例11.8多重继承派生类的构造函数:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Teacher//声明基类
{
public://基类公用成员
Teacher(string nam,int a,string t )//基类构造函数
{
name = nam;
age=a;
title = t;
}
void display()
{
cout << "name:" << name << endl;
cout << "age:" <<age << endl;
cout << "title:" << title << endl;
}
protected://基类保护成员
string name;
int age;
string title;
};
class Student //基类Student
{
public:
Student(string nam,string s,float sco)
//定义基类构造函数
{
name1= nam;
sex = s;
score = sco;
}
void display1()
{
cout << "name:" << name1 << endl;
cout << "sex:" << sex << endl;
cout << "score:" << score << endl;
}
protected:
string name1;
string sex;
float score;
};
class Graduate :public Teacher, public Student//声明多重继承派生类Graduate
{
public:
Graduate(string nam, int a, string t, string s, float sco, float w)
:Teacher(nam, a, t), Student(nam, s, sco)
{
wage = w;
}
//多重继承的构造函数
void show()
{
cout << "name:" << name << endl;
cout << "age:" << age << endl;
cout << "title:" << title << endl;
cout << "sex:" << sex << endl;
cout << "score:" << score << endl;
cout << "wages" << wage << endl;
}
private:
float wage;
};
int main()
{
Graduate gradl("Wang-li",24,"f","assistant", 89.5,1200);
gradl.show();
return 0;
}
程序执行效果如图;
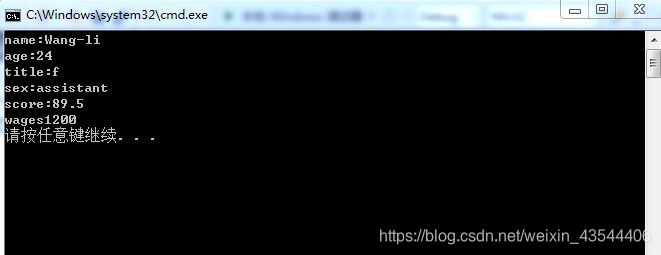
例11.9 虚基类的简单应用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Person
{
public://基类公用成员
Person(string nam, string s, int a)//基类构造函数
{
name = nam;
sex=s;
age=a;
}
protected://基类保护成员
string name;
string sex;
int age;
};
class Teacher:virtual public Person//声明Person为公用继承的虚基类
{
public:
Teacher(string nam,int a,string s,string t ):Person(nam,s,a)
//构造函数
{
title = t;
}
protected://保护成员
string title;
};
class Student:virtual public Person //用public方式声明派生类Student1
{
public:
Student(string nam, string s, int a, float sco) :
Person(nam, s, a), score(sco){}//初始化表构造函数
protected:
float score;
};
class Graduate :public Teacher, public Student//声明多重继承派生类Graduate
{
public:
Graduate(string nam, int a, string t, string s, float sco, float w)
:Person(nam, s, a), Teacher(nam,a, s, t), Student(nam, s, a, sco),
wage(w){}
//多重继承的构造函数初始化表
void show()
{
cout << "name:" << name << endl;
cout << "age:" << age << endl;
cout << "title:" << title << endl;
cout << "sex:" << sex << endl;
cout << "score:" << score << endl;
cout << "wages" << wage << endl;
}
private:
float wage;
};
int main()
{
Graduate gradl("Wang-li",24,"f","assistant", 89.5,1200);
gradl.show();
return 0;
}
程序执行结果如图:

例111.10,用指向基类的指针输出派生类数据:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Student
{
public:
Student(int, string, float);
void display();
private:
int num;
string name;
float score;
};
Student::Student(int n, string nam, float s)
//类外定义构造函数需要指明作用域
{
num = n;
name = nam;
score = s; }
void Student::display()
{
cout << endl<< "num:" << num << endl;
cout << "name:" << name << endl;
cout << "score:" << score << endl;
}
class Graduate :public Student//声明公用派生类Graduate
{public:
Graduate(int, string, float, float);
void display();
private:
float wage;
};
Graduate::Graduate(int n, string nam, float s, float w)
//类外定义构造函数需要指明作用域
: Student(n, nam, s), wage(w){}
//定义构造函数多重继承的构造函数初始化表
void Graduate::display()
{
Student::display();
cout << "wages=" << wage << endl;
}
int main()
{
Student stud1(1001, "Li", 87.5);
Graduate gradl(2001,"wang", 89.5,1000);
Student *pt = &stud1;//定义指向基类Student对象的指针
pt->display();
pt = &gradl;/*指针指向派生类Graduate的对象gradl,但是该指针只能访问派生类中的基类成员,而不能访问派生类中新增加的成员,要想访问派生类新增成员可以使用虚函数*/
pt->display();
return 0;
}
程序执行效果如图:
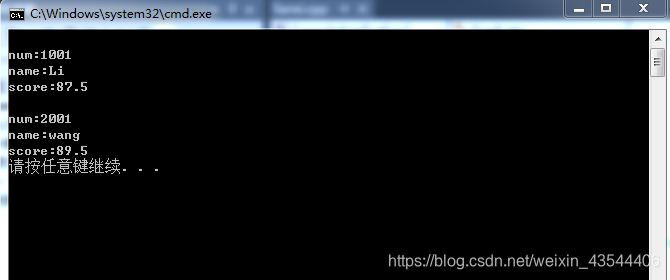








 本文详细介绍了C++中的多重继承和虚基类的概念,通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何在多重继承中正确地使用构造函数初始化列表,并解释了虚基类在解决菱形继承问题中的作用。
本文详细介绍了C++中的多重继承和虚基类的概念,通过具体的代码示例,展示了如何在多重继承中正确地使用构造函数初始化列表,并解释了虚基类在解决菱形继承问题中的作用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








