nginx中的定时器实际上就是一颗红黑树,本文主要对红黑树进行一下解读。
红黑树的由来
红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,提起二叉查找树,每个人都能快速反应过来是什么,下面简单的列出二叉查找树的结点插入与删除方法。
1) 二叉查找树
插入方法:
tree_s * insert_node(tree_s * root, int n)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
root = new tree_s(n);
return root;
}
if(root->value < n)
{
root->right = insert_node(root->right, n);
}
else
{
root->left = insert_node(root->left, n);
}
}
删除方法:
二叉查找树结点的删除相较于插入要麻烦,需要考虑三种情况:
(1)删除的是否是叶子结点,若是叶子结点直接删除,整棵树无需进行调整。
(2)删除的结点是否具有左子树或者右子树,若有,可以将子节点直接移到被删除元素的位置。
(3)删除的结点若既有左子树又有右子树,删除结点时,取待删除几点的左子树最大结点(最右边的结点)或右子树最小结点(最左边结点)与待删除结点进行交换,交换后,删除交换的结点。
//获取左子树最右边叶子结点
tree_s * getmaxnode(tree_s * root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while(root->right)
{
root = root->right;
}
return root;
}
//获取右子树最左边叶子结点
tree_s * getminnode(tree_s * root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while(root->left)
{
root = root->left;
}
return root;
}
tree_s * delete_node(tree_s * root, int n)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if(root->value == n)
{
//叶子结点,直接删除
if((root->left == NULL) && (root->right == NULL))
{
delete root;
root = NULL;
return root;
}
//左右子树都存在
else if((root->left != NULL) && (root->right != NULL))
{
tree_s * tmp = getmaxnode(root->left);
root->value = tmp->value;
//删掉tmp结点,防止tmp含有左子树,仍递归删除
root->left = delete_node(root->left,tmp->value);
}
else if(root->left != NULL)
{
tree_s * tmp = root->left;
delete root;
root = NULL;
return tmp;
}
else if(root->right != NULL)
{
tree_s * tmp = root->right;
delete root;
root = NULL;
return tmp;
}
}
else if(root->value < n)
{
root->right = delete_node(root->right);
}
else if(root->value > n)
{
root->left = delete_node(root->left);
}
}
2) 平衡二叉树(AVL树)
二叉查找树在一定程度上提升了查找的效率,但在某些特殊的情况下,如一直向根节点的左子树插入结点,会使二叉树退化为一个链表,导致查找的效率下降,即最坏的时间复杂度为O(n),n为结点个数,为了优化这种情况,产生了一种平衡二叉树(AVL),即AVL的左右两颗子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,其查找的时间复杂度均为O(logn)。
AVL树在插入或者删除结点时,需要检查操作后树是否平衡,若不平衡,需要对失衡的结点进行旋转,树失衡有以下四种情况:

左左型:在原来平衡的二叉树上,在节点的左子树的左子树下插入一个新节点,需进行单次旋转操作,右旋。
左右型:在原来平衡的二叉树上,在节点的左子树的右子树下插入一个新节点,需进行单两次旋转操作,先对待旋转结点的左孩子进行左旋,再对结点进行右旋。
右左型:在原来平衡的二叉树上,在节点的右子树的左子树下插入一个新节点进行单两次旋转操作,先对待旋转结点的右孩子进行右旋,再对结点进行左旋。
右右型:在节点的右子树的右子树下插入一个新节点,需进行单次旋转操作,左旋。
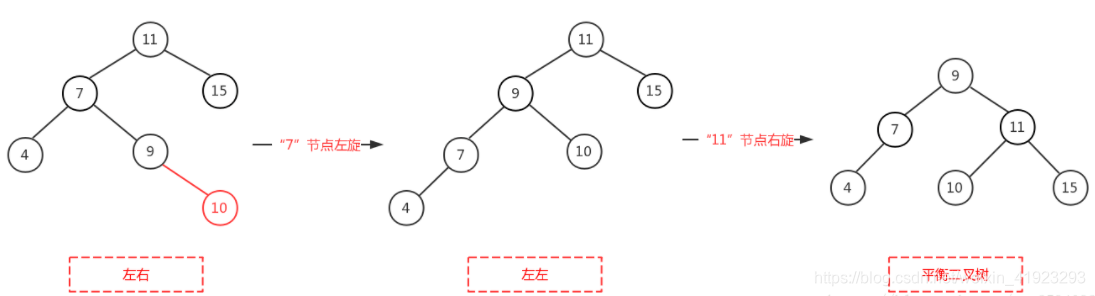
(图片来源自网络,侵删)
旋转代码示例:
int height(tree_s * node)
{
if(node == NULL)
return -1;
return node->height;
}
tree_s * left_rot(tree_s * node)
{
tree_s * tmp = node->right;
node->right = tmp->left;
tmp->left = node;
//计算调整后的结点高度
tmp->height =max(height(tmp->left) , height(tmp->left)) + 1;
node->height = max(height(node->left) , height(node->left)) + 1;
return tmp;
}
tree_s * right_rot(tree_s * node)
{
tree_s * tmp = node->left;
node->left = tmp->right;
tmp->right = node;
//计算调整后的结点高度
tmp->height = max(height(tmp->left) , height(tmp->left)) + 1;
node->height = max(height(node->left) , height(node->left)) + 1;
return tmp;
}
//左右旋转的类型,先对结点的孩子进行左旋,再对结点进行右旋
tree_s * lr_rot(tree_s * node)
{
node->left = left_rot(node->left);
return right_rot(node);
}
//右左旋转的类型,先对结点的孩子进行右旋,再对结点进行左旋
tree_s * rl_rot(tree_s * node)
{
node->right = right_rot(node->right);
return left_rot(node);
}
插入结点;
tree_s * insert_node(tree_s * root, int n)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
root = new tree_s(n);
}
if(root->value > n)
{
root->left = insert_node(root->left, n);
//插入结点后,进行平衡检查,因为是插入到左子树,只需检查左子树减去右子树,下方同理
if(height(root->left) - height(root->right) > 1)
{
//左左型
if(n < root->left->value)
{
root = right_rot(root);
}
else //左右型
{
root = lr_rot(root);
}
}
}
else if(root->value < n)
{
root->right = insert_node(root->right, n);
if(height(root->right) - height(root->left) > 1)
{
//右右型
if(n > root->right->value)
{
root = right_rot(root);
}
else //右左型
{
root = lr_rot(root);
}
}
}
//重新计算根节点的高度
root->height = max(height(root->left) , height(root->left)) + 1;
return root;
}
删除结点:
tree_s * delete_node(tree_s * root, int n)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if(root->value == n)
{
//叶子结点,直接删除
if((root->left == NULL) && (root->right == NULL))
{
delete root;
root == NULL;
return root;
}
//左右子树都存在
else if((root->left != NULL) && (root->right != NULL))
{
//计算左右子树的高度,为尽量保持平衡,删除较高子树上的结点
if(height(root->left) > height(root->left))
{
tree_s * tmp = getmaxnode(root->left);
root->value = tmp->value;
//删掉tmp结点,防止tmp含有左子树,仍递归删除
root->left = delete_node(root->left,tmp->value);
}
else
{
tree_s * tmp = getminnode(root->right);
root->value = tmp->value;
root->left = delete_node(root->right,tmp->value);
}
}
else if(root->left != NULL)
{
tree_s * tmp = root->left;
delete root;
root = NULL;
return tmp;
}
else if(root->right != NULL)
{
tree_s * tmp = root->right;
delete root;
root = NULL;
return tmp;
}
}
else if(root->value < n)
{
root->right = delete_node(root->right);
if(height(root->left) > height(root->right) > 1)
{
if(height(root->left->left) > height(root->left->right))
{
//左左型,右旋
right_rot(root);
}
else
{
//左右型
lr_rot(root);
}
}
else
{
root->height = max(height(root->left), height(root->left)) + 1;
}
}
else if(root->value > n)
{
root->left = delete_node(root->left);
if(height(root->right) > height(root->left) > 1)
{
if(height(root->right->left) > height(root->right->right))
{
//右左型
rl_rot(root);
}
else
{
//右右型
left_rot(root);
}
}
else
{
root->height = max(height(root->left), height(root->left)) + 1;
}
}
}
整体介绍完AVL树后,可发现AVL树在插入或删除结点导致树失衡的情况时,需要维护从被删除结点到根节点整条路径的平衡,因此旋转的复杂度为O(logn)。而接下来要引出的红黑树在结点插入或删除时,最多只需要三次旋转即可维持平衡,复杂度为O(1),在对结点需要进行频繁插入/删除操作时,且对查询的性能要求不高的场景多选用红黑树,如nginx中的定时器,以及STL等。下一节回仔细讲述红黑树的原理,以及与AVL树的差异。







 本文介绍了红黑树作为自平衡二叉查找树的特性,对比了普通二叉查找树和AVL树。在二叉查找树的基础上,详细阐述了AVL树的平衡原理及旋转操作,展示了插入和删除节点可能导致的四种失衡情况及对应的旋转修复。红黑树在插入或删除时仅需最多三次旋转即可维持平衡,复杂度为O(1),适用于频繁插入/删除操作且对查询性能要求不高的场景,例如nginx中的定时器。
本文介绍了红黑树作为自平衡二叉查找树的特性,对比了普通二叉查找树和AVL树。在二叉查找树的基础上,详细阐述了AVL树的平衡原理及旋转操作,展示了插入和删除节点可能导致的四种失衡情况及对应的旋转修复。红黑树在插入或删除时仅需最多三次旋转即可维持平衡,复杂度为O(1),适用于频繁插入/删除操作且对查询性能要求不高的场景,例如nginx中的定时器。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








