一JDBC简介:
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity,java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序。
二:连接数据库进行操作步骤:
1:加载驱动;
2:建立连接;
3:执行SQL语句;
4:处理结果集;
5:关闭连接;
做这些操作的前提是我们需要导入jar包。
三:导入jar包
1:首先是在项目中建立一个folder,起名叫做lib,然后将jar包放到lib下,
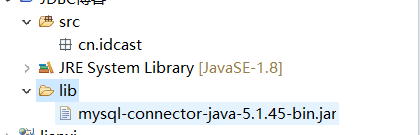
2:然后再将jar包导入:
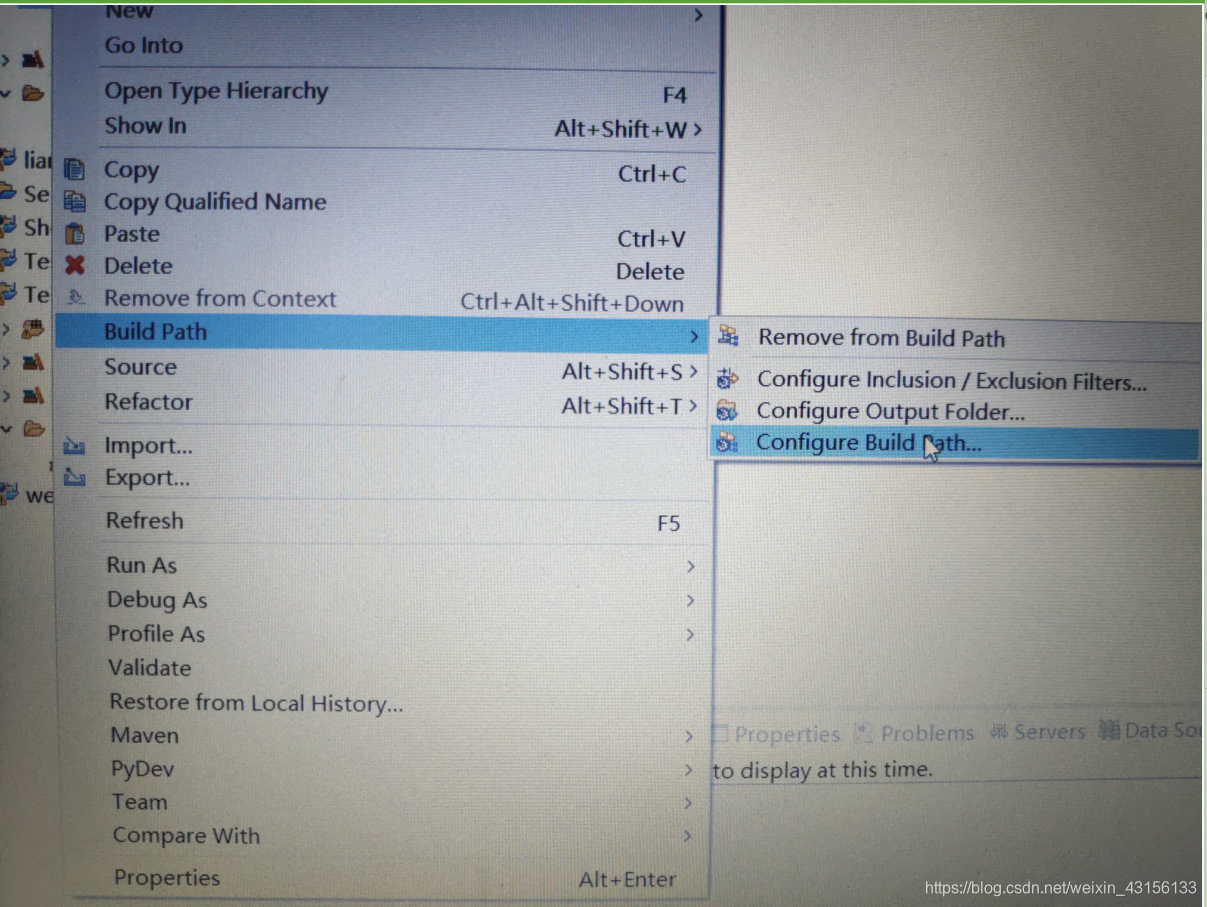
然后再点击Librares,再点击![]()
然后点击刚才放到Lib下的jar包最后点击OK,这样jar包就导好了。

四:现在进行连接数据库
第一步:加载驱动:
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//加载驱动,再抛出异常
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
如果没有导入jai包会出现错误:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
第二步:建立连接:
Connection conn=null;
try {
conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01","root","root");
////连接里面写主机名称,连接端口,数据库名称,账号和密码
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
第三步:执行SQL语句:
1:首先创建数据库,创建表
create database jdbc;--创建数据库
create table student(id int primary key comment '20170000',name varchar(20),sex char(10),adress varchar(20));--创建学生表
insert into student values(20170001,'小陈','男','西安');
insert into student values(20170002,'小王','男','宝鸡');
insert into student values(20170003,'小张','女','咸阳');--随便插入三条数据
第四步:处理结果集:
PreparedStatement ps=null;//这里用PreparedStatement接口而不用他的父亲Statement的原因是它的可读性强,执行效率高
String sql="select *from student";
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
//执行此 PreparedStatement对象中的SQL查询,并返回查询 PreparedStatement的 ResultSet对象。
while(rs.next()){
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);//这个检索的当前行中指定列的值 ResultSet对象为String
String sex=rs.getString(3);
String adress=rs.getString(4);
System.out.println(id+"----"+name+"-----"+sex+"-----"+adress);

第五步:关闭连接
再关闭连接时要先关闭ResultSet,然后PreparedStatement,最后关闭Connection。
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(ps!=null){
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
五:代码整合
1:将与数据库的连接写到一个类里面,减少代码的重复使用
package cn.idcast;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
static Connection conn=null;
public static Connection connection(){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
try {
conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc","root","root");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;//返回连接对象
}
}
2:进行简单的增删改查操作
package cn.idcast;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ConnDemo01 {
private Connection conn=null;
private ResultSet rs=null;
private PreparedStatement ps=null;
public void select(){
try {
conn=DBUtil.connection();//获取连接
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
//这里用PreparedStatement接口而不用他的父亲Statement的原因是它的可读性强,执行效率高
String sql="select *from student";
try {
ps=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
//执行此 PreparedStatement对象中的SQL查询,并返回查询 PreparedStatement的 ResultSet对象。
while(rs.next()){
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString(2);//这个检索的当前行中指定列的值 ResultSet对象为String
String sex=rs.getString(3);
String adress=rs.getString(4);
System.out.println(id+"----"+name+"-----"+sex+"-----"+adress);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
rs.close();
ps.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void insert(){
try {
conn=DBUtil.connection();//获取连接对象
} catch (Exception e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
String insert="insert into student values(?,?,?)";
try {
ps=conn.prepareStatement(insert);
System.out.println("请输入学生编号");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=sc.nextInt();
ps.setObject(1, num);//使用给定对象设置指定参数的值。可以设定任意类型
System.out.println("请输入学生姓名");
Scanner sc2=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc2.next();
ps.setObject(2, name);
System.out.println("请输入学生的家庭地址");
Scanner sc3=new Scanner(System.in);
String adress=sc3.next();
ps.setObject(3, adress);
int result=ps.executeUpdate();//返回一个int值,大于0表示成功,否则失败
if(result>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}else{
System.out.println("插入失败");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ps.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void delete(){
conn=DBUtil.connection();//获取连接对象
String delete="delete from student where id=?";
try {
ps=conn.prepareStatement(delete);
System.out.println("请输入学生的编号");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int id=sc.nextInt();
ps.setObject(1, id);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void change() throws Exception{
conn=DBUtil.connection();//获取连接对象
System.out.println("1代表修改学生的id,2代表修改学生的姓名,3代表修改学生的地址");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int choice=sc.nextInt();
switch(choice){
case 1:
String change="update student set name=? where id=?";
System.out.println("请输入需要修改学生的姓名");
Scanner sc3=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc3.next();
ps.setObject(2, name);
Scanner sc2=new Scanner(System.in);
int newid=sc.nextInt();
ps.setObject(1, newid);
int result=ps.executeUpdate();
if(result>1){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
break;
case 2:
String change2="update student set nane=? where id=?";
System.out.println("请输入需要修改学生的编号");
Scanner s1=new Scanner(System.in);
int id=s1.nextInt();
ps.setObject(1, id);
Scanner s2=new Scanner(System.in);
String newname=s2.next();
ps.setObject(2, newname);
int result2=ps.executeUpdate();
if(result2>1){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
break;
case 3:
String change3="update student set id=? where adress=?";
System.out.println("请输入需要修改学生的编号");
Scanner s3=new Scanner(System.in);
int id3=s3.nextInt();
ps.setObject(1, id3);
Scanner s4=new Scanner(System.in);
String newadreress=s4.next();
ps.setObject(2, newadreress);
int result3=ps.executeUpdate();
if(result3>1){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
break;
default:System.out.println("输入错误");
break;
}
}
}
3:测试类
package cn.idcast;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
static ConnDemo01 cd=new ConnDemo01();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("请输入编号 1:代表浏览信息,2代表插入信息,3代表删除信息,4代表修改学生信息");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int a=sc.nextInt();
while(true){
switch(a){
case 1:
cd.select();
break;
case 2:
cd.insert();
break;
case 3:
cd.delete();
case 4:
cd.change();
default:System.out.println("输入错误");
break;
}
}
}
}























 4493
4493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








