Dynamic Programming(DP) refers to a collection of algorithms that can be used to compute optimal policies given a perfect model of the environment as a MDP.
Dynamic—sequential or temporal component to the problem
Programming—optimising a “program”, i.e. a policy
The key idea of DP, and of reinforcement learning generally, is the use of value funtions to organize and structure the search for good policies.
As we shall see, DP algorithms are obtained by turning Bellman equations such as these into assignments, that is, into update rules for improving approximations of the desired value functions.
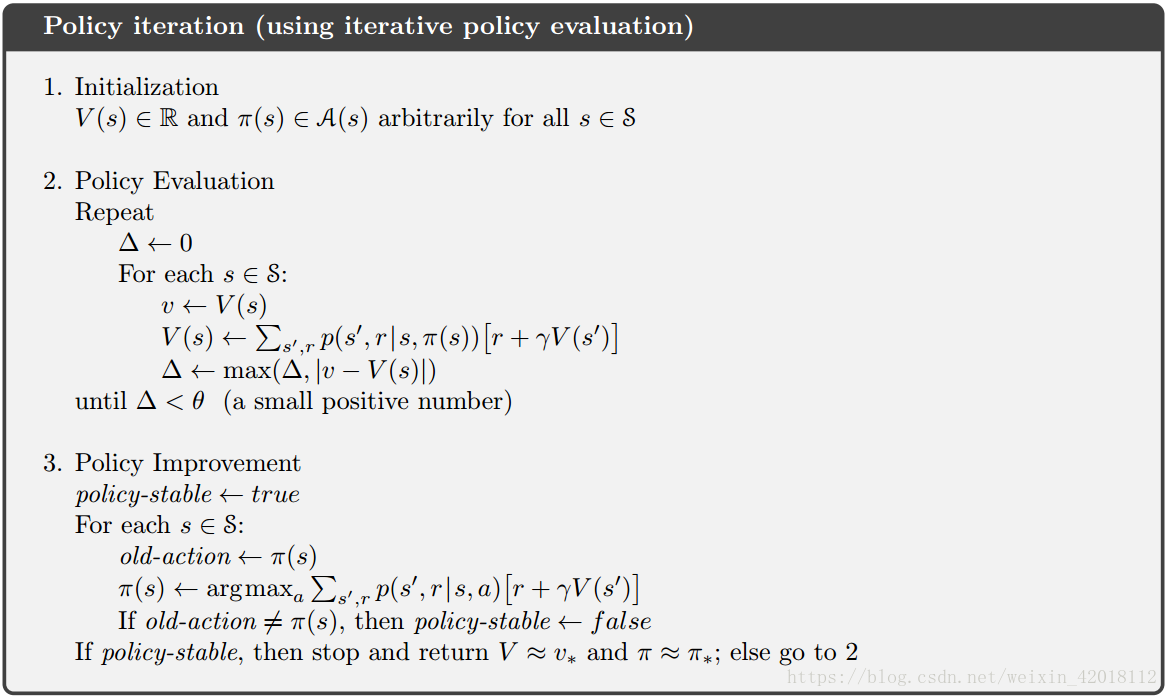
1. Policy Evaluation (Prediction)
Policy evaluation (Prediction problem) refers to the problem that how to compute the state-value function vπv_{\pi}vπ for an arbitrary policy π\piπ.
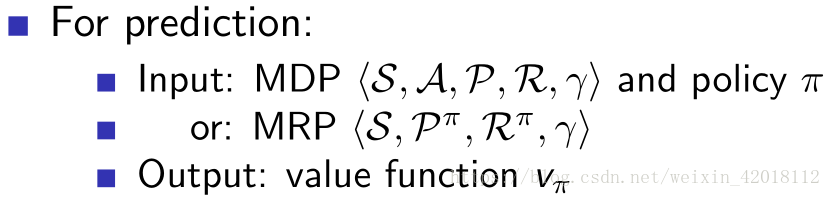
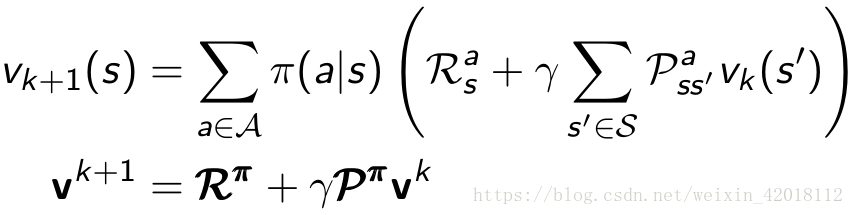
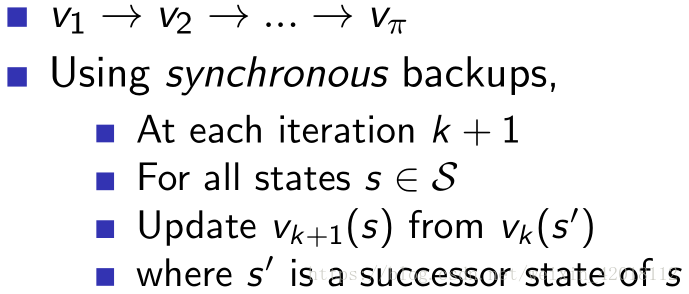

2. Policy Improvement (Policy Iteration)
The basis of policy improvement:

The process of policy improvement:
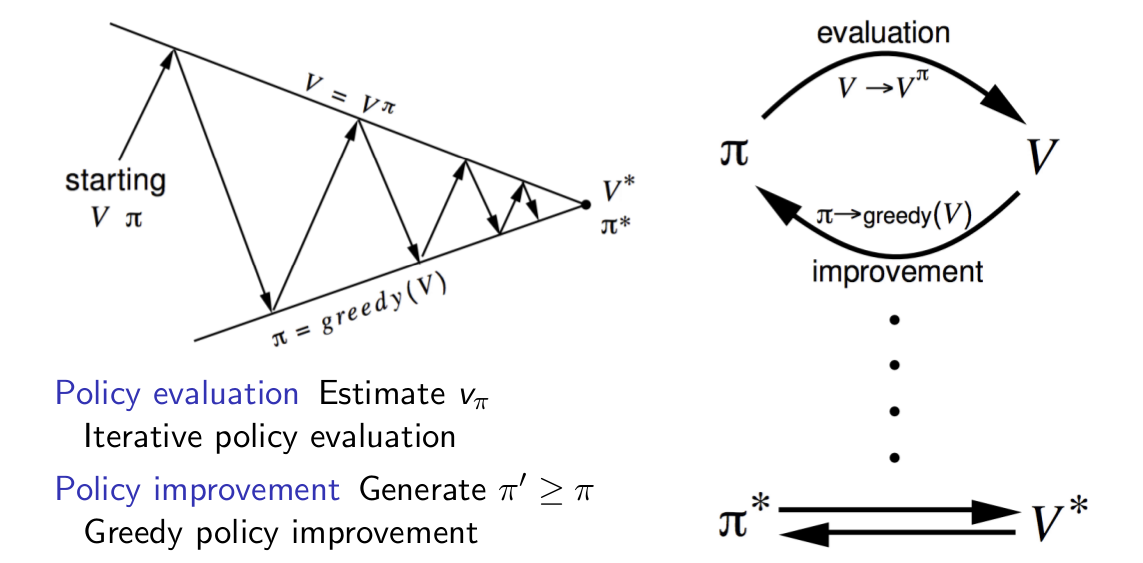
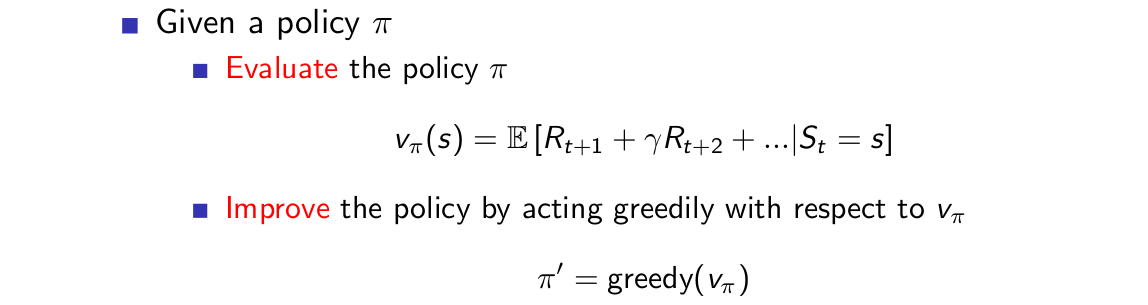
The proof of policy improvement:

策略迭代在每一个迭代步总是先对策略进行值函数估计,直至收敛,那我们能否在策略估计还未收敛时就进行策略改进呢?比如说引入epsilon收敛 ,比如简单地在对策略估计迭代k次之后就进行策略改进,甚至,k=1就进行策略改进又会怎么样呢?下面我们将会讲到,k=1的情形就是值迭代方法。
3. Value Iteration
4. Asynchronous DP
5. Generalized Policy Iteration
Generalized policy iteration (GPI) refer to the general idea of letting policy evaluation and policy improvement processes interact, independent of the granularity and other details of the two processes.





 本文介绍了动态规划在强化学习中的应用,包括策略评估、策略改进、值迭代等算法,并探讨了通用策略迭代的概念。
本文介绍了动态规划在强化学习中的应用,包括策略评估、策略改进、值迭代等算法,并探讨了通用策略迭代的概念。
















 312
312

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








