1.
解法一:创建一个栈来模拟整个栈的压入和弹出,看看弹出的元素是否和弹出数组中的元素一一对应相等。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int pushindex = 0;//存入栈内元素的索引
for(int popindex = 0;popindex<popped.length;popindex++){//控制Stack弹出的次数
while(pushindex < pushed.length && (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() !=popped[popindex])){//模拟的是将pushed数组压入栈的过程
//首先pushed数组中还有数没被压入,然后stack为空或者stack第一个元素和poped准备弹出的元素不一致
stack.push(pushed[pushindex]);
pushindex++;
}
if(stack.peek() != popped[popindex]){
return false;
}else{
stack.pop();
}
}
return true;
}
}解法二:就是在解法一的基础上优化一下,不再单独弄一个Stack栈来储存了,而是就是pushed数组来实现一个栈,定义一个指针,指向栈顶元素。
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
//用stack指针和原pushed数组模拟一个栈,指针所指即为栈顶元素,其他与上一种解法一致
//入栈数组的指针,必须维护,才知道此时应该是哪个数入栈
int stack = -1, pushIndex = 0;
//遍历要出栈的数组,如果可以全部出栈成功,那么返回TRUE
for (int poppedIndex = 0; poppedIndex < popped.length; ++poppedIndex) {
//这个条件很关键,当 还有数可以入栈 && (栈为空,那么直接入栈,或者栈顶元素与要弹出的数不一样,那么继续入栈)
while (pushIndex < pushed.length && (stack < 0 || pushed[stack] != popped[poppedIndex])) {
pushed[++stack] = pushed[pushIndex++];
}
//能走到这里,要么没有数可以继续入栈了,要么此时的栈顶元素和要弹出的数一致
//如果栈顶元素和要弹出的数不一致,那么直接返回FALSE,因为正如上面所说,能走到这里还可能是因为没有数可以继续入栈了
if (pushed[stack] != popped[poppedIndex])
return false;
//如果一致,那么出栈
else
--stack;
}
//走到这里说明全部出栈成功,那么返回TRUE
return true;
}
}2.

思路:这道题是一道自定义排序的题。首先将Int类型的数组转化为string类型的数组。使用快速排序将string数组排序,只不过排序规则需要自定义。原来Int类型比较大小就是谁小谁在前,直接大于小于符号比较。这里需要定义如下的比较方式:
x+y>y+x(+相当于拼接)说明y更小,x更大。JAVA中字符串大小比较,用compareTo方法
这里如果不能使用内置sort函数的话,那就必须能手写快速排序,并在此基础上修改。
代码思路如下:
基础的快速排序:针对Int数组的排序
public static void quickSort(int [] arr,int left,int right) {
int pivot = 0;
if(left < right) {
pivot = partition(arr,left,right);
quickSort(arr,left,pivot-1);
quickSort(arr,pivot+1,right);
}
}
private static int partition(int[] arr,int left,int right) {
int key = arr[left];
while(left < right) {
while(left < right && arr[right] >= key) {
right--;
}
arr[left] = arr[right];
while(left < right && arr[left] <= key) {
left++;
}
arr[right] = arr[left];
}
arr[left] = key;
return left;
}在基础的快排基础上修改成我们的比较规则:
class Solution {
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
String[] str = new String[nums.length];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
str[i] =String.valueOf(nums[i]);
}
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length-1;
quicksort(str,left,right);
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String a:str){
res.append(a);
}
return res.toString();
}
public void quicksort(String[] str,int left,int right){
int pivot = 0;
if(left < right){
pivot = helpper(str,left,right);
quicksort(str,left,pivot-1);
quicksort(str,pivot+1,right);
}
}
public int helpper(String[] str,int left,int right){
String key = str[left];
while(left < right){
while(left<right && (str[right]+key).compareTo(key+str[right])>=0) right--;
str[left] = str[right];
while(left<right && (str[left]+key).compareTo(key+str[left])<=0) left++;
str[right] = str[left];
}
str[left] = key;
return left;
}
}如果允许使用内置函数:
class Solution {
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
String[] strs = new String[nums.length];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
strs[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]);
Arrays.sort(strs, (x, y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x));
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : strs)
res.append(s);
return res.toString();
}
}
3.

思路:前序遍历+回溯法
依次往Path里添加节点的值,然后对目标值tar依次减去每个节点的值,如果最终tar值归0且左右子节点皆为空(已经遍历到叶节点了),就代表目前path里存储的值可以加入到最终结果res里面。依次递归左右节点,如果递归结束,tar依旧不为0,说明这一条支路
class Solution {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
recur(root, sum);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode root, int tar) {
if(root == null) return;
path.add(root.val);
tar -= root.val;
if(tar == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null)
res.add(new LinkedList(path));
recur(root.left, tar);
recur(root.right, tar);
path.removeLast();
}
}
4.

第一种解法:数学推导(最难想到但是最简单)

为什么切成3是最优的?推导如下:

class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n <= 3) return n-1;
int a = n / 3;
int b = n - 3*a;
if(b==0) return (int)Math.pow(3,a);
if(b==1) return (int)Math.pow(3,a-1)*4;
return (int)Math.pow(3,a)*2;
}
}
解法二:动态规划
首先,先递推,找出状态转移方程
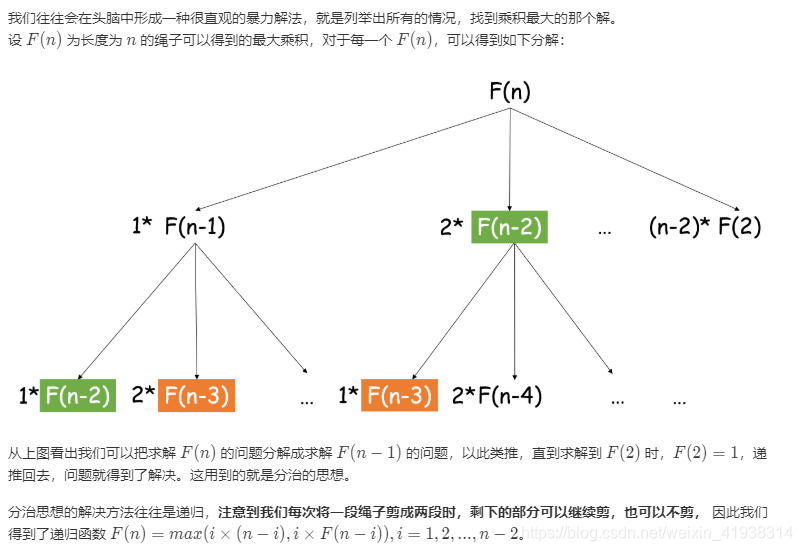

这里为什么最后要和dp[i]求最大值,因为dp[i]的值需要不断被更新,从1*f(n-1),2*f(n-2),3*f(n-3,.......,(n-1)*f(1)之中,挑一个最大的,所以这里的dp[i],其实保留的前一次比较的最大值。
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if (n < 2) {
return 0;
}
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[2] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
//dp[i] = Math.max(j * dp[i - j], j * (i - j));
dp[i] = Math.max(Math.max(j * dp[i - j], j * (i - j)), dp[i]);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
5.

这道题使用的是深度优先搜索,难度表较高,比较绕,我是仿真几次才理清了代码思路。
贴上大佬的思路:


代码实现:
class Solution {
char [] c;//用于存放s中各个字符
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();//将字符串s转换为字符数组c
dfs(0);
return list.toArray(new String[list.size()]);
}
//深度搜索方法,实际上参数x代表固定位的索引值
void dfs(int x){
//收集满了,可以添加进list中
if(x == c.length - 1){
//把c这个字符数组转化为字符串加入到list中
list.add(String.valueOf(c));
return ;//判定依据是s字符串最后一位了,所以加入后,dfs这个函数就可以结束了
}
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();//用于存放字符,检验重复性的,并不是把这个set的内容最终加入到list中,作为结果返回
for(int i=x;i<c.length;i++){
if(set.contains(c[i])) continue;//如果重复了,不进行交换后续操作了,直接结束
set.add(c[i]);
swap(i,x);
dfs(x+1);//递归调用下一个位,固定下一位
swap(i,x);//交换回来,为什么要交换回来?
}
}
//交换函数
void swap(int a,int b){
char tmp = c[a];
c[a] = c[b];
c[b] = tmp;
}
}6.

我分析下来,觉得这题挺明显的就是动态规划。
状态转移方程:f(n) = f(n-1)+f(n-2),这里的n指的是位数
我的初版代码:效率极低
class Solution {
public int translateNum(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
int [] res = new int[c.length+1];
if(c.length ==1) return 1;
res[0] = 0;
res[1] = 1;
if((c[0]+""+c[1]).compareTo("25")>0){
res[2] = 1;
}else{
res[2] = 2;
}
//if(c.length>=3)
for(int i=3;i<=c.length;i++){
if((c[i-2]+""+c[i-1]).compareTo("25")<=0 && (c[i-2]+""+c[i-1]).compareTo("10")>=0){
//本位和前一位加起来的值比25要小
res[i] = res[i-1]+res[i-2];
}else{
res[i] = res[i-1];
}
}
return res[c.length];
}
}我这代码有几个地方可以优化:
1.不需要res这么大的数组,因为f(n)只和f(n-1)、f(n-2)有关,一共三个数,所以完全可以用a,b,c三个数,然后每次循环完对它进行一次更新即可。
2.这里将int类型的num转为string的字符串,后面是没必要转为字符数组,因为后续要用到的地方就是最后2位和10和25比较大小,可以使用substring方法去截取子字符串即可。
所以优化后的代码如下:
class Solution {
public int translateNum(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
int a = 1, b = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i++) {
String tmp = s.substring(i - 2, i);
int c = tmp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
}
7.

有一定难度,思想:递归分治 本题中13265,可以确定最后一个一定是二叉搜索树的根节点,从头开始遍历,发现的第一个大于根节点的那就是分割线了,左边就是左子树,右边就是右子树。

实现代码:
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
boolean res = recur(postorder,0,postorder.length-1);
return res;
}
public boolean recur(int[] postorder,int i,int j){
if(i >= j) return true;//初始判断
int p = i;//i的初始索引
while(postorder[p] < postorder[j]) p++;//这相当于在遍历左子树
int m = p;//记录左右子树分割的地方
while(postorder[p] > postorder[j]) p++;//这相当于在遍历右子树
return p==j && recur(postorder,i,m-1) && recur(postorder,m,j-1);
}
}8.

使用一个队列和一个双向队列可以实现,和前面有一个也是求队列最大值的题目很像,建议复习时一起翻看
class MaxQueue {
//其实就是要求设计一个队列,能实现3个功能,求最大值、从队列后加入元素、从最前面pop元素
Queue<Integer> queue;
Deque<Integer> deque;
public MaxQueue() {
//初始化的
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
deque = new LinkedList<Integer>();//用于储存队列的最大值
}
public int max_value() {
if(deque.isEmpty()) return -1;
return deque.peek();
}
public void push_back(int value) {
queue.offer(value);
while(deque.size() >0 && deque.peekLast() < value){//查询队尾元素
deque.pollLast();//推出队尾元素
}
deque.offerLast(value);
}
public int pop_front() {
if(queue.isEmpty()) return -1;
int pop = queue.poll();
if(deque.size() >0 && pop == deque.peek()){//查询队首元素
deque.poll();//推出队首元素
}
return pop;
}
}
/**
* Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MaxQueue obj = new MaxQueue();
* int param_1 = obj.max_value();
* obj.push_back(value);
* int param_3 = obj.pop_front();
*/9.

思路:深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索
准备工作:


方法一:深度优先搜索(dfs)

class Solution {
int m, n, k;
boolean[][] visited;
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
this.m = m; this.n = n; this.k = k;//这里为什么要写this,因为这里的方法里有m,方法外也有m,同理n,k也是一样,this.m指的是方法外的m,而后面的m指的是参数里的m值。
this.visited = new boolean[m][n];
return dfs(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
public int dfs(int i, int j, int si, int sj) {
if(i >= m || j >= n || k < si + sj || visited[i][j]) return 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
return 1 + dfs(i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj) + dfs(i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8);
}
}
方法二:广度优先搜索:(bfs),要理解bfs和dfs有何不同之处

class Solution {
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
int res = 0;
Queue<int[]> queue= new LinkedList<int[]>();
queue.add(new int[] { 0, 0, 0, 0 });
while(queue.size() > 0) {
int[] x = queue.poll();
int i = x[0], j = x[1], si = x[2], sj = x[3];
if(i >= m || j >= n || k < si + sj || visited[i][j]) continue;
visited[i][j] = true;
res ++;
queue.add(new int[] { i + 1, j, (i + 1) % 10 != 0 ? si + 1 : si - 8, sj });
queue.add(new int[] { i, j + 1, si, (j + 1) % 10 != 0 ? sj + 1 : sj - 8 });
}
return res;
}
}
10.

算法思路:

代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if(A == null || B == null) return false;//如果A或者B为空,则返回false
return (recur(A,B) || isSubStructure(A.left,B) || isSubStructure(A.right,B));//其实这样进行的就是先序遍历
}
public boolean recur(TreeNode A, TreeNode B){//判断A,B是否一致
if(B == null) return true;
if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return (recur(A.left,B.left) && recur(A.right,B.right));
}
}
























 1251
1251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








