例9.8 对象的引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time
{
public:
Time(int, int, int);//声明构造函数
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
};
Time::Time(int h, int m, int s)//定义构造函数
{
hour = h;
minute = m;
sec = s;
}
void fun(Time &t)//形参t是Time类对象的引用
{
t.hour = 18;
}
int main()
{
Time t1(10, 13, 56);
fun(t1); //实参是Time类对象,可以通过引用来修改实参t1的值
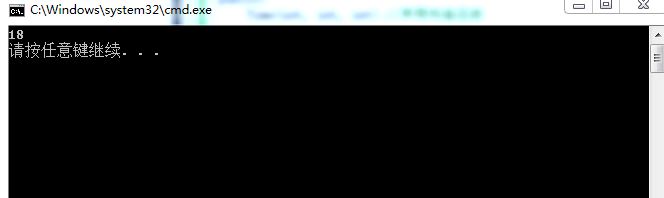
cout << t1.hour << endl;//输出t1.hour的值为18
return 0;
}
程序执行结果如图:
例9.9 对象的赋值和复制
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
Box(int=10, int=10, int=10);//声明带默认参数的构造函数
int volumn();
private:
int height;
int width;
int length;
};
Box::Box(int h, int w, int l)//在类外定义带参数的构造函数
{
height = h;
width = w;
length = l;
}
int Box::volumn()//定义成员函数
{
return(height*width*length);
}
int main()
{
Box box1(15, 30, 25),box2;//建立对象box1,box2,并指定box1的高宽长的值
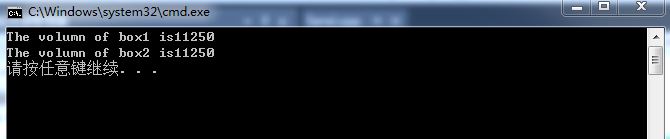
cout << "The volumn of box1 is" << box1.volumn() << endl;
box2 = box1;//将box1的值赋给box2
cout << "The volumn of box2 is" << box2.volumn() << endl;
}
执行结果如图:
例10 静态数据成员(可以通过对象名引用,也可以通过类名引用)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
Box(int, int);//声明带参数的构造函数
int volumn();
static int height;
int width;
int length;
};
Box::Box(int w, int l)//在类外定义带参数的构造函数
{
width = w;
length = l;
}
int Box::volumn()//定义成员函数
{
return(height*width*length);
}
int Box::height = 10;
int main()
{
Box a(15, 20),b(20,30);//建立对象a,b,并指定a,b的宽长的值
cout << a.height << endl;//通过对象名a引用静态数据成员height
cout << b.height << endl;//通过对象名b引用静态数据成员height
cout << Box::height << endl;//通过类名引用静态数据成员height
cout << "The volumn of box1 is" << a.volumn() << endl;
return 0;
}
程序执行效果如图:

例9.11静态成员函数:统计学生平均成绩
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student(int n, int a, float s) :num(n), age(a), score(s){}
void total();//声明成员函数
static float average();//声明静态成员函数
private:
int num;
int age;
float score;
static float sum;//静态成员数据
static int count;//静态成员数据
};
void Student::total()//定义非静态成员函数
{
sum += score;
count++;
}
float Student::average()//定义静态成员函数
{
return(sum / count);
}
float Student::sum = 0;//静态数据成员在类外进行初始化
int Student::count = 0;//静态数据成员在类外进行初始化
int main()
{
Student stud[3] = {
Student(1001, 18, 70),
Student(1002, 19, 78),
Student(1005, 20, 98)
};//定义对象数组并初始化
int n;
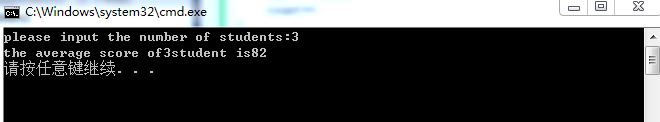
cout << "please input the number of students:";
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
stud[i].total();//调用n次total函数
cout << "the average score of" << n << "student is" <<
Student::average() << endl;
return 0;
}
程序执行效果如图:
例9.13:友元成员函数:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date;//对Date类的提前引用声明
class Time//声明Time类
{
public:
Time(int, int, int);//声明构造函数
void display(Date&);//display是成员函数,形参是Date类对象的引用
//即该函数是Date的友元函数可以访问Date类的成员
private:
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
};
class Date//声明Date类
{
public:
Date(int, int, int);//声明构造函数
friend void Time:: display(Date&);
//声明Time类中的display函数为本类的友元函数
private:
int month;
int day;
int year;
};
Time::Time(int h, int m, int s)//定义Time类构造函数
{
hour = h;
minute = m;
sec = s;
}
void Time::display(Date &d)//形参d是Date类对象的引用
{
cout << d.month << "/" << d.day << "/" << d.year << "/" << endl;
//引用Date类对象中的私有数据
cout << hour << ":" << minute << ":" << sec << endl;
}
//引用Date类对象中的私有数据
Date::Date(int m, int d, int y)//类Date的构造函数
{
month = m;
day = d;
year = y;
}
int main()
{
Time t1(10, 13, 56);
Date d1(12,25,2004); //实参是Time类对象,可以通过引用来修改实参t1的值
t1.display(d1);
return 0;
}
程序执行结果如图:

9.14类模板的使用:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class numtype>//生命类模板,虚拟类型名为numtype
class Compare//类模板为compare
{
public:
Compare(numtype a,numtype b)//定义构造函数
{x = a; y = b;}
numtype max()//函数类型暂定为numtype
{return(x > y) ? x : y;}
numtype min()
{return(x < y) ? x : y;}
private:
numtype x, y;
};
int main()
{
Compare<int>cmp1(3, 7);//定义对象cop1,用于两个整数的比较
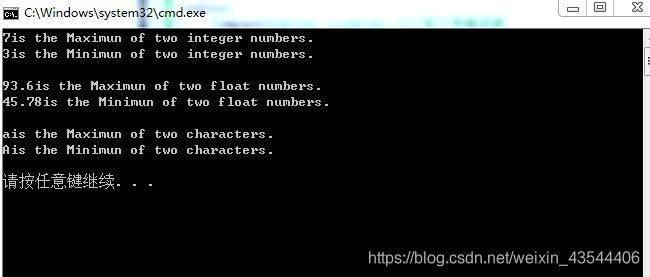
cout << cmp1.max() << "is the Maximun of two integer numbers." << endl;
cout << cmp1.min() << "is the Minimun of two integer numbers." << endl << endl;
Compare<float>cmp2(45.78, 93.6);
cout << cmp2.max() << "is the Maximun of two float numbers." << endl;
cout << cmp2.min() << "is the Minimun of two float numbers." << endl << endl;
Compare<char>cmp3('a','A');
cout << cmp3.max() << "is the Maximun of two characters." << endl;
cout << cmp3.min() << "is the Minimun of two characters." << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
执行结果如图:








 本文深入探讨了C++中的面向对象编程概念,包括对象的引用、赋值与复制、静态数据成员和成员函数、友元函数以及类模板的使用。通过具体实例,详细解释了这些概念的应用和实现。
本文深入探讨了C++中的面向对象编程概念,包括对象的引用、赋值与复制、静态数据成员和成员函数、友元函数以及类模板的使用。通过具体实例,详细解释了这些概念的应用和实现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








