1.方法引用

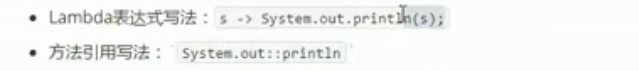

2.通过对象名引用方法

public interface Printable {
void print(String s);
}
public class MethodRerObject {
public void printUpp(String s){
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
}
}
public static void pringString(Printable p){
p.print("Hello");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
pringString((s)->{
MethodRerObject mr=new MethodRerObject();
mr.printUpp(s);
});
//使用方法引用来优化
pringString(new MethodRerObject()::printUpp);
}
3.通过类名引用静态方法
使用前提:类已经存在,静态成员方法已经存在
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Calcable {
int calsabs(int a);
}
public class Demo02 {
public static int method(int number, Calcable c){
return c.calsabs(number);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(-10,(n)->{
return Math.abs(n);
});
//利用方法引用简化
method(-10,Math::abs);
}
}
4.通过super引用父类成员方法
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Greetable {
void greet();
}
public class Human {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
public class Man extends Human {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello,我是man");
}
public void method(Greetable g){
g.greet();
}
public void show(){
method(()->{
Human hm=new Human();
hm.sayHello();
});
//简化lambda表达式
method(()-> super.sayHello());
//利用super引用父类的方法
method(super::sayHello);
}
}
5.通过this引用本类成员
method(this::sayHello);
6.类的构造器引用
@FunctionalInterface
public interface PersonBuilder {
Person buildP(String name);
}
public static void build(String name,PersonBuilder p){
Person person = p.buildP(name);
System.out.println(person.getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
build("张洒",(String name)->{
return new Person(name);
});
build("李四",Person::new);
}
7.数组的构造器引用
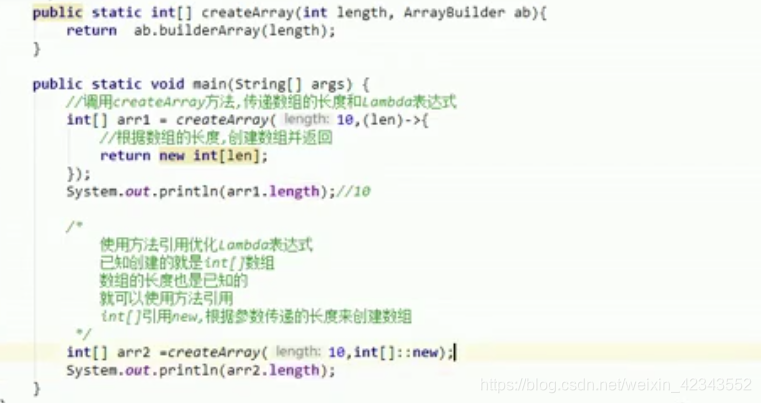







 本文深入探讨了Java中方法引用的概念,包括通过对象名、类名、super、this以及构造器和数组的引用方式,展示了如何简化lambda表达式,提高代码的可读性和效率。
本文深入探讨了Java中方法引用的概念,包括通过对象名、类名、super、this以及构造器和数组的引用方式,展示了如何简化lambda表达式,提高代码的可读性和效率。
















 313
313

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








