BIO与AIO的区别
BIO:
同步阻塞IO买服务器实现模型为一个连击一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,当然可以通过线程池机制改善,适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构。
传统的同步阻塞模型BIO是通过Socket和ServerSocket实现的,ServerSocket监听端口,Socket进行连接。
这种情况不适合处理多个请求:
1,生成较多的Socket会消耗过多的本地资源,
2,Socket连接的速度比较慢,
3,BIO一般都是采取accpet获取Socket后,给一个请求分配一个线程,不管连接是否有真正的数据请求,都需要开辟一个 新的线程,开辟过多线程会导致效率低下,栈溢出 OutOfMemory异常等。
一个简单的Demo:
客户端:
public class BIOClient {
//默认的端口号
private static int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 12345;
private static String DEFAULT_SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1";
private static Socket socket = null;
public static void send(Socket socket){
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
input.useDelimiter("\n");
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入发送消息:");
String line = input.nextLine();
out.println(line);
System.out.println("服务端返回:" + in.readLine());
if ("exit".equals(line)) {
System.out.println("客户端退出了");
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//一下必要的清理工作
if(in != null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
in = null;
}
if(out != null){
out.close();
out = null;
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_IP,DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT);
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
in.useDelimiter("\n");
BIOClient.send(socket);
}
}
服务端:
public class BIOServer {
//默认的端口号
private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345;
//单例的ServerSocket
private static ServerSocket server;
//根据传入参数设置监听端口,如果没有参数调用以下方法并使用默认值
public static void start() throws IOException {
//使用默认值
start(DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public synchronized static void start(int port) throws IOException{
if(server != null) return;
try{
//通过构造函数创建ServerSocket
//如果端口合法且空闲,服务端就监听成功
server = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port);
//通过循环监听客户端连接
//如果没有客户端接入,将阻塞在accept操作上。
while(true){
Socket socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("客户端"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+" 连接上了。。。");
//当有新的客户端接入时,会执行下面的代码
//然后创建一个新的线程处理这条Socket链路
new Thread(new ServerHandler(socket)).start();
}
}finally{
//一些必要的清理工作
if(server != null){
System.out.println("服务器已关闭。");
server.close();
server = null;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BIOServer.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ServerHandler:
public class ServerHandler implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public ServerHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try{
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true);
String expression;
String result;
while(true){
//通过BufferedReader读取一行
//如果已经读到输入流尾部,返回null,退出循环
//如果得到非空值,就尝试计算结果并返回
if(((expression = in.readLine())==null) || "".equals(expression)) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"消息:" + expression);
result = "Bio服务端收到消息\n";
out.println(result);
if (expression.equals("exit")) {
System.out.println("客户端"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+" 退出了。。。");
break;
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//一些必要的清理工作
if(in != null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
in = null;
}
if(out != null){
out.close();
out = null;
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
}
}
}
结果:
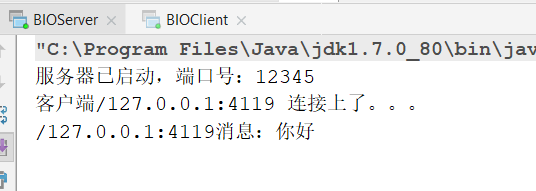

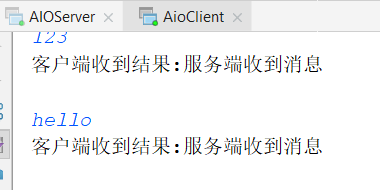
AIO:
异步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个有效请求一个线程,客户端的IO请求首先要获得一个IO权限再通知服务器应用去启动线程进行处理,使用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,如相册服务器。
简单的Demo:
服务端:
public class AIOServer {
private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345;
private static ServerHandler serverHandle;
public volatile static long clientCount = 0;
public static void start(){
start(DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public static synchronized void start(int port){
if(serverHandle!=null)
return;
serverHandle = new ServerHandler(port);
new Thread(serverHandle,"Server").start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AIOServer.start();
}
}
客户端:
public class AioClient {
private static String DEFAULT_HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345;
private static ClientHandler clientHandle;
public static void start(){
start(DEFAULT_HOST,DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public static synchronized void start(String ip,int port){
if(clientHandle!=null)
return;
clientHandle = new ClientHandler(ip,port);
new Thread(clientHandle,"Client").start();
}
//向服务器发送消息
public static boolean sendMsg(String msg) throws Exception{
if(msg.equals("exit")) return false;
clientHandle.sendMsg(msg);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
AioClient.start();
System.out.println("请输入请求消息:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(AioClient.sendMsg(scanner.nextLine()));
}
}
ServerHandler:
public class ServerHandler implements Runnable{
private AsynchronousServerSocketChannel channel;
// public CountDownLatch count;
public ServerHandler(int port) {
try {
//创建服务端通道
channel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务端已启动,端口号:"+port);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
channel.accept(this, new AcceptHandler());
//该步操作是异步操作 防止当前线程直接执行结束
//方案1: while(true)+sleep
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// //方案2 CountDownLatch 作用:在完成一组正在执行的操作之前,允许当前的现场一直阻塞 此处,让现场在此阻塞,防止服务端执行完成后退出
//
// CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(1);
// channel.accept(this, new AcceptHandler());
// try {
// count.await();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
// CompletionHandler<V,A>
// V-IO操作的结果,这里是成功建立的连接,AsynchronousSocketChannel
// A-IO操作附件,这里传入AsynchronousServerSocketChannel便于继续接收请求建立新连接
class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, ServerHandler> {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel, ServerHandler serverHandler) {
//创建新的Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//异步读 第三个参数为接收消息回调的业务Handler
channel.read(buffer, buffer, new ReadHandler(channel));
//继续接受其他客户端请求
serverHandler.channel.accept(null, this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ServerHandler serverHandler) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
//用户读取或者发送消息的channel
private AsynchronousSocketChannel channel;
public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel) {
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
attachment.flip();
byte[] msg = new byte[attachment.remaining()];
attachment.get(msg);
try {
String expression = new String(msg, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("服务器收到消息: " + expression);
String result1 = "服务端收到消息\n";
//向客户端发送消息
doWrite(result1);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//发送消息
private void doWrite(String msg) {
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put(bytes);
buffer.flip();
//异步写数据
channel.write(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler <Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
//如果没有发送完,继续发送
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(attachment, attachment, this);
} else {
//创建新的Buffer
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//异步读 第三个参数为接收消息回调的业务Handler
channel.read(allocate, attachment, new ReadHandler(channel));
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
try {
channel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
try {
channel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ClientHandler
public class ClientHandler implements Runnable{
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
private String host;
private int port;
private CountDownLatch latch;
public ClientHandler(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
try {
//创建异步的客户端通道
clientChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
//创建CountDownLatch等待
// latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
//发起异步连接操作,回调参数就是这个类本身,如果连接成功会回调completed方法
clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port), this, new AcceptHandler());
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// try {
// latch.await();
// } catch (InterruptedException e1) {
// e1.printStackTrace();
// }
// try {
// clientChannel.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
//向服务器发送消息
public void sendMsg(String msg){
byte[] req = msg.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
//异步写
clientChannel.write(writeBuffer, writeBuffer,new WriteHandler(clientChannel));
}
/**
* 接收类
*/
class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<Void, ClientHandler> {
public AcceptHandler() {}
@Override
public void completed(Void result, ClientHandler attachment) {
System.out.println("连接服务器成功");
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ClientHandler attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
try {
attachment.clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class WriteHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel channel;
public WriteHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel) {
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
//完成全部数据的写入
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
clientChannel.write(attachment, attachment, this);
} else {
//读取数据
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
clientChannel.read(readBuffer, readBuffer, new ReadHandler(clientChannel));
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
try {
channel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel) {
this.clientChannel = clientChannel;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result,ByteBuffer buffer) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String body;
try {
body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("客户端收到结果:"+ body);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc,ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.err.println("数据读取失败...");
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
结果:


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








