版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。欢迎访问 AIUAI.CN 交流学习. https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/oJiMoDeYe12345/article/details/79895804 </div>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/ck_htmledit_views-f57960eb32.css">
<div id="content_views" class="markdown_views">
<!-- flowchart 箭头图标 勿删 -->
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="display: none;"><path stroke-linecap="round" d="M5,0 0,2.5 5,5z" id="raphael-marker-block" style="-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"></path></svg>
<h1 id="faster-r-cnn-中-rpn-原理"><a name="t0"></a>Faster R-CNN 中 RPN 原理</h1>
1.RPN 原理
RPN 的用途在于, 判断需要处理的图片区域(where), 以降低推断时的计算量.
RPN 快速有效的扫描图片中每一个位置, 以判断给定区域是否需要进一步处理. 其产生 k 个 bounding-box proposals, 每一个 box proposal 有两个分数, 分别表示该 box 中是 object 的概率.
anchor 用于寻找 boxes proposals.
anchor boxes 是参考 boxes, 所选择的 anchors 具有不同的长宽比(aspect ratios) 和尺度(scale), 以囊括不同类型的 objects.
细长的 objects, 如 buses, 则不能用方形square bounding box 来合适的表示.
Faster R-CNN 采用了 k=9 个 anchors, 分别为 3 aspect ratios 和 3 scales.
RPN 的每个 regressor 只计算与对应参考 anchor box 的 4 个偏移值 (w, h, x, y).
RPN 采用 3×33×3. 因此, RPN 在生成 proposals 时用到了大量的内容信息.
RPN 主要可以包括三步:
输入图片经卷积网络(如 VGGNet 和 ResNet)处理后, 会输出最后一个卷积层的 feature maps;

在 feature maps 上进行滑窗操作(sliding window). 滑窗尺寸为 n×nn×n, 但 anchors 具有 3 种不同的长宽比(aspect ratios) 和 3 种不同的尺度(scales), 计算是相对于原始图片尺寸的, 如下图:
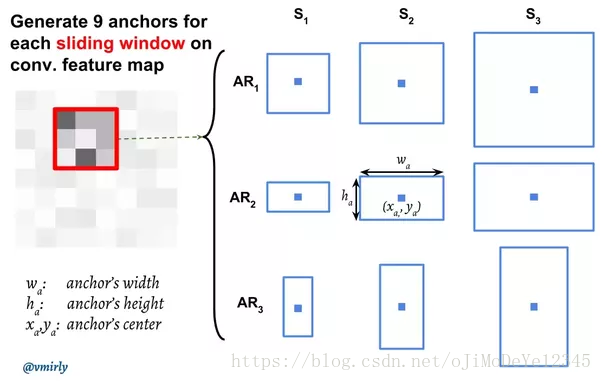
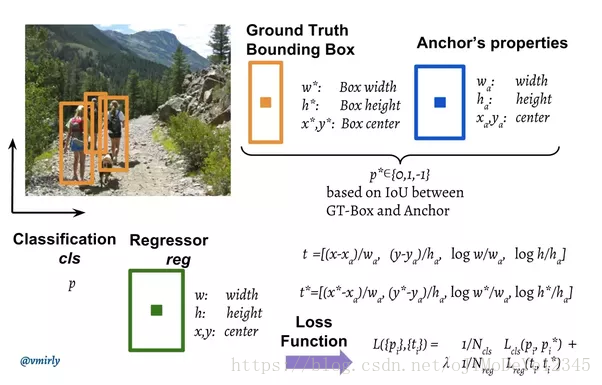
对于每个 anchor, 计算 anchor 与 ground-truth bounding boxes 的重叠部分(overlap) 值 p∗p∗ - IoU(intersection over union ):
如果 IoU > 0.7, 则 p∗=1p∗=1;
如果 IoU < 0.3, 则 p∗=−1p∗=−1
其它, p∗=0p∗=0
3. 从 feature maps 中提取 3×33×3 的空间特征(上图中红色方框部分), 并将其送入一个小网络. 该网络具有两个输出任务分支: classification(cls) 和 regression(reg).
regression 分支输出预测的边界框bounding-box: (x, y, w, h).
classification 分支输出一个概率值, 表示 bounding-box 中是否包含 object (classid = 1), 或者是 background (classid = 0), no object.
2.Anchors 生成示例
Detectron 中 generate_anchors.py 给出了 anchors 的实现.
主要包括两步:
保持 anchor 面积固定不变, 改变长宽比(aspect ratio)
_ratio_enum(anchor, ratios)
保持 anchor 长宽比固定不变,缩放尺度scale
_scale_enum(anchor, scales)
最终生成 5*3=15 个 anchors.
""" generate_anchors.py """ import numpy as np # Verify that we compute the same anchors as Shaoqing's matlab implementation: # # >> load output/rpn_cachedir/faster_rcnn_VOC2007_ZF_stage1_rpn/anchors.mat # >> anchors # # anchors = # # -83 -39 100 56 # -175 -87 192 104 # -359 -183 376 200 # -55 -55 72 72 # -119 -119 136 136 # -247 -247 264 264 # -35 -79 52 96 # -79 -167 96 184 # -167 -343 184 360 # array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.], # [-175., -87., 192., 104.], # [-359., -183., 376., 200.], # [ -55., -55., 72., 72.], # [-119., -119., 136., 136.], # [-247., -247., 264., 264.], # [ -35., -79., 52., 96.], # [ -79., -167., 96., 184.], # [-167., -343., 184., 360.]]) def generate_anchors(stride=16, sizes=(32, 64, 128, 256, 512), aspect_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2)): """ 生成 anchor boxes 矩阵,其格式为 (x1, y1, x2, y2). Anchors 是以 stride / 2 的中心,逼近指定大小的平方根面积(sqrt areas),长宽比 Anchors are centered on stride / 2, have (approximate) sqrt areas of the specified sizes, and aspect ratios as given. """ return _generate_anchors(stride, np.array(sizes, dtype=np.float) / stride, np.array(aspect_ratios, dtype=np.float) ) def _generate_anchors(base_size, scales, aspect_ratios): """ 通过枚举关于参考窗口window (0, 0, base_size - 1, base_size - 1) 的长宽比(aspect ratios) X scales, 来生成 anchore 窗口(参考窗口 reference windows). """ anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size], dtype=np.float) - 1 anchors = _ratio_enum(anchor, aspect_ratios) anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(anchors[i, :], scales) for i in range(anchors.shape[0])]) return anchors def _whctrs(anchor): """ 返回 anchor 窗口的 width, height, x center, y center. """ w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1 h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1 x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1) y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1) return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr): """ 给定 center(x_ctr, y_ctr) 及 widths (ws),heights (hs) 向量,输出 anchors窗口window 集合. """ ws = ws[:, np.newaxis] hs = hs[:, np.newaxis] anchors = np.hstack( (x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1), y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1), x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1), y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1) ) ) return anchors def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios): """ 对于每个关于一个 anchor 的长宽比aspect ratio,枚举 anchors 集合. """ w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) size = w * h size_ratios = size / ratios ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) hs = np.round(ws * ratios) anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) return anchors def _scale_enum(anchor, scales): """ 对于每个关于一个 anchor 的尺度scale,枚举 anchors 集合. Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.""" w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) ws = w * scales hs = h * scales anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) return anchors if __name__ == '__main__': print 'Anchor Generating ...' anchors = generate_anchors() print anchors print 'Done.'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
Related
[1] - Faster R-CNN - 目标检测详解
[2] - How does the region proposal network (RPN) in Faster R-CNN work?
[3] - 论文阅读学习 - Faster R-CNN








 本文详细解析了Faster R-CNN中的区域提议网络(RPN)工作原理,阐述了RPN如何通过生成候选区域减少计算量,介绍了anchors的生成过程及其在不同长宽比和尺度下的应用。
本文详细解析了Faster R-CNN中的区域提议网络(RPN)工作原理,阐述了RPN如何通过生成候选区域减少计算量,介绍了anchors的生成过程及其在不同长宽比和尺度下的应用。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








