项目背景:
结合历史天气数据下共享单车的使用模式,来预测华盛顿共享自行车的租赁需求,数据提供了跨越两年的每小时租赁数据,其中包含天气信息和日期信息,训练集由每月前19天的数据组成,测试集是每月第二十天到月底的数据
提出问题:
通过测试集中的天气等特征值预测总租赁数量
变量说明:
(1) 日期时间datetime:年/月/日/时间,例:2011/1/1 0:00
(2) 季节season:1=春,2=夏,3=秋天,4=冬天
(3) 假日holiday:是否是节假日(0=否,1=是)
(4) 工作日workingday:是否是工作日(0=否,1=是)
(5) 天气weather:1=晴天、多云等(良好),2=阴天薄雾等(普通),3=小雪、小雨等(稍差),4=大雨、冰雹等(极差)
(6) 实际温度(℃)temp
(7) 感觉温度(℃)atemp
(8) 湿度humidity
(9) 风速windspeed
(10)未注册用户租借数量casual
(11)注册用户租借数量registered
(12)总租借数量count
1.数据探索
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from datetime import datetime
#忽略警告提示
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
%matplotlib inline
查看数据信息
train=pd.read_csv('data/train.csv')
train.info()
test = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv')
test.info()
训练集数据信息如下:
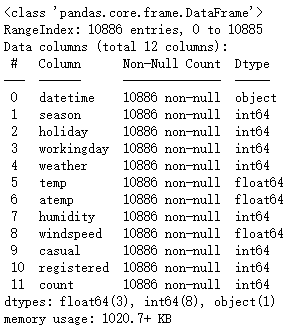
测试集数据信息如下:
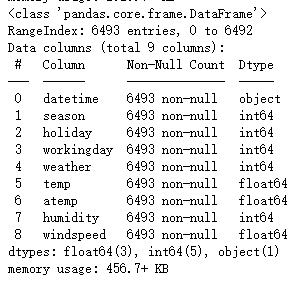
1.1 查看后发现,数据没有缺失值,但是并不代表没有异常值,所以对count,casual,registered进行异常值检测
# 查看是否符合高斯分布
fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,3)
# 设置图形的尺寸,单位为英寸。1英寸等于2.54cm
fig.set_size_inches(18,5)
sns.distplot(train['count'],bins=100,ax=axes[0])
sns.distplot(train['casual'],bins=100,ax=axes[1])
sns.distplot(train['registered'],bins=100,ax=axes[2])
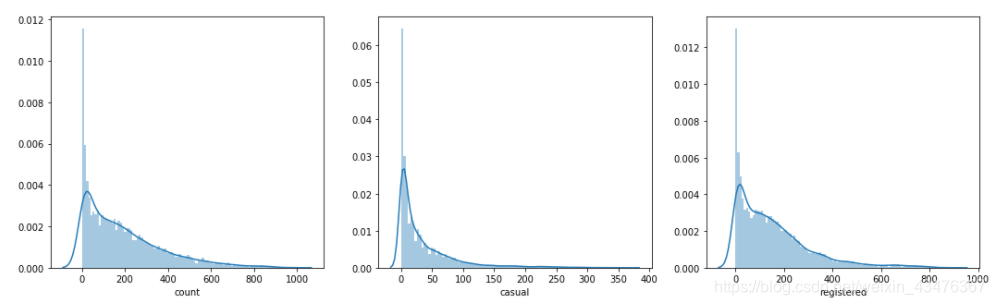
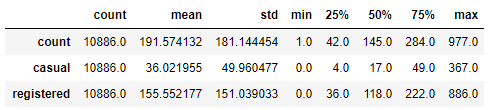
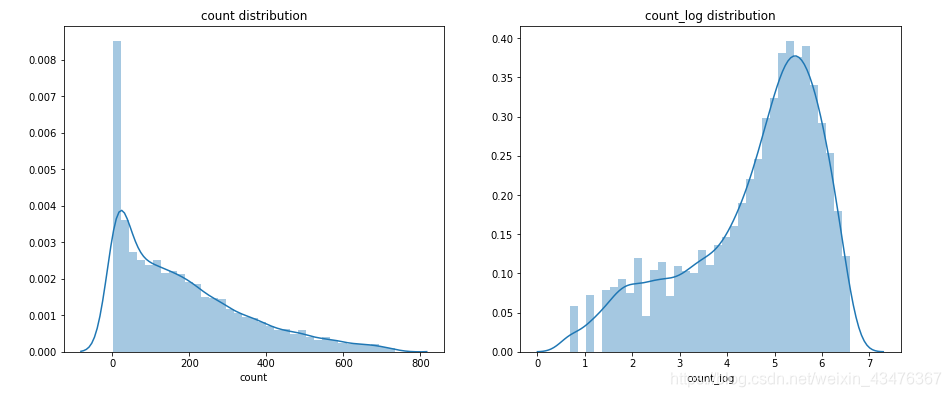
发现count右侧有一条很长的尾巴,对数据进行查看
train[['count','casual','registered']].describe().T
画出箱线图
fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,3)
fig.set_size_inches(12,6)
sns.boxplot(data = train['count'],ax=axes[0])
axes[0].set(xlabel='count')
sns.boxplot(data = train['casual'], ax=axes[1])
axes[1].set(xlabel='casual')
sns.boxplot(data = train['registered'], ax=axes[2])
axes[2].set(xlabel='registered')
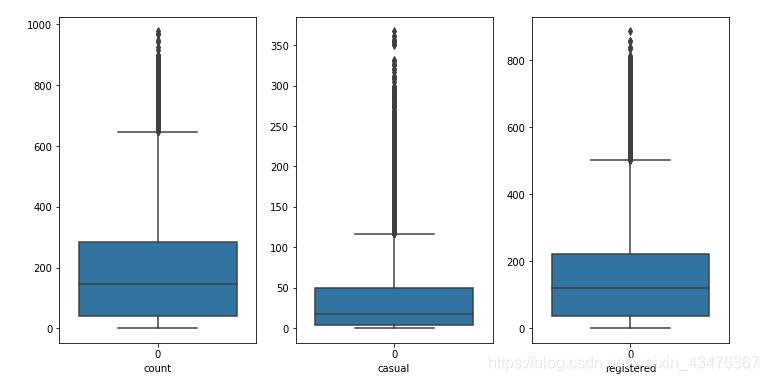
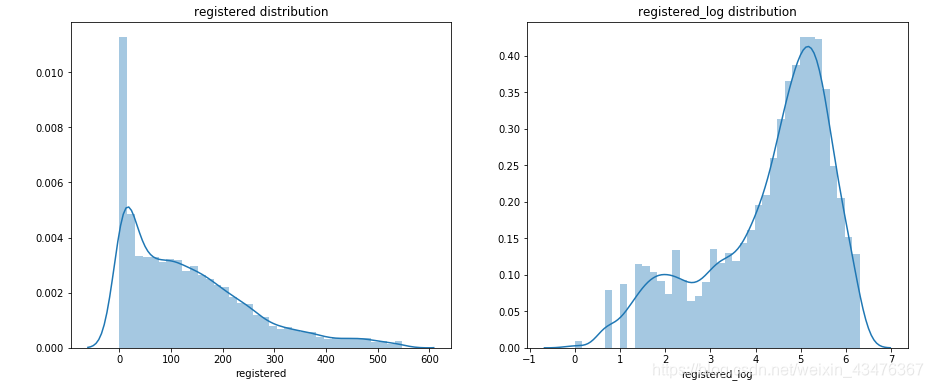
count:均值191,标准差181,50%分位数是145,75%分位数是284,最大值977,说明右侧存在长尾。将大于μ+3σ的数据值作为异常值去除,而我们希望波动相对稳定,否则容易产生过拟合,选择对数变化,使得数据相对稳定。
# 去除异常值 将大于μ+3σ的数据值作为异常值
def drop_outlier(data,col):
mask = np.abs(data[col]-data[col].mean())<(3*data[col].std())
data = data.loc[mask]
# 可视化剔除异常值后的col和col_log
data[col+'_log'] = np.log1p(data[col])
fig, [ax1, ax2] = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(15,6))
sns.distplot(data[col], ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title(col+' distribution')
sns.distplot(data[col+'_log'], ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title(col+'_log distribution')
return data
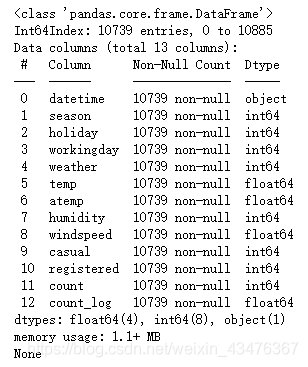
train = drop_outlier(train,'count')
print(train.info())
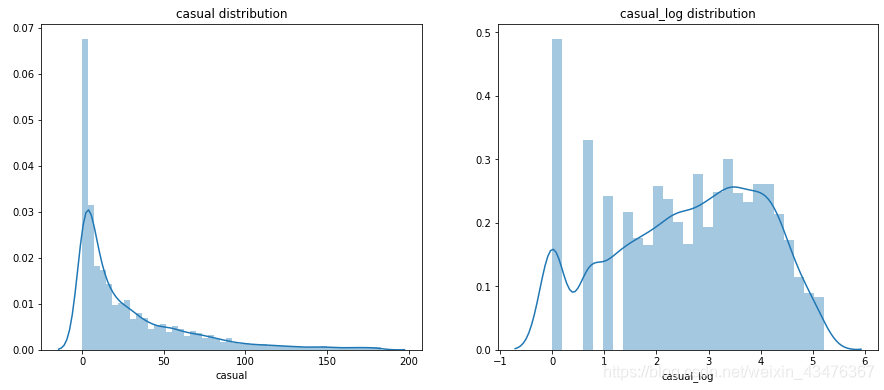
train = drop_outlier(train,'casual')
train = drop_outlier(train,'registered')
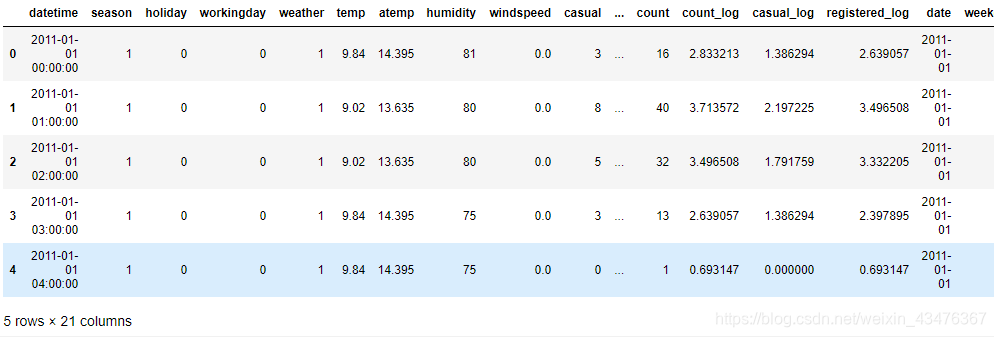
1.2 特征分解,将datetime特征拆分为日期、星期、年、月、日、小时
def split_datetime(data):
data['date'] = data['datetime'].apply(lambda x:x.split()[0])
data['weekday'] =data['date'].apply(lambda x:datetime.strptime(x,'%Y-%m-%d').isoweekday())#返回1-7
data['year'] = data['date'].apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[0]).astype('int')
data['month'] = data['date'].apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[1]).astype('int')
data['day'] = data['date'].apply(lambda x:x.split('-')[2]).astype('int')
data['hour'] = data['datetime'].apply(lambda x:x.split()[1].split(':')[0]).astype('int')
return data
train = split_datetime(train)
train.head()
1.3 可视化分析,数值型数据分布分析,类别型数据箱线图分布分析
1.3.1 先观察温度,体感温度,湿度,风速四个数值型数据
train.info()
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2)
fig.set_size_inches(16,14)
sns.distplot(train['temp'],bins=60,ax=axes[0,0])
sns.distplot(train['atemp'],bins=60,ax=axes[0,1])
sns.distplot(train['humidity'],bins=60,ax=axes[1,0])
sns.distplot(train['windspeed'],bins=60,ax=axes[1,1])
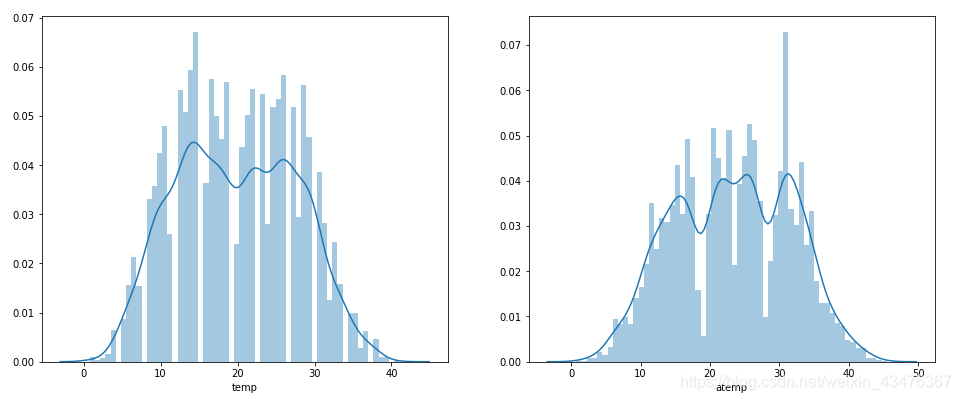
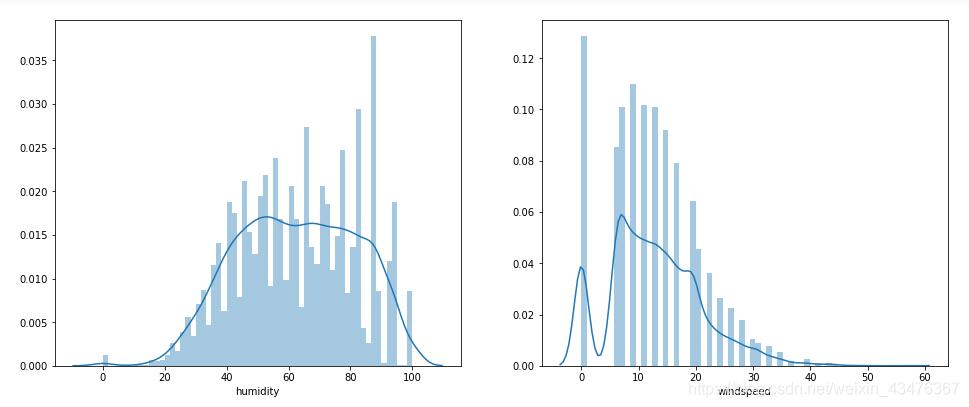
通过这个分布可以发现一些问题,风速的0数据很多,观察发现空缺值在1-6之间, 从这里可以推测出来,数据本身是有缺失值的,但是用0来填充了,但这些风速为0的数据会对预测产生干扰, 希望使用随机森林根据相同年份,月份,季节,温度,湿度等几个特征来预测一下风速的缺失值。
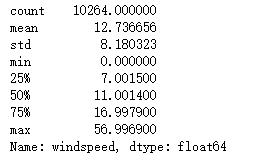
train['windspeed'].describe()
np.sum(train['windspeed'] == 0),train['windspeed'].shape[0]
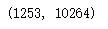
# 使用随机森林填充风速
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
def RFG_windspeed(data):
# 将数据分成风速等于0和不等于0的两部分
mask = data['windspeed'] == 0
wind_0 = data[mask]
wind_1 = data[~mask]
if len(wind_0.index)==0:
return data
Model_wind = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000,random_state=42)
# 选取特征
cols = ["season","weather","humidity","month","temp","year","atemp"]
windspeed_X = wind_1[cols]
# 预测值
windspeed_y = wind_1['windspeed']
windspeedpre_X 




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3136
3136

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








