Bean的销毁过程
应用场景
通过实现DisposableBean接口,或者使用注解@PreDestroy都行:
@Component
public class OrderService implements DisposableBean {
public void test() {
System.out.println("orderService test");
}
@PreDestroy//注解方式,没有数量限制
public void a(){
System.out.println("orderService 销毁之前");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("orderService destory");
}
}
Bean销毁是发生在Spring容器关闭过程中的。
在Spring容器关闭时,比如:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
OrderService userService = (OrderService) context.getBean("orderService");
OrderService.test();
// 容器关闭
context.close();
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 注册关闭钩子也行
ontext.registerShutdownHook(); //jvm实现的,向jvm里注册一个关闭钩子
OrderService userService = (OrderService) context.getBean("orderService");
OrderService.test();

registerShutdownHook
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#registerShutdownHook
public void registerShutdownHook() {
if (this.shutdownHook == null) {
// No shutdown hook registered yet.
this.shutdownHook = new Thread(SHUTDOWN_HOOK_THREAD_NAME) {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
}
}
};
//注册了一个线程,当jvm正常关闭的时候会调用这个线程
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
}
源码分析
注册销毁Bean
直接快进看创建Bean实例的方法
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {...}
// 实例化阶段
if (instanceWrapper == null) {...}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {...}
// BeanDefinition后置处理
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {...}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {...}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//属性填充阶段
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//初始化阶段
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {...}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {...}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
//注册销毁Bean
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {...}
return exposedObject;
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
//不是多例,且需要销毁
//1.判断是否需要销毁
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction
// work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors,
// DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method.
//2.注册DisposableBean
registerDisposableBean(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(
bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware, acc));
}
else {
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
//2.注册DisposableBean
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(
bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware, acc));
}
}
}
只有多例的情况不会执行销毁。
1. 判断是否需要销毁
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#requiresDestruction
protected boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//1.1DisposableBeanAdapter.hasDestroyMethod:是否有销毁方法
//1.2hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors:判断容器里是否有DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
//1.3DisposableBeanAdapter.hasApplicableProcessors:判断是否有生效的DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
return (bean.getClass() != NullBean.class && (DisposableBeanAdapter.hasDestroyMethod(bean, mbd) ||
(hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors() && DisposableBeanAdapter.hasApplicableProcessors(
bean, getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware))));
}
1.1 判断是否有销毁方法
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#hasDestroyMethod
//是否有销毁方法
public static boolean hasDestroyMethod(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//是否是DisposableBean
//inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary获取销毁方法,是否为null
return (bean instanceof DisposableBean || inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary(bean, beanDefinition) != null);
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary
- 优先取beanDefinition中指定的销毁方法destroyMethodName
- 如果destroyMethodName=“(inferred)” 或者 destroyMethodName=null且bean instanceof AutoCloseable,会查找"close"、"shutdown"方法作为销毁方法
//获取销毁方法
private static String inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//先从beanDefinition的“缓存”获取(缓存中有说明之前解析过了)
String destroyMethodName = beanDefinition.resolvedDestroyMethodName;
if (destroyMethodName == null) {
//获取beanDefinition指定的销毁方法名
destroyMethodName = beanDefinition.getDestroyMethodName();
boolean autoCloseable = (bean instanceof AutoCloseable);
//销毁方法推断,前提:
// destroyMethodName = INFER_METHOD = "(inferred)"
// 或者 destroyMethodName == null && autoCloseable = true
//如果满足以上条件会找close或者shutdown方法作为销毁方法
if (AbstractBeanDefinition.INFER_METHOD.equals(destroyMethodName) ||
(destroyMethodName == null && autoCloseable)) {
// Only perform destroy method inference in case of the bean
// not explicitly implementing the DisposableBean interface
destroyMethodName = null;
// 只有在bean没有显式实现DisposableBean接口的情况下才执行destroy方法推断
if (!(bean instanceof DisposableBean)) {
if (autoCloseable) {
//CLOSE_METHOD_NAME="close"
destroyMethodName = CLOSE_METHOD_NAME;
}
else {
try {
//CLOSE_METHOD_NAME="close"
destroyMethodName = bean.getClass().getMethod(CLOSE_METHOD_NAME).getName();
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
try {
//SHUTDOWN_METHOD_NAME="shutdown"
destroyMethodName = bean.getClass().getMethod(SHUTDOWN_METHOD_NAME).getName();
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex2) {...}
}
}
}
}
beanDefinition.resolvedDestroyMethodName = (destroyMethodName != null ? destroyMethodName : "");
}
return (StringUtils.hasLength(destroyMethodName) ? destroyMethodName : null);
}
1.2 判断容器里是否有DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
protected boolean hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors() {
return !getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware.isEmpty();
}
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口有两个方法:
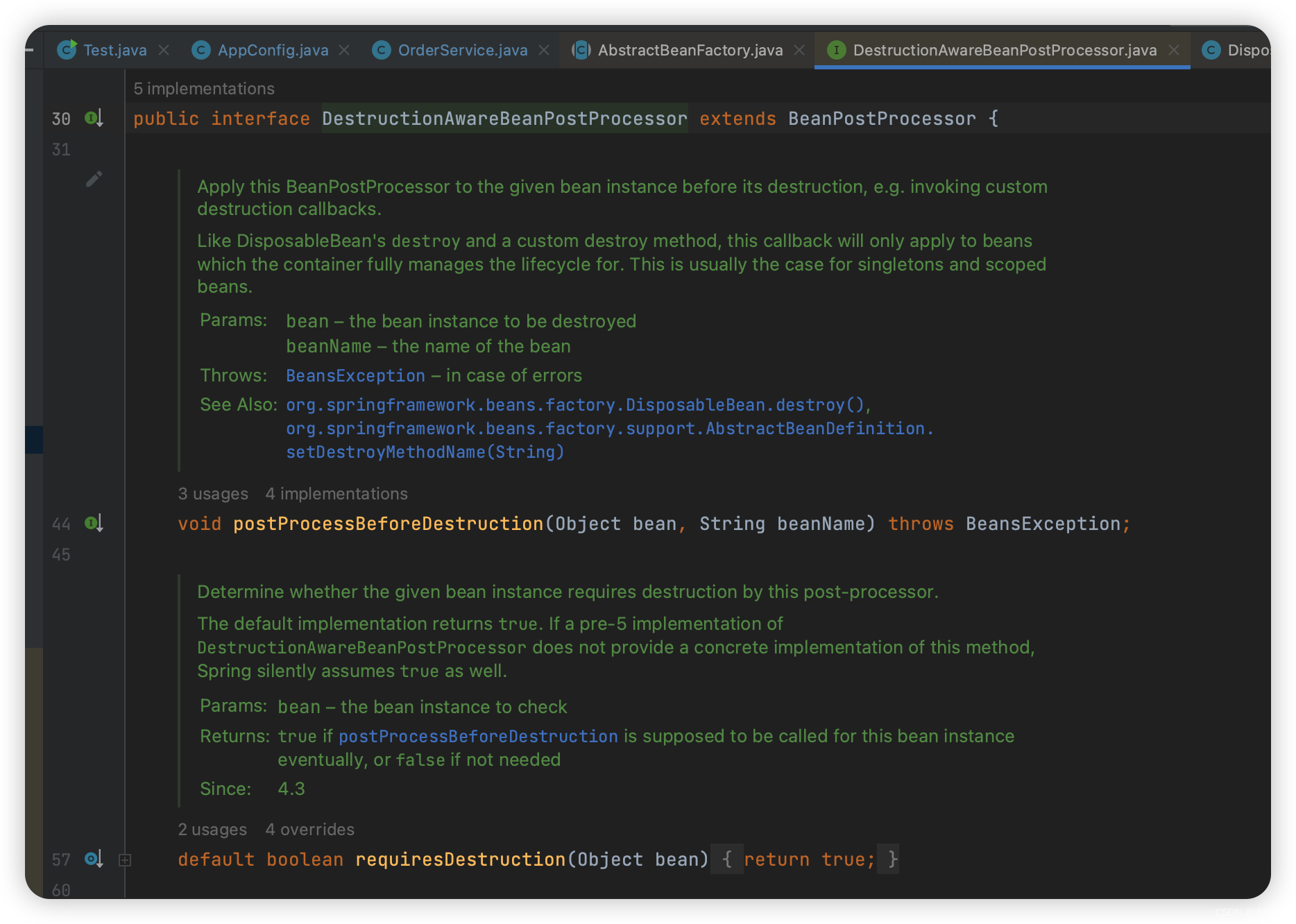
- requiresDestruction:判断某一个Bean是否需要销毁
- postProcessBeforeDestruction:具体销毁要执行的逻辑
1.3 判断是否有生效的DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
如果注册过DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的话,就调用
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#hasApplicableProcessors
判断注册的DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor中是否有对当前Bean生效的
public static boolean hasApplicableProcessors(Object bean, List<DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(postProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : postProcessors) {
if (processor.requiresDestruction(bean)) {
//有生效的就true
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor应用场景
Spring中提供的@PreDestroy注解就是通过InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现的。
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#requiresDestruction
public boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean) {
//判断当前Bean中是否有销毁方法,即被@PreDestroy标记的方法
return findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()).hasDestroyMethods();
}
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
// 这里 构建生命周期的元数据
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
// 这里 构建生命周期的元数据
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildLifecycleMetadata
此方法会收集@PostConstruct(初始化前)、@PreDestroy(销毁前)标记的方法
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) {...}
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历当前类中的所有方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
//initAnnotationType就是初始化前方法对应的注解类型
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {...}
}
//destroyAnnotationType是销毁前方法对应的注解类型
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {...}
}
});
//父类的初始化方法在前面(即先执行父类的初始化方法,再执行子类的)
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
//注意这里有do while,是为了遍历父类
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata :
new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
}
initAnnotationType和destroyAnnotationType的注解类型是在子类CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造中设置的:

2. 注册DisposableBean
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#registerDisposableBean
public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
就是存到disposableBeans的map

其中用到适配器模式,目的:兼容各种设置销毁方法的场景(比如通过实现DisposableBean接口、使用@PreDestroy注解方式…),最后统一调用org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy就可以了。


总结
在Bean创建过程中,在最后(初始化之后),有一个步骤会去判断当前创建的Bean是不是DisposableBean:
- 当前Bean是否实现了DisposableBean接口
- 或者,当前Bean是否实现了AutoCloseable接口
- BeanDefinition中是否指定了destroyMethod
- 调用DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor.requiresDestruction(bean)进行判断
a. ApplicationListenerDetector中直接使得ApplicationListener是DisposableBean
b. InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中使得拥有@PreDestroy注解了的方法就是DisposableBean - 把符合上述任意一个条件的Bean适配成DisposableBeanAdapter对象,并存入disposableBeans中(一个LinkedHashMap)
销毁方法执行时机
看下容器关闭方法:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#close
public void close() {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:
// We've already explicitly closed the context.
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {...}
}
}
protected void doClose() {
// Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary...
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {...}
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {...}
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
// 发布ContextClosedEvent事件
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {...}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
//Spring容器生命周期
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {...}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
// 销毁Bean
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
onClose();
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) {...}
// Switch to inactive.
this.active.set(false);
}
}
销毁Bean
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#destroyBeans
protected void destroyBeans() {
//销毁所有单例Bean(不管有没有定义销毁方法)
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#destroySingletons
public void destroySingletons() {
//调用父类
super.destroySingletons();
updateManualSingletonNames(Set::clear, set -> !set.isEmpty());
clearByTypeCache();
}
父类方法
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#destroySingletons
public void destroySingletons() {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {...}
//标记单例Bean正在销毁中
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {...}
String[] disposableBeanNames;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
//收集之前注册的有定义销毁方法的Bean
disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());
}
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//遍历处理所有定义过销毁方法的Bean
destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);
}
this.containedBeanMap.clear();
this.dependentBeanMap.clear();//某个Bean被哪些Bean依赖了的Map
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear();//某个Bean依赖了哪些Bean的Map
clearSingletonCache();//清空单例池等Map
}
protected void clearSingletonCache() {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.clear();//单例池
//后面和循环依赖有关,先不看
this.singletonFactories.clear();
this.earlySingletonObjects.clear();
this.registeredSingletons.clear();
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#destroySingleton
public void destroySingleton(String beanName) {
// Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any.
// 先从单例池中移除掉
removeSingleton(beanName);
// Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance.
DisposableBean disposableBean;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
//将自己从销毁BeanMap中移除
disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
}
//执行销毁逻辑
destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean);
}
//先从单例池中移除掉
protected void removeSingleton(String beanName) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.remove(beanName);
}
}
执行销毁逻辑
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#destroyBean
protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) {
// dependentBeanMap表示某Bean被哪些Bean依赖了
// 所以现在要销毁某个Bean时,如果这个Bean还被其他Bean依赖了,那么也得销毁其他Bean
// Trigger destruction of dependent beans first...
Set<String> dependencies;
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
// Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set
dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
//dependencies就是依赖当前Bean的Bean,需要先销毁它们,才能销毁自己
if (dependencies != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {...}
for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) {
//销毁其他依赖当前Bean的Bean
destroySingleton(dependentBeanName);
}
}
// Actually destroy the bean now...
if (bean != null) {
try {
//执行destroy方法
//这个bean就是DisposableBeanAdapter
bean.destroy();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {...}
}
// Trigger destruction of contained beans...
// 如果这个disposableBean还包含了inner beans,将这些Bean从单例池中移除掉
Set<String> containedBeans;
synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) {...}
if (containedBeans != null) {
for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) {
destroySingleton(containedBeanName);
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean from other beans' dependencies.
// 当前Bean已经销毁了,从其他bean的依赖项中删除
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next();
Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue();
dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName);
if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean's prepared dependency information.
// dependenciesForBeanMap:某个Bean依赖了哪些Bean的Map,这个信息也可以移除了
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
总结
在Spring容器关闭过程时:
- 首先发布ContextClosedEvent事件
- 调用lifecycleProcessor的onClose()方法
- 销毁单例Bean
- 遍历disposableBeans
- 把每个disposableBean从单例池中移除
- 调用disposableBean的destroy()
- 如果这个disposableBean还被其他Bean依赖了,那么也得销毁其他Bean
- 如果这个disposableBean还包含了inner beans,将这些Bean从单例池中移除掉
(inner bean参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#beans-inner-beans)
- 清空manualSingletonNames,是一个Set,存的是用户手动注册的单例Bean的beanName
- 清空allBeanNamesByType,是一个Map,key是bean类型,value是该类型所有的beanName数组
- 清空singletonBeanNamesByType,和allBeanNamesByType类似,只不过只存了单例Bean
- 遍历disposableBeans
这里涉及到一个设计模式:适配器模式
在销毁时,Spring会找出实现了DisposableBean接口的Bean。
但是我们在定义一个Bean时,如果这个Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,或者实现了AutoCloseable接口,或者在BeanDefinition中指定了destroyMethodName,那么这个Bean都属于“DisposableBean”,这些Bean在容器关闭时都要调用相应的销毁方法。
所以,这里就需要进行适配,将实现了DisposableBean接口、或者AutoCloseable接口等适配成实现了DisposableBean接口,所以就用到了DisposableBeanAdapter。
会把实现了AutoCloseable接口的类封装成DisposableBeanAdapter,而DisposableBeanAdapter实现了DisposableBean接口。



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










