个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一.SpringBoot 的版本与启动过程
1.SpringBoot都是jar工程
2.SpringBoot 版本问题
大版本1:内置的Spring是大版本4
1.5.8
1.5.12
大版本2:内置的Spring是大
版本5
3.SpringBoot启动过程观察
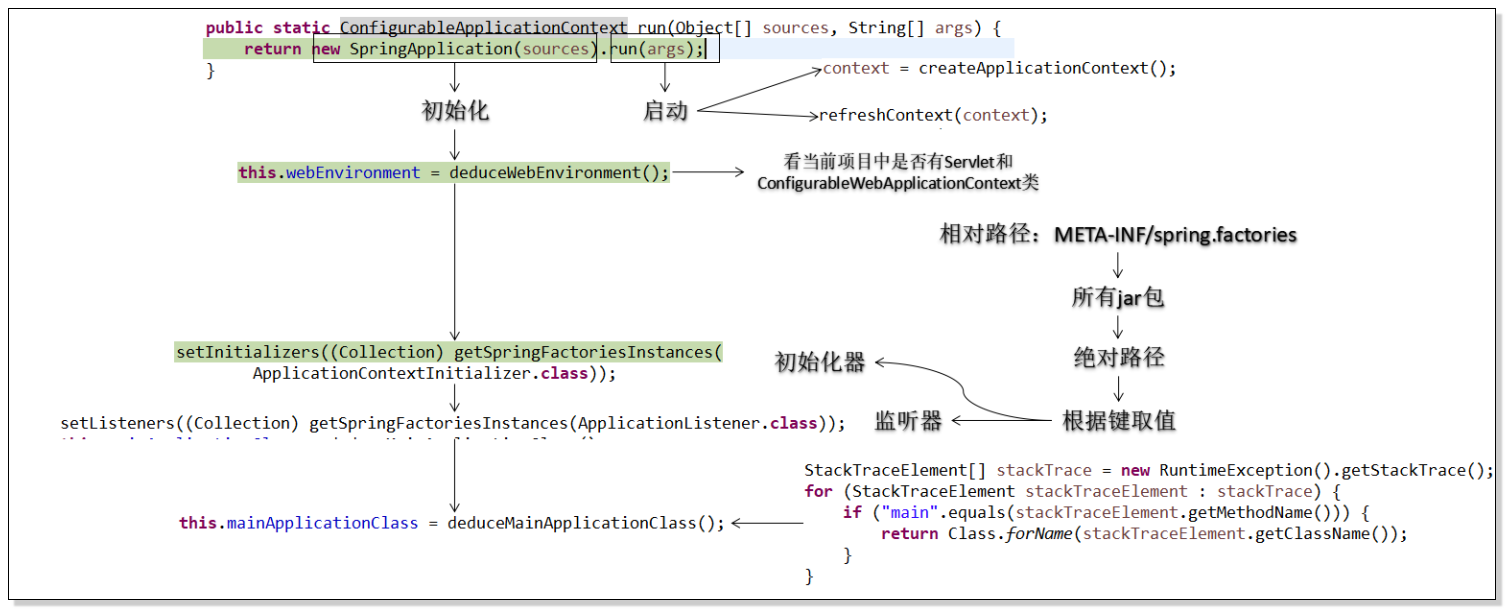
① 核心机制:
② 重要注解
| 注解名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| @SpringBootApplication | 声明一个SpringBoot程序,并使 @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan等注解生效 |
| @SpringBootConfiguration | 相当于@Configuration注解的重新定义 |
| @Configuration | 声明一个Spring配置类 |
| @Bean | 在@Configuration注解标记的类中将标记了@Bean的方法返回值对象加入IOC容器,可以对应XML配置文件中的bean标签来理解 |
| @EnableAutoConfiguration | 启用自动配置 |
| @AutoConfigurationPackage | 当前包下包含需要自动扫描的类 |
| @ComponentScan | 指定要扫描的包 |
4.扫描包的问题
- 自动扫描
需要被扫描的类(@Controller、@Service)所在的包是主启动类所在包的子类。
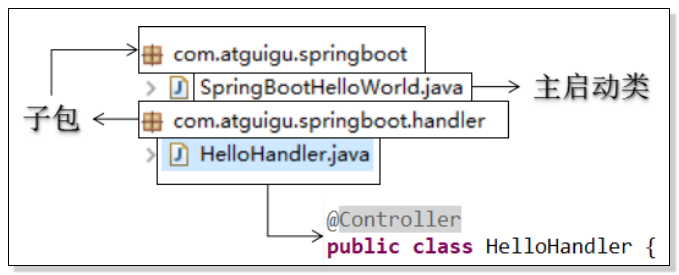
- 手动指定扫描的包
在主启动类上使用@ComponeneScan(“com.webcode.spring2boot.handler”)注解
5.@Configuration 注解
/**
* <bean id="message" class="com.webcode.springboot.entities.Message"/>
* @author Lenovo
* 当前这个类必须能够被扫描到
*/
@Configuration
public class MyBean {
@Bean//这个方法返回的对象会被加入到IOC容器中
public Message getMessageBean() {
return new Message();
}
}6.扫描Mapper接口的两种方式
- 方式一: 使用 @MapperScan
@MapperScan("com.webcode.springboot.mappers")标记在主启动类上
- 方式二: 使用@Mapper
标记在Mapper接口上
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper{
......................
}
7. 为Mybatis配置实体类包
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath*:/mybatis/mappers/*Mapper.xml
type-aliases-package: com.atguigu.springboot.entities8.SpringBoot环境下配置文件
①总述
SpringBoot环境下常用的配置文件有两种,一种是properties 属性文件,一种是yml文件。二者各有特点,语法也有很大区别,但是最终效果基本一致。
②Properties 文件使用
文件名: application.properties
语法格式:
xxx.xxx.xxx=xxx
server.port = 8181 //用于指定handler访问的端口号
③yml文件的使用
1.yml简介
yml是YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)语言的文件,以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件。
2.yml语法
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格
缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
大小写敏感
3.YAML 支持的三种数据结构
- 对象: 键值对的集合
- 数值:一组按次序排列的值
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值
spring:
application:
name: apple
//微服务的名字
server:
port: 8181
context-path: /banana
用于指定handler访问的路径
主服务器
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan("com.webcode.springBoot")
public class SpringBootHelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootHelloWorld.class, args);
}- application.properties
server.port=8081 #指定访问的端口- application.yml
spring:
application :
name : applie
- entity
public class Message {
public String getmessage() {
return "this is message";
}
}- component
@Configuration
public class MyBean {
@Bean
public Message getMessageBean() {
return new Message();
}
}
- handler
@Controller
public class HelloHandler {
@Autowired
private Message message;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/springboot/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println(message.getmessage());
String getmessage = message.getmessage();
// return "this is helloworld ss"+ message.getmessage();
return "this is helloworld ss"+ getmessage;
}
}








 本文深入解析SpringBoot的版本特性、启动流程及配置机制,包括自动配置原理、注解功能、扫描包策略、MyBatis集成方法及配置文件应用,适合初学者快速掌握SpringBoot核心知识。
本文深入解析SpringBoot的版本特性、启动流程及配置机制,包括自动配置原理、注解功能、扫描包策略、MyBatis集成方法及配置文件应用,适合初学者快速掌握SpringBoot核心知识。
















 515
515

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








