1 IO流分类
a:按照数据流向
输入流 读入数据
输出流 写出数据
b:按照数据类型
字节流 可以读写任何类型的文件 比如音频 视频 文本文件
字符流 只能读写文本文件
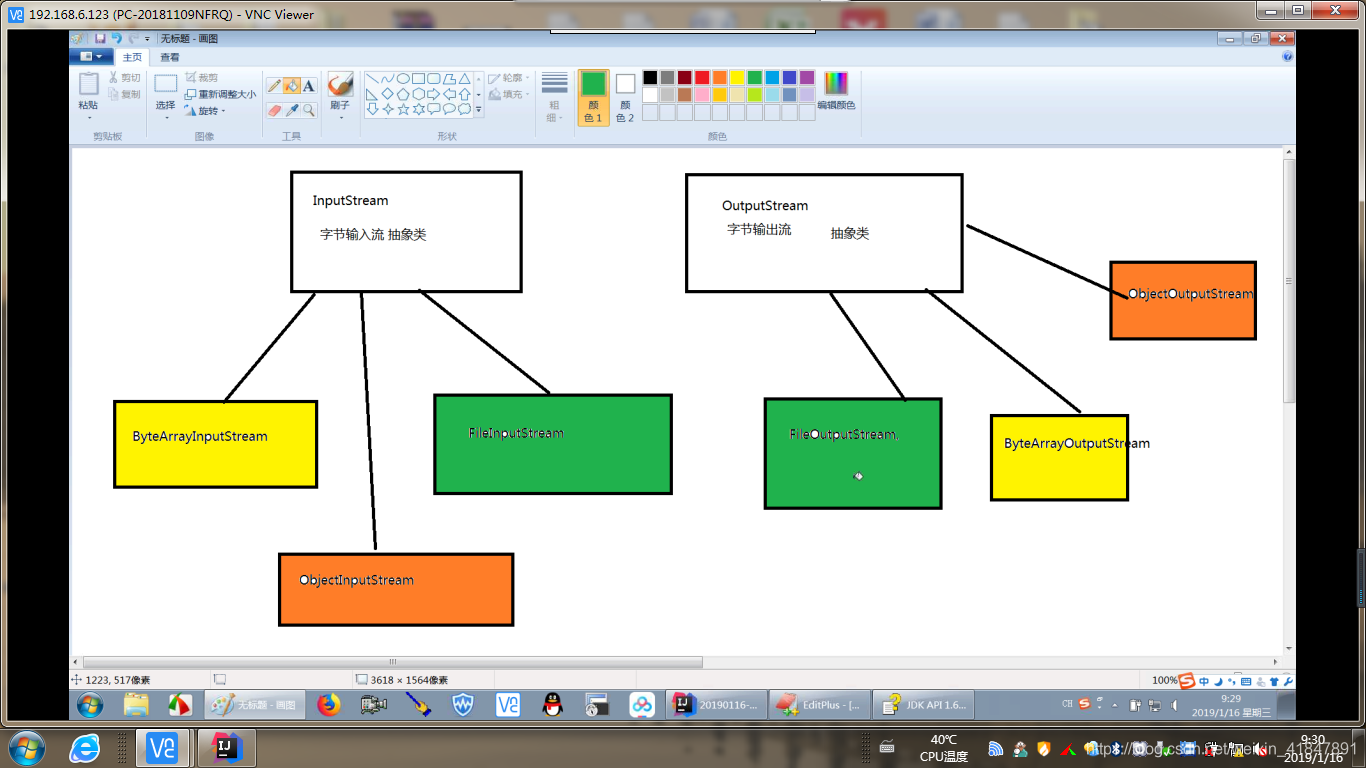
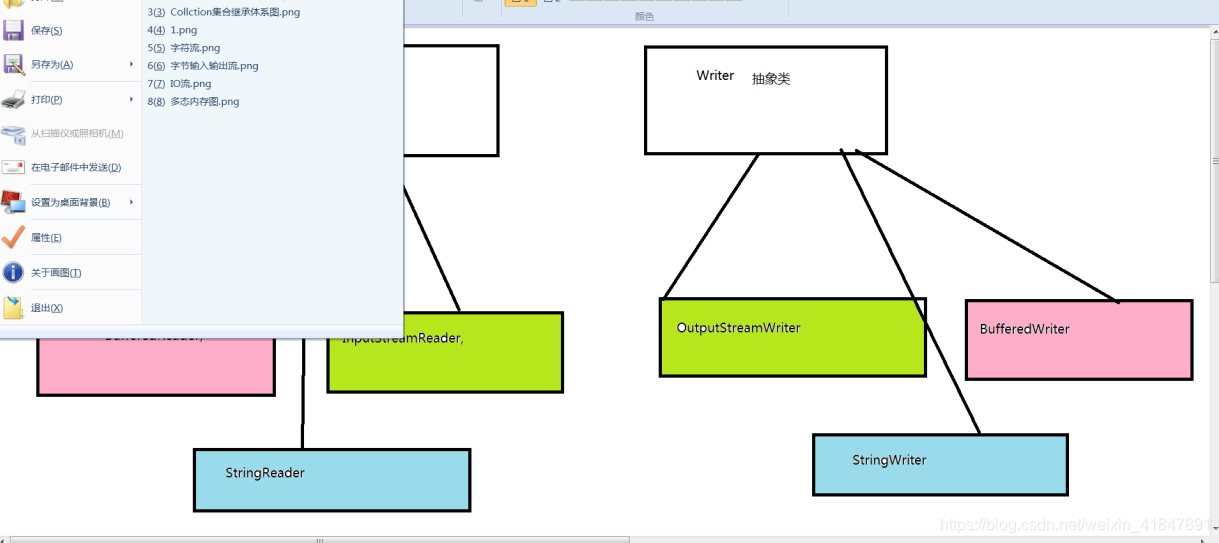
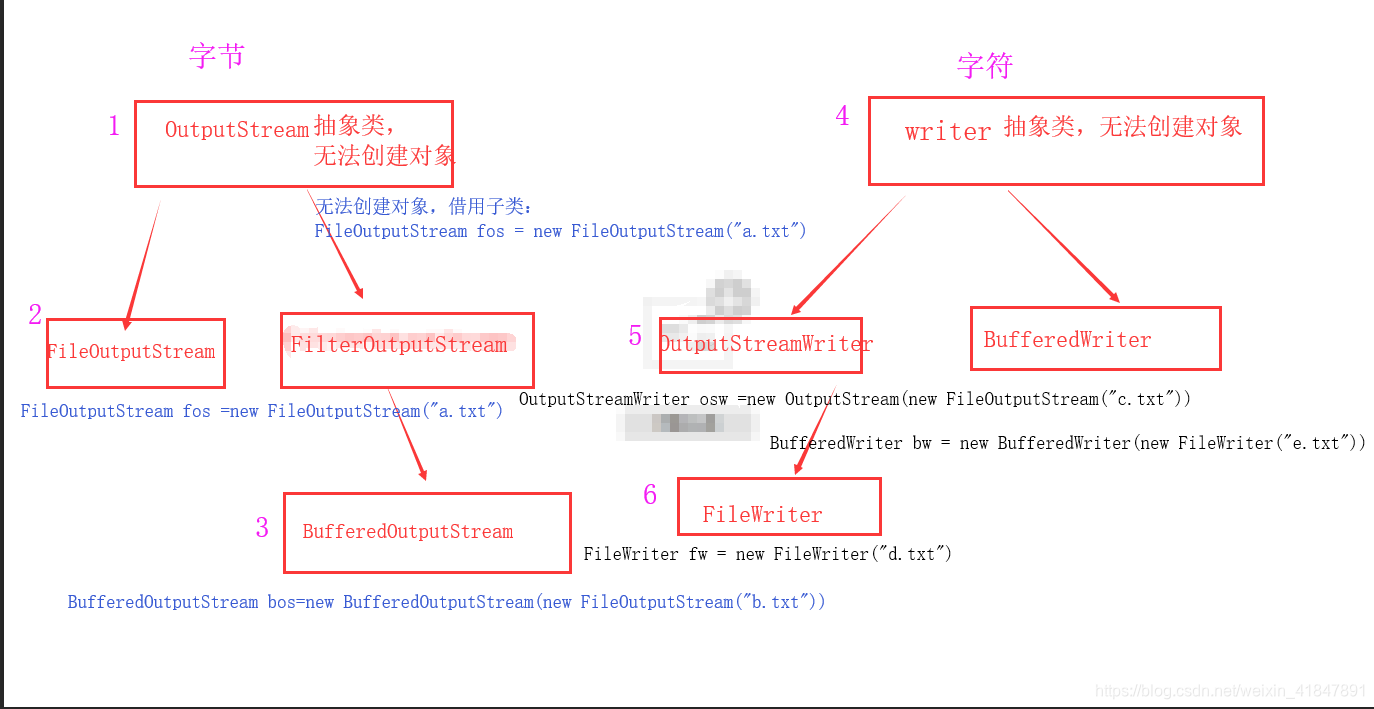
2 字节流与字符流神图
字节流的抽象基类:
InputStream ,OutputStream。
字符流的抽象基类:
Reader , Writer。
3 write方法
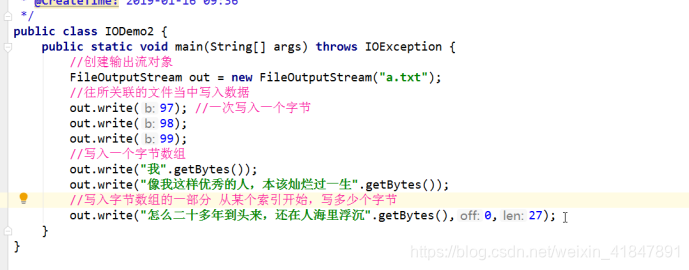
FileOutputStream的三个write()方法
public void write(int b):写一个字节 超过一个字节 砍掉前面的字节
public void write(byte[] b):写一个字节数组
public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len):写一个字节数组的一部分
FileOutputStream写出数据如何实现数据的换行
windows下的换行符只用是 \r\n
OutputStreamWriter的write()方法
public void write(int c) 写一个字符
public void write(char[] cbuf) 写一个字符数组
public void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) 写一个字符数组的 一部分
public void write(String str) 写一个字符串
public void write(String str,int off,int len) 写一个字符串的一部分
4 read方法
FileInputStream的read()方法
int read():一次读取一个字节
int read(byte[] b):一次读取一个字节数组,如果没有读到 返回-1
OutputStreamReader的read()方法
public int read() 一次读取一个字符
public int read(char[] cbuf) 一次读取一个字符数组 如果没有读到 返回-1
5 IO流(String类中的编码和解码问题)
编码 把一个字符串转换成一个字节数组
* public byte[] getBytes();
解码: 把字节数组转换成字符串
* public String(byte[] bytes): 构造一个新的 new String(bytes)
编码:把看得懂的变成看不懂的: String -- byte[]
解码:把看不懂的变成看得懂的: byte[] -- String
6 FileReader和FileWriter的出现
转换流的名字比较长(OutputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter),所以,为了简化我们的书写,转换流提供了对应的子类。
FileWriter
FileReader

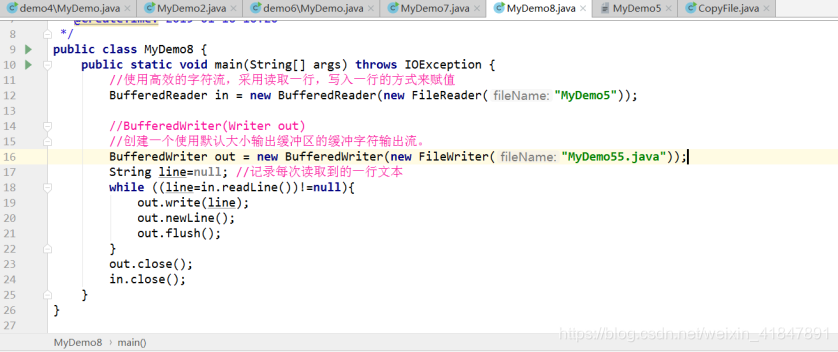
7 字符缓冲流的特殊功能
BufferedWriter: public void newLine():根据系统来决定换行符 具有系统兼容性的换行符
BufferedReader: public String readLine():一次读取一行数据 是以换行符为标记的 读到换行符就换行 没读到数据返回null
包含该行内容的字符串,不包含任何行终止符,如果已到达流末尾,则返回 null
8 BufferedRead典型模板
9 例题1:编写程序,获取指定目录下 所有的.java结尾的文件, 打印出文件的绝对路径(包含 子文件夹中的.java文件)
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\文件");
select(f);
}
private static void select(File f) {
File[] files = f.listFiles();
for(File f2 :files){
if(f2.isFile() && f2.getName().endsWith(".java")){
System.out.println(f2.getAbsolutePath());
}else{
select(f2);
}
}
}
}
例题2 :(典型模板)采用多种方式,把d:\\video01.avi的内容复制到d:\\video02.avi中
方式1:基本字节流一次读写一个字节
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\video01.avi");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\video02.avi");
int len;
while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
方式2:基本字节流一次读写一个字节数组
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\video01.avi");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\video02.avi");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
方式3:高效字节流一次读写一个字节
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\video01.avi"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\video02.avi"));
int len;
while((len=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
方式4:高效字节流一次读写一个字节数组
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\video01.avi"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\video02.avi"));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
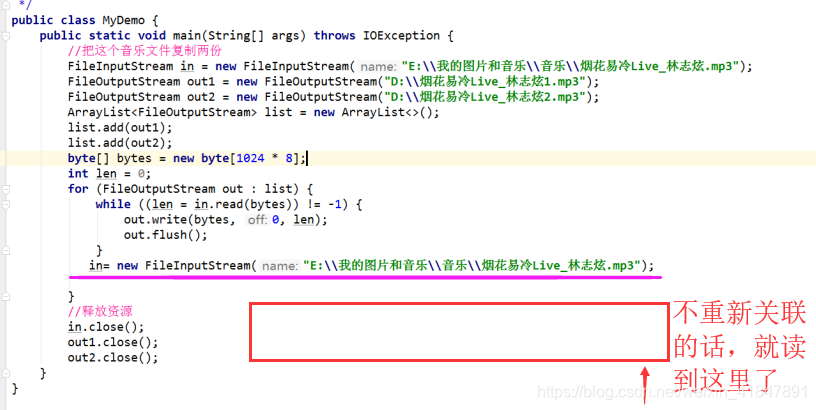
10 注意
1

2
3
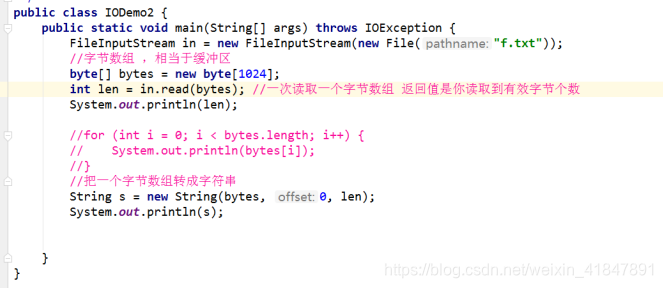
4
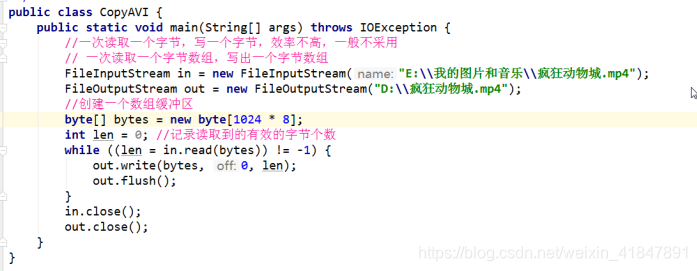
5 流的异常处理
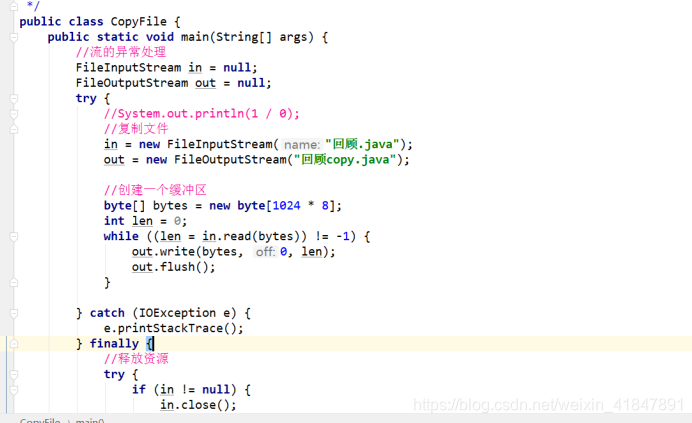
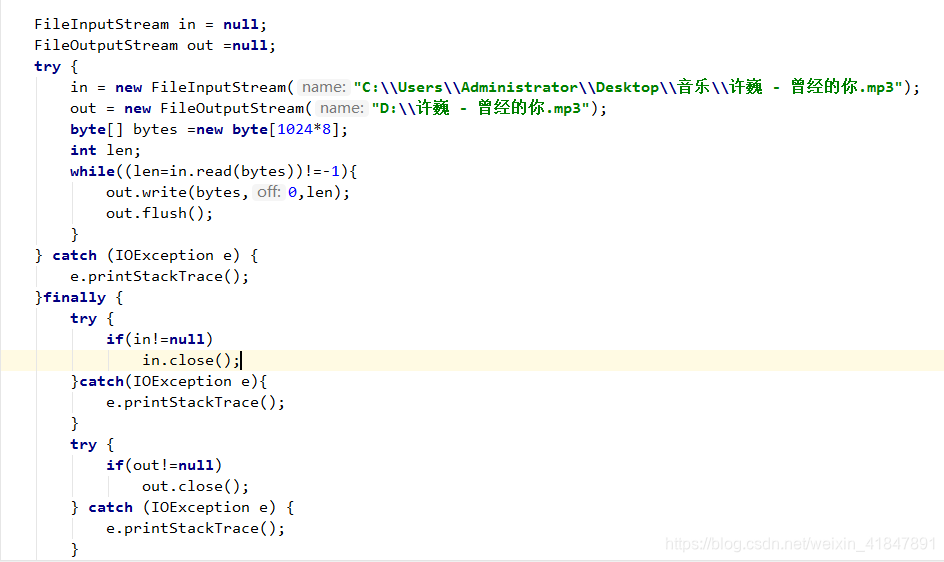
6







 本文深入讲解Java IO流的分类、字节流与字符流的区别、FileInputStream与FileOutputStream的使用方法,包括read与write操作,以及FileReader和FileWriter的应用。通过实例演示了文件复制的不同方式,展示了BufferedReader和BufferedWriter的高级功能。
本文深入讲解Java IO流的分类、字节流与字符流的区别、FileInputStream与FileOutputStream的使用方法,包括read与write操作,以及FileReader和FileWriter的应用。通过实例演示了文件复制的不同方式,展示了BufferedReader和BufferedWriter的高级功能。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








