#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ms(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define N 30
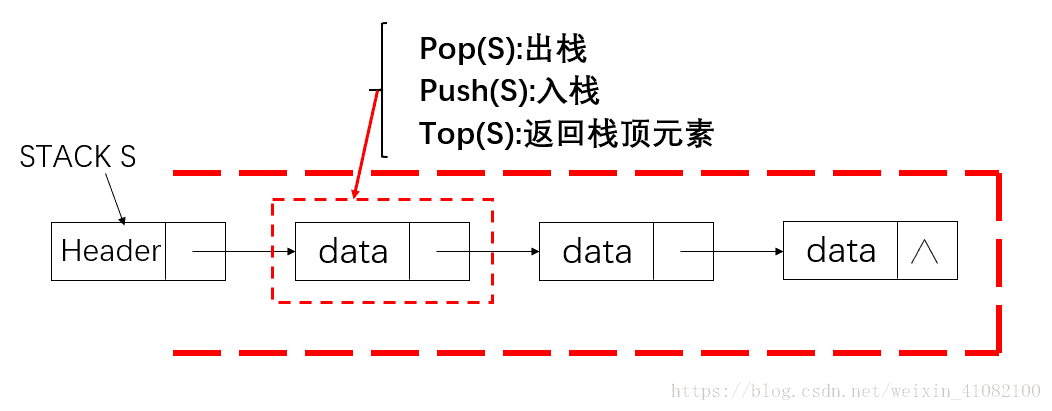
//栈 需要一个表头
typedef int Elementtype;
struct node{
Elementtype Element;
node* next=NULL;
};
typedef node* STACK;
typedef node* ptrnode;
//判断栈是否为空,空返回 1;
int IsEmpty(STACK S){
return S->next==NULL;
}
// 压栈
void Push(Elementtype x,STACK &S){
ptrnode tem=new node;
tem->Element=x;
tem->next=S->next;
S->next=tem;
}
// 返回栈顶元素
Elementtype Top(STACK S){
if(IsEmpty(S)){
cout<<"The stack is empty."<<endl;
}
else{
return S->next->Element;
}
}
// 出栈
void Pop(STACK &S){
ptrnode tem;
if(IsEmpty(S)){
cout<<"The stack is empty."<<endl;
return ;
}
tem=S->next;
S->next=tem->next;
delete(tem);
}
//置空栈
void MakeEmpty(STACK S){
while(!IsEmpty(S)){
Pop(S);
}
}
//创建一个栈
STACK CreateStack(){
STACK S;
S=new node;
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
}
//打印栈中所有元素
void Print(STACK S){
if(IsEmpty(S)){
cout<<"The stack is empty."<<endl;
return ;
}
ptrnode tem=S->next;
while(tem!=NULL){
cout<<tem->Element<<" ";
tem=tem->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
STACK S=CreateStack();
Push(5,S);
Push(4,S);
Push(3,S);
Push(2,S);
Push(1,S);
Print(S);
cout<<Top(S)<<endl;
Pop(S);
Print(S);
Pop(S);
Print(S);
Pop(S);
Print(S);
cout<<Top(S)<<endl;
return 0;
}






















 953
953

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








