Problem 15 : Lattice paths
Starting in the top left corner of a 2×2 grid, and only being able to move to the right and down, there are exactly 6 routes to the bottom right corner.
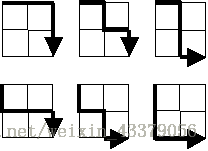
How many such routes are there through a 20×20 grid?
1. 格路 (Lattice paths)
格路计数问题是组合计数中比较重要的问题之一。
从2×2网格的左上角开始,只能向右和向下移动,只有6条路到达右下角。
20×20网格有多少这样的路线?
2. 求解分析
这道经典的格路计数题有三种解决方法。点击网页链接,可以看详细的方法介绍。
3. C++ 代码实现
PE0015的类图如下:

成员变量m_maxNumOfGrids 定义了最大的网格数 20。
成员变量m_matrix[m_maxNumOfGrids+1][m_maxNumOfGrids+1] 定义了二维数组。
成员函数getGridRoutesNew()和iterativeCountRoutes()完成用迭代方法求解。
成员函数getGridRoutes()和recursiveCountRoutes()完成用递归方法求解。
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert> // assert()
#include <cstring> // memset()
using namespace std;
#define RECURSIVE_SOLUTION
class PE0015
{
private:
static const int m_maxNumOfGrids = 20;
long long int m_matrix[m_maxNumOfGrids+1][m_maxNumOfGrids+1];
long long int recursiveCountRoutes (int px, int py);
long long int iterativeCountRoutes (int px, int py);
public:
long long int getGridRoutes (int gridSize);
long long int getGridRoutesNew (int gridSize);
};
long long int PE0015::getGridRoutesNew (int gridSize)
{
memset(m_matrix, 0, sizeof(m_matrix));
long long int numOfRoutes = iterativeCountRoutes(gridSize, gridSize);
return numOfRoutes;
}
long long int PE0015::getGridRoutes (int gridSize)
{
memset(m_matrix, 0, sizeof(m_matrix));
long long int numOfRoutes = recursiveCountRoutes (gridSize, gridSize);
return numOfRoutes;
}
long long int PE0015::recursiveCountRoutes (int px, int py)
{
if (0==px || 0==py)
{
return 1;
}
if (m_matrix[px][py] != 0)
{
return m_matrix[px][py];
}
m_matrix[px][py] = recursiveCountRoutes(px, py-1) + recursiveCountRoutes(px-1, py);
return m_matrix[px][py];
}
long long int PE0015::iterativeCountRoutes (int px, int py)
{
for(int i=0; i<=px; i++)
{
m_matrix[i][0] = 1;
}
for(int j=0; j<=py; j++)
{
m_matrix[0][j] = 1;
}
for(int i=1; i<=px; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=py; j++)
{
m_matrix[i][j] = m_matrix[i-1][j] + m_matrix[i][j-1];
}
}
return m_matrix[px][py];
}
int main()
{
PE0015 pe0015;
assert(6 == pe0015.getGridRoutes(2));
#ifdef RECURSIVE_SOLUTION
cout << "There are routes " << pe0015.getGridRoutes(20);
cout << " through a 20x20 grid." << endl;
#else // ITERATIVE_SOLUTION
cout << "There are routes " << pe0015.getGridRoutesNew(20) ;
cout << " through a 20x20 grid." << endl;
#endif
return 0;
}
4. Python 代码实现
Python的实现方法跟C++一样,也分别实现了迭代和递归求解方法。
特别要注意的是:Python列表list用于二位数组matrix[i][j]是有条件的: 就是可以读取值,不能赋值,为了解决这个局限,我们使用了numpy,matrix[i][j]既可以读取值也可以赋值。
通过这句:matrix = np.zeros((px+1, py+1)) ,就完成了二维数组matrix的定义和初始化。
Python 代码
import numpy as np
def getGridRoutesNew(gridSize):
numOfRoutes = iterativeCountRoutes(gridSize, gridSize)
return numOfRoutes
def iterativeCountRoutes(px, py):
""" take iterative method """
matrix = np.zeros((px+1, py+1))
for i in range(0, px+1):
matrix[i][0] = 1
for j in range (0, py+1):
matrix[0][j] = 1
for i in range(1, px+1):
for j in range(1, py+1):
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i-1][j] + matrix[i][j-1];
return int(matrix[px][py])
def getGridRoutes (gridSize):
numOfRoutes = recursiveCountRoutes (gridSize, gridSize)
return numOfRoutes
def recursiveCountRoutes(px, py):
""" take recursive method """
matrix = np.zeros((px+1, py+1))
if (0==px or 0==py):
return 1;
if 0 != matrix[px][py]:
return matrix[px][py]
matrix[px][py] = recursiveCountRoutes(px, py-1) + recursiveCountRoutes(px-1, py);
return int(matrix[px][py])
def main():
assert 6 == getGridRoutes(2)
print("There are routes", getGridRoutesNew(20)," through a 20x20 grid.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()











 本文探讨了一个经典的组合计数问题——格路计数,具体为从2×2网格左上角到右下角有6条路径,求20×20网格的路径数。提供了C++和Python的递归与迭代解决方案。
本文探讨了一个经典的组合计数问题——格路计数,具体为从2×2网格左上角到右下角有6条路径,求20×20网格的路径数。提供了C++和Python的递归与迭代解决方案。
















 210
210

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








