Simpsons’ Hidden Talents(字符串-KMP算法)
judge:HDUOJ 2594
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)
Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
source:HDU 2010-05 Programming Contest
Problem Description
Homer: Marge, I just figured out a way to discover some of the talents we weren’t aware we had.
Marge: Yeah, what is it?
HDUOJ 2594
Input
Output
Sample Input
clinton
homer
riemann
marjorie
Sample Output
0
rie 3
题意
给你两个字符串a和b,其中a的前缀可能和b的后缀有重合部分,让你求出重合部分并输出。
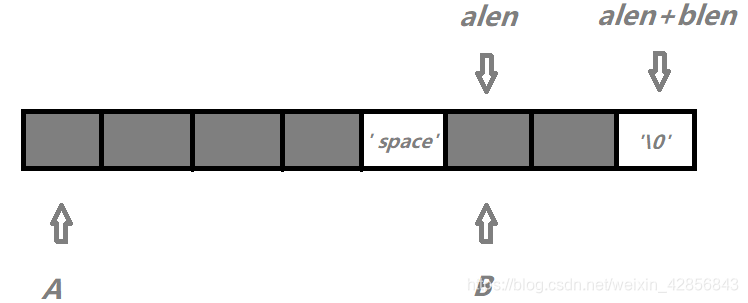
先在a的末尾加一个原来没有的字符(如’ ‘或者’#’,加完不要忘记长度也要更新),然后把b复制到a的末尾,跑一波KMP求next数组,最后看Next[alen + blen]就完事了
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#define _for(i, a) for(int i = 0; i < (a); i++)
#define _rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 100005;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
using namespace std;
int Next[maxn];
char a[maxn], b[maxn];
void GetNext(char p[], int len) {
int plen = strlen(p);
Next[0] = -1;
int j = 0, k = -1;
while (j < plen) {
if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) {
k++;
j++;
Next[j] = k;
}
else {
k = Next[k];
}
}
}
int main() {
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
while (cin >> a >> b) {
int alen = strlen(a),
blen = strlen(b);
a[alen++] = ' ';
_for(i, blen) {
a[alen + i] = b[i];
}
GetNext(a, alen + blen);
int ans = Next[alen + blen];
_for(i, ans) printf("%c", a[i]);
if (ans) printf(" ");
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}










 本文深入探讨了KMP算法的原理与应用,通过解决字符串匹配问题,展示如何利用KMP算法发现两个字符串间的隐藏才能。文章提供了详细的代码实现与样例输入输出,帮助读者理解并掌握KMP算法。
本文深入探讨了KMP算法的原理与应用,通过解决字符串匹配问题,展示如何利用KMP算法发现两个字符串间的隐藏才能。文章提供了详细的代码实现与样例输入输出,帮助读者理解并掌握KMP算法。
















 382
382

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








