目录
什么是哈希表
哈希表,也称散列表,是实现字典操作的一种有效的数据结构。
尽管在最坏的情况下,散列表查找一个元素的时间复杂度与链表中查找的时间相同,达到了O(n),然而实际应用中,散列表查找的性能是极好的,在一些合理的假设下,在散列表中可以查找一个元素的平均时间复杂度是O(1)。
哈希表的例子:
比如我们要存26个字母,开了一个 freq 数组:

但是并不是所有时候,都能实现键和索引一一对应的。
若是存身份证号码,总不可能开18位数的空间去存每个身份证号码,所以我们想到的解决方式是通过一种人为约定的规则去把每个键放到对应的索引里,这样每个索引里放多个键,可以少开一点空间。
这里设计一个人为约定的规则就是设计一个哈希函数,
把每个键放到对应的索引里,我们怎么在同一个索引里找到相应的键,这就叫产生了哈希冲突 ,
我们要做的事情就是解决两个问题,索引如何设计(哈希函数的设计)以及解决哈希冲突(即由键转换的索引与之前的相同)。

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
哈希函数的设计
也就是设计索引的范围。
整型
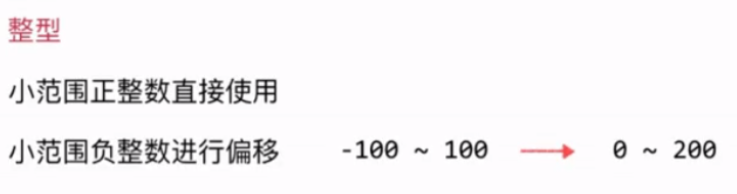

数组空间并不是开越大越好的,像上图一样,开4位就可以了,若是开6位,因为这是身份证,开6位的话前2位是生日的日期,只有可能是01-31,那么32-99都被浪费掉了,这就导致分布不均匀,所以我们要具体问题具体分析。
那我们要怎么取模?
如果随便模一个数的话容易导致分布不均匀。在这里我们可以模一个素数解决分布不均匀的情况(已有数学证明)。
举个例子:

若是模合数,那只出现0和2,导致了分布不均匀;若是模素数,则分布变均匀了。
那这个素数怎么取?
对数据规模的不同取不同素数。
已有人做出了一个表,在以下网址可查阅到。

该表的使用:给出一个数据的上界和下界,比如若数据在2的5次方到2的6次方之间的话,那么模的素数就可以选择53。
浮点型数和字符串数
浮点型数和字符串数都可以转换成整型处理:

- 可以把字符串看作是26进制的数,然后来计算它的hash值;
- B为抽象写法,表示B进制。
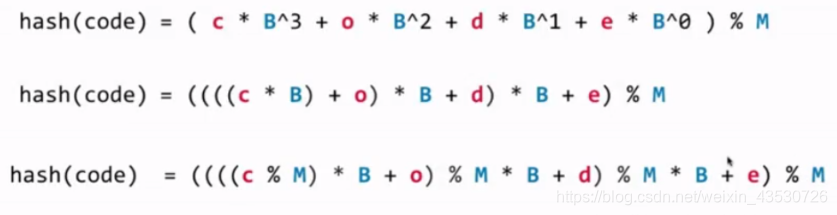
- 在运算的过程中,为了防止高次方的运算,可以利用多项式的拆解来处理提高运算效率;
- 为了防止大整数的溢出,取模的时候我们每次运算一次就进行取模,和最后取模的效果是一样的;
hash(code) 代码的表示:

复合类型
和字符串处理一样,对于字符串来说,可理解为多个字符组成的复合类型。

哈希函数设计原则:

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
重写 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法
我们可以使用 java 自带的 hashCode() ,但要通过重写 hashCode() 来计算我们的 hash 值。
因为如果没有重写 hashCode() 的话,默认是根据每个对象的地址把它映射成整型。
所以虽然是同样的数据,但是两次 new 会产生两个对象,指向不一样的地址。
如果重写了,只要数据相同,不管怎么 new 都是同一个值。
由于不能仅仅只按照 hashCode 来比较两个对象是否相同,所以就要重写 equals 方法,自己写的 hashCode 只是计算 hash 函数的值,但是产生 hash 冲突的时候(虽然 hash 函数值相等),还是要比较两个不同的对象是否相等 。(equals 在产生哈希冲突的时候,用来区分两个类对象的不同)
例如下面的 Student 类,我们计算 hash 的值的方法如下:
public class Student {
private int grade;//年级
private int cls; //班级
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Student(int grade, int cls, String firstName, String lastName) {
this.grade = grade;
this.cls = cls;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
//复合类型重写 Object类中的hashCode()方法
// Object类中已经写了,是通过地址比较的
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hash = 0;
int B = 31; //这里B进制为31进制
hash = hash*B + grade;
hash = hash*B + cls;
hash = hash*B + firstName.toLowerCase().hashCode();
hash = hash*B + lastName.toLowerCase().hashCode();
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(getClass() != obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
Student another = (Student)obj;
return this.grade == another.grade &&
this.cls == another.cls &&
this.firstName.toLowerCase().equals(another.firstName.toLowerCase()) &&
this.lastName.toLowerCase().equals(another.lastName.toLowerCase());
}
}
相关测试:
public class HashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 测试各个类型的hashCode() 都是使用一个整数映射
*/
int a = 42;
System.out.println(((Integer)a).hashCode()); //42
int b = -42;
System.out.println(((Integer)b).hashCode()); //-42
double c = 3.1415926;
System.out.println(((Double)c).hashCode()); //219937201
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1); //-2147483648
Student student = new Student(3, 2, "xinxin", "zheng");
System.out.println(student.hashCode()); //-1941420881
Student student2 = new Student(3, 2, "xinxin", "zheng");
System.out.println(student2.hashCode()); //-1941420881
System.out.println(student.hashCode() == student2.hashCode()); //true
System.out.println(student == student2); //false
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
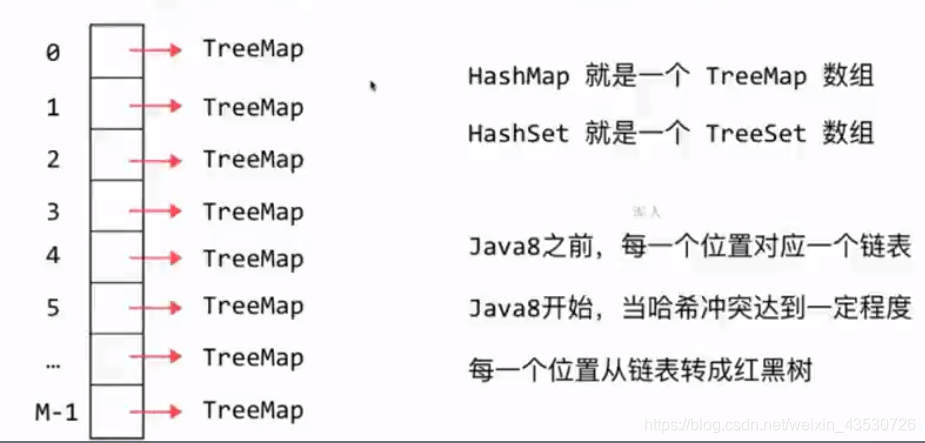
使用数组+红黑树实现 HashMap
- 数组的里面是红黑树实现。
- 因为JDK中的红黑树使用的 TreeMap 实现,所以这里直接使用 TreeMap 当做红黑树使用。
public class MyHashMap<K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
//素数表
private final int[] capacity = {
53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741
};
private static final int upperTol = 10; /**每一个TreeMap内部超过这个就要扩容 --> size >= upperTol * M */
private static final int lowerTol = 2; /** 每一个TreeMap内部小于这个就要缩容 --> size < lowerTol * M */
private int capacityIndex = 0; /**这个是容量数组的下标,一开始是capacity[0]的容量*/
private TreeMap<K,V>[] hashtable;/** hash数组,每一个数组对应的都是一棵红黑树 */
private int size; /**总的元素个数*/
private int M; /**数组大小*/
public MyHashMap(){
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];//一开始大小为53
size = 0;
hashtable = new TreeMap[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
hashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
/** 计算hash值(也就是对应数组的索引) 使用hashCode % M 的方法 注意hashCode()要取绝对值*/
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M; //取绝对值的写法
}
/** add */
public void put(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)]; //找到对应的数组index
if(map.containsKey(key)){
map.put(key,value);
}else {
map.put(key,value);
size++;
/**判断是否要扩容 */
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length) {//需要扩容且可以扩容
capacityIndex++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]); //扩容到容量数组的下一个值
}
}
}
public V remove(K key){
V ret = null;
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(map.containsKey(key)){
ret = map.remove(key);
size--;
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex--;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
return ret;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
TreeMap<K,V>[] newHashtable = new TreeMap[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newHashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[i];
for(K key : map.keySet()){
newHashtable[hash(key)].put(key,map.get(key));
}
}
this.hashtable = newHashtable;
}
// 相当于put
public void set(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(!map.containsKey(key))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + "doesn't exist!");
map.put(key,value);
}
public boolean contains(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].containsKey(key);
}
public V get(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].get(key);
}
}
注意:
- capacity 数组是用来 resize(扩容,缩容) 的时候使用的数组,因为我们上面说过,M要设计成素数会更好的均匀分布;
- upperTol 和 lowerTol 表示平均 TreeMap 数组内的容量达到这两个容量的时候就进行扩容或者缩容;
- java 中的 hashCode 取出来的结果有可能是负值,而数组从0开始,对应不了负值,所以要去符号。
- 去符号方法:
16进制法中,每一位表示4个bit,所以这个数有31位1,而最高位是符号位。
对31位的1进行按位与,这样前面的符号和0与完后就变成0。
(key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M; 其实就是Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % M;
- 去符号方法:
- resize()函数中的 int oldM = this.M; this.M = newM; 使用oldM来保存之前的M的做法是为了在下面求hash(key)求的是新的hash函数的值,不是旧的hash的值,这点很容易忽视;
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
使用数组+链表实现 HashMap
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 自定义map的升级版,查询效率较高
* map底层实现 : 数组+链表
*/
public class LinkHashMap<K,V> {
private class Node{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private final int[] capacity
= {53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741}; //素数表,可以保持每次resize后M都是素数
private static final int upperTol = 10;
private static final int lowerTol = 2;
private int capacityIndex = 0;
private LinkedList<Node>[] linkedLists;
private int size;
private int M;
public int size() {
return size;
}
public LinkHashMap() {
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];
size = 0;
linkedLists = new LinkedList[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
linkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
Node node = new Node(key, value);
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if (list == null) {
list = new LinkedList<>();
linkedLists[hash] = list;
list.add(node);
} else {
Node node2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
node2 = list.get(i);
if (node2.key.equals(key)) {
node2.value = value;
return;
}
}
linkedLists[hash].add(node);
}
size++;
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length){
capacityIndex ++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
public V remove(K key) {
int hash = hash(key);
V ret = null;
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list != null){
Node node2 = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node2 = list.get(i);
if(node2.key.equals(key)){
ret = node2.value;
list.remove(i);// list.remove(node2);
size--;
//resize
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex --;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
return ret;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
LinkedList<Node>[]newLinkedLists = new LinkedList[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newLinkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM; //写这句的目的是,下面的newLinkedLists[hash(node.key)].add(node)中的hash函数,里面是对M取模的,如果不赋值要出大事
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[i];
for(int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++){
node = list.get(j);
newLinkedLists[hash(node.key)].add(node);
}
}
this.linkedLists = newLinkedLists;
}
public boolean contains(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
if(linkedLists[hash].get(i).key.equals(key))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public V get(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
node = linkedLists[hash].get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key))
return node.value;
}
return null;
}
public void set(K key,V value){
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node = list.get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key)){
node.value = value;
return;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
}
}
现在问题来了,

因为M是固定的,而N是一直增大的,所以就不是O(1)。为了让M也能随之增大,我们让它动态扩容,才有了O(1)。

需要注意的是,哈希表的均摊复杂度为O(1),牺牲了有序性。
这也说明了若某些结构性能更优,就说明它牺牲了某些性质(比如缺失顺序性,没有寻址最大值、前驱等操作)或多了空间
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
更多处理冲突的方法
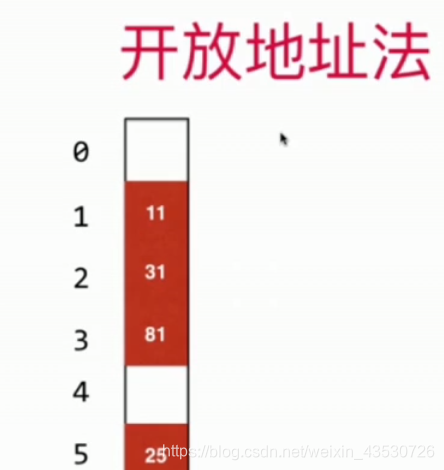
开放地址法
- 线性探测: 遇到哈希冲突+1;
- 平方探测: + 1 ,+ 4 ,+9,+16;
- 二次hash:hash2(key);





 哈希表,又称散列表,是一种高效的字典数据结构。通过哈希函数将键转化为索引,实现快速查找。哈希冲突是哈希表中的常见问题,解决方法包括开放地址法、链表法等。在Java中,HashMap的实现结合了数组和红黑树或链表。设计哈希函数时,需考虑数据类型,如整型、浮点型、字符串和复合类型,并确保分布均匀。同时,重写hashCode()和equals()方法是避免冲突的关键。
哈希表,又称散列表,是一种高效的字典数据结构。通过哈希函数将键转化为索引,实现快速查找。哈希冲突是哈希表中的常见问题,解决方法包括开放地址法、链表法等。在Java中,HashMap的实现结合了数组和红黑树或链表。设计哈希函数时,需考虑数据类型,如整型、浮点型、字符串和复合类型,并确保分布均匀。同时,重写hashCode()和equals()方法是避免冲突的关键。
















 856
856

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








