[] params = {"ww", 789};
BeanHandler<User> rsh = new BeanHandler<User>(User.class);
User user = runner.query(sql, rsh, params);
System.out.println(user);
}
DBUtils的增删改的学习
增删改都无需要对结果集进行封装
//增
@Test
public void test_insert() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 update 方法
String sql = "insert into user values(?,?,?,?);";
Object[] params = {5, "小七", "123", "xiaoqi@itcast.cn"};
queryRunner.update(sql, params);
}
//删
@Test
public void test_delete() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 update 方法
String sql = "delete from user where id=?;";
queryRunner.update(sql, 5);
}
//改
@Test
public void test_update() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 update 方法
String sql = "update user set username=?, password=? where id=?;";
Object[] params = {"李四", "888", 2};
queryRunner.update(sql, params);
}
DBUtils 工具的 查询操作
查询因为需要对结果的封装,这里引出了ResultSetHandler 接口
@Test
public void test_query() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 query 方法
String sql = "select * from user where id = ?;";
User user = queryRunner.query(sql, new ResultSetHandler<User>(){
@Override
public User handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
String password = rs.getString("password");
String email = rs.getString("email");
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
user.setEmail(email);
return user;
}
return null;
}
}, 3);
System.out.println(user);
}

ResultSetHandler 的实现类使用

ResultSetHandler 在DBUtils 框架中提供九个默认 实现类,直接使用九个默认实现类,可以完成常规操作,而不需要自定义结果集封装,最常见最常用的就是以下三个
BeanHandler: 将结果集中第一条记录封装到一个指定的javaBean中。
BeanListHandler:将结果集中每一条记录封装到指定的javaBean中,将这些javaBean在封装到List集合中
ScalarHandler :它是用于单数据。例如select count(*) from 表操作
(1)BeanHandler的案例
sql结果为对象
@Test
public void test_BeanHandler() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建QueryRunner对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 query 方法
String sql = "select * from user where id=?;";
User user = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanHandler<User>(User.class), 3);
System.out.println(user);
}

(2)BeanListHandler的案例
sql结果为对象集合
@Test
public void test_BeanListHandler() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建QueryRunner对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 query 方法
String sql = "select * from user;";
List<User> list = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<User>(User.class));
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}

(3)ScalrHandler的案例
sql结果为数字
@Test
public void test_scalarHandler() throws SQLException {
// 1. 创建QueryRunner对象, 同时将 `数据库` 对象传入
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
// 2. 执行 query 方法
String sql = "select count(*) from user;";
Long result = queryRunner.query(sql, new ScalarHandler<Long>());
System.out.println(result);
}

DBUtils的事务实现
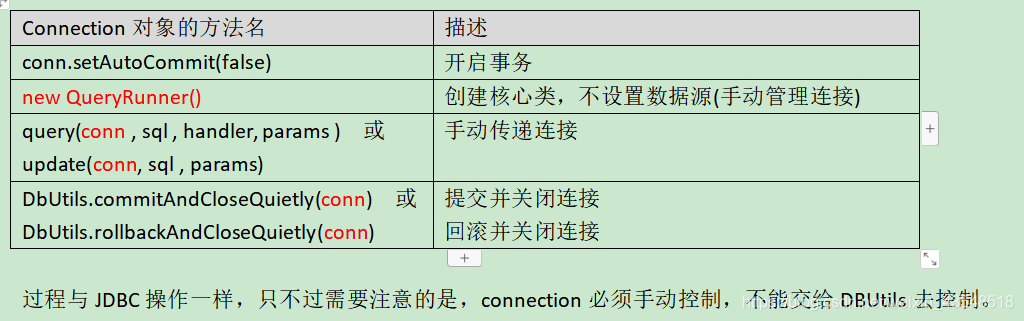
(1) service 层使用DBUtils 事务的启动,提交, 回滚
//开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//提交事务
DbUtils.commitAndCloseQuietly(conn);
//回滚事务
DbUtils.rollbackAndCloseQuietly(conn);
(2) Dao层因为要和service层使用一样的连接,所以使用无惨构造创建QueryRunner()
执行sql时候再出入connection代替dataSouce
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
queryRunner.update(conn, sql, params);
(3)最主要的是控制web service Dao 三层使用的connetion 是同一个
这里JDBCUtils使用的是ThreadLocal实现connection线程单例的
public class JDBCUtils {
//dataSource 单例
private static final ComboPooledDataSource dataSource =
new ComboPooledDataSource();
public static DataSource getDataSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
return dataSource;
}
/**
* connection 使用ThreadLocal 实现线程单例
*/
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> map = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
//同一个线程取得都是同一个connection
//不同线程取得是不同的connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = map.get();
if (connection == null) {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
map.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
// 释放资源
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
rs = null;
}
release(conn, stmt);
}
private static void release(Connection conn, Statement stmt) {
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
stmt = null;
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
conn = null;
}
}
}








 DBUtils是一个简化DAO层代码的工具类,核心是QueryRunner和ResultSetHandler接口。它提供了九个预定义的ResultSetHandler实现,如BeanHandler、BeanListHandler和ScalarHandler,方便对查询结果进行封装。此外,DBUtils还支持事务管理,可以在service层启动、提交或回滚事务,并确保Dao层使用相同的连接。
DBUtils是一个简化DAO层代码的工具类,核心是QueryRunner和ResultSetHandler接口。它提供了九个预定义的ResultSetHandler实现,如BeanHandler、BeanListHandler和ScalarHandler,方便对查询结果进行封装。此外,DBUtils还支持事务管理,可以在service层启动、提交或回滚事务,并确保Dao层使用相同的连接。
















 645
645

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








