一、Promise 介绍与基本使用
es6中 进行异步编程 的新解决方案 代替回调函数。
异步编程:定时器,ajax , fs 的I/O , 数据库I/O
优势:支持链式调用,解决回调地狱(不好看)问题
基本使用:
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeOut(() => {
let n = read(1,100);
// 判断
if(n <=30){
resolve(n); // 将 promise 对象的状态设置为 【成功】
} else {
reject(); // 将 promise 对象的状态设置为 【失败】
}
}, 1000);
})
// 调用 then 方法 第一个函数是成功调用的,第二个函数是失败时调用的
p.then((value)=>{
alert(`恭喜中奖, 中奖号码为${value}`)
}, ()=>{
alert(`再接再厉`)
})
promise的状态( promiseState )改变:pending->resolved(fulfilled) / pending -> rejected
Promise的值(promiseResult): 保存异步任务成功或者失败的结果
promise工作流程:
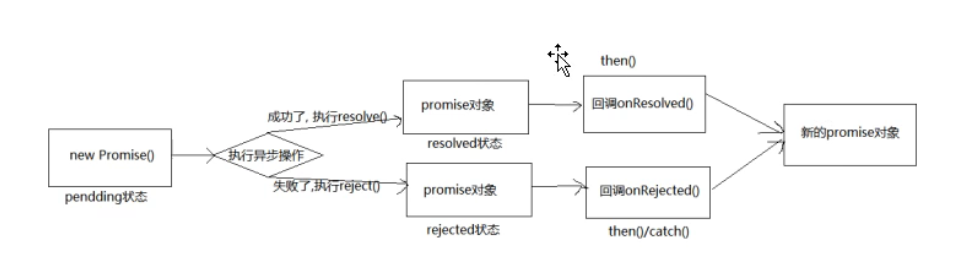
二、Promise API
1. Promise函数:Promise (excutor) { }
- excutor函数(promise函数的参数): 执行器 (resolve, reject) => { }
- resolve 函数:内部定义成功时 调用的函数 value => { }
- reject 函数:内部定义失败时 ,调用的函数 reason => { }
- excutor 会在 Promise 内部立即同时调用,异步操作在执行器中执行
2. Promise.prototype.then 方法:(onResolved, onRejected)=> { }
指定用于得到成功 value 的成功回调 和 用于得到失败 reason 的失败回调,返回一个新的 promise 对象
3. Promise.prototype.catch 方法 (onRejected)=> { }
失败的回调函数
4. Promise.resolve 方法 , 该方法属于 promise 对象的而非实例对象
如果传入的参数为 非 Promise 类型的对象,则返回的结果为成功的promise对象
如果传入的参数为 promise对象,则参数的结果决定了 resolve 的结果
5. Promise.reject: 返回一个失败的promise对象,可以打印出来看看
6. Promise.all 方法(promises)=> { }:
- promises:promiseState为包含 n 个值 的数组
- 返回一个新的 promise 只有所有的promise都成功才成功,只要有一个失败了就直接失败
7. Promise.race 方法 :
(promises)=> { }返回一个新的promise, 第一个完成的prmise 的结果状态就是最终的结果状态
三、Promise关键问题
1. 如何改变 promise 的状态
resolve(value) : pending -> resolved reject(reson) : pending -> rejected 抛出异常: pending -> rejected
2. 能否执行多个回调: 当 PromiseState 改变后(不在为pending) 对于状态的回调就都会执行
3. 改变promise状态 与 then方法/catch方法指定回调 顺序问题
- 都有可能,一般是先指定回调函数再改变promise状态。
- 不论顺序如何,回调函数都会被调用,得到返回数据
4. Promise.then() 方法返回结果 (新的Promise Object) 由什么决定
// then 方法返回结果由什么决定
let p = new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
resolve('ok')
});
let result = p.then(value => {
// console.log(value);
/** 1. 抛出错误, result的状态是失败的状态
throw '出了问题';
*/
/**2. 返回结果是非 Promise 类型的对象
return 521;
*PromiseState 为 fulfilled, PromiseResult is 521
*/
/**3.返回结果是 Promise 对象
* PromiseState is fulfilled, PromiseResult is success,
* return new Promise((resolve, reject)=> {
resolve('success');
});
*/
}, reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
console.log(result);
5. promise 如何串联多个操作任务
- promise 的 then() 方法 返回一个新的promise, 可以看成 then() 的链式调用
- 通过 then 的链式调用 串联多个同步/异步任务
// promise 如何串联多个操作任务
let p = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('ok');
},1000);
});
p.then( value => {
console.log(value);// ok
return new Promise( (resolve) => {
resolve('success');
})
}).then( value => {
console.log(value);
}).then( value => console.log(value) //undefined
);
6. Promise 异常穿透
// promise 异常穿透
let p = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('ok');
},1000);
});
p.then( value => {
console.log(value);// ok
return new Promise( (resolve) => {
resolve('success');
})
}).then( value => {
console.log(value);
throw '出错啦'; // 直接略过下面的then 调 catch
}).then( value => console.log(111)
).then( value => console.log(222)
).catch( reason => console.warn(reason) ); // 输出 出错啦
7. 中断 Promise 链
// 中断 promise 链条
let p = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('ok');
},1000);
});
p.then( value => {
console.log(value);// ok
return new Promise( (resolve) => {
resolve('success');
})
}).then( value => {
console.log(value); //success
}).then( value => {
console.log(111);
/**
* 有且只有一个方法,
* 返回一个 PromiseState is pending 的 Promise 对象
*/
return new Promise( ()=>{} );
}).then( value => console.log(222)
).then( value => console.log(333)
).catch( reason => console.warn(reason) ); //这里无输出
四、Promise 自定义封装(手写Promise)
根据关键问题封装Promise
class Promise{
//构造方法
constructor(executor){
// console.log(this); //Promise
// 添加属性
this.PromiseState = 'pending';
this.PromiseResult = 'null';
//保存回调函数的分配,
this.callbacks = [];
//改变this指向
const self = this;
//2. 定义 resolve 和 reject 函数
function resolve(data){
//4. 加判断 保证 promiseState 只能改变一次
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
// console.log(this); // window
self.PromiseState = 'fulfilled';
self.PromiseResult = data;
// 异步中会调用 resolve(),
setTimeout(()=>{
self.callbacks.forEach( item => {
item.onResolved(data); //data 也可以是PromiseResult
})
})
};
function reject(data){
//加判断 保证 promiseState 只能改变一次
if(self.PromiseState !== 'pending') return;
self.PromiseState = 'rejected';
self.PromiseResult = data;
setTimeout(()=>{
self.callbacks.forEach( item => {
item.onRejected(data); //data 也可以是PromiseResult
})
})
};
//3. try catch 封装 throw 抛出异常
//抛出异常 相当于执行一次 reject
try{
//1. 同步调用 【执行器函数】
executor(resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
//then 方法封装
then(onResolved, onRejected){
//判断回调函数参数 异常穿透
if(typeof onRejected !== 'function'){
onRejected = reason => { throw reason; };
}
//值传递
if(typeof onResolved !== 'function'){
onResolved = value => value;
}
// 8. then 方法的返回值也是一个Promise对象,该Promise的属性由回调函数决定
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=> {
const self = this;
//封装函数
function callBack(type){
try{
//获取回调函数的执行结果
let result = type(self.PromiseResult);
if(result instanceof Promise){
result.then( res=>{
resolve(res);
}, rej=>{
reject(rej);
})
} else {
//改变promise状态 and result
resolve(result)
}
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
// 调用回调函数 是异步的
// p 调用then, this 的指向是Promise 的实例对象 p
if(this.PromiseState === 'fulfilled'){
setTimeout(()=>{
callBack(onResolved);
})
}
if(this.PromiseState === 'rejected'){
setTimeout(()=>{
callBack(onRejected);
})
}
// 6. 异步 ,先保存分配回调函数,再改变状态。。
// 7. 多个回调都能被执行
if(this.PromiseState ==='pending'){
this.callbacks.push({
onResolved: function(){
callBack(onResolved);
},
onRejected : function(){
callBack(onRejected);
},
})
}
})
}
//catch 方法封装
catch(onRejected){
return this.then(undefined, onRejected);
}
//添加 resolve 方法,
//resolve是Promise的方法,要加static
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise ( (resolve, reject)=>{
if(value instanceof Promise){
value.then(ov =>{
resolve(ov);
}, or =>{
reject(or);
})
} else {
resolve(value);
}
})
}
//添加 reject 方法
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise ( (resolve, reject)=>{
reject(reason);
})
}
//添加 all 方法
static all(promises){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let count = 0;
let arr =[];
for(let i=0; i<promises.length; i++){
promises[i].then(v =>{
count++
arr[i]=v
// 全部成功
if(count === promises.length){
resolve(arr)
}
}, r=>{
reject(r)
})
}
})
}
//race 方法:
static race(promises){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
for(let i=0 ; i<promises.length;i++){
promises[i].then(v=>{
resolve(v)
},r=>{
reject(r)
})
}
})
}
}
五、async 与 await
async 函数:
- 函数的返回值为 promise 对象
- promise 对象的结果由 async 函数执行的返回值决定
await 表达式:
- await 右侧的表达式一般为 promise 对象,但也可以是其他的值
- 如果表达式是 promise 对象,await返回的是promise 成功的值
- 如果表达式是其他值,直接 将值作为await 的返回值
let btn = document.querySelector('#btn);
btn.addEventListener('click',async function(){
let result = await sentAjax("url");
console.log(result);
// result 对象是promise对象,
});







 本文详细介绍了Promise在ES6中的异步编程解决方案,包括基本使用、API详解、关键问题如状态控制、then/catch决定结果、链式操作、async/await应用。重点讲解了如何封装自定义Promise以及与async/await的结合,帮助理解异步编程的最佳实践。
本文详细介绍了Promise在ES6中的异步编程解决方案,包括基本使用、API详解、关键问题如状态控制、then/catch决定结果、链式操作、async/await应用。重点讲解了如何封装自定义Promise以及与async/await的结合,帮助理解异步编程的最佳实践。
















 4676
4676

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








