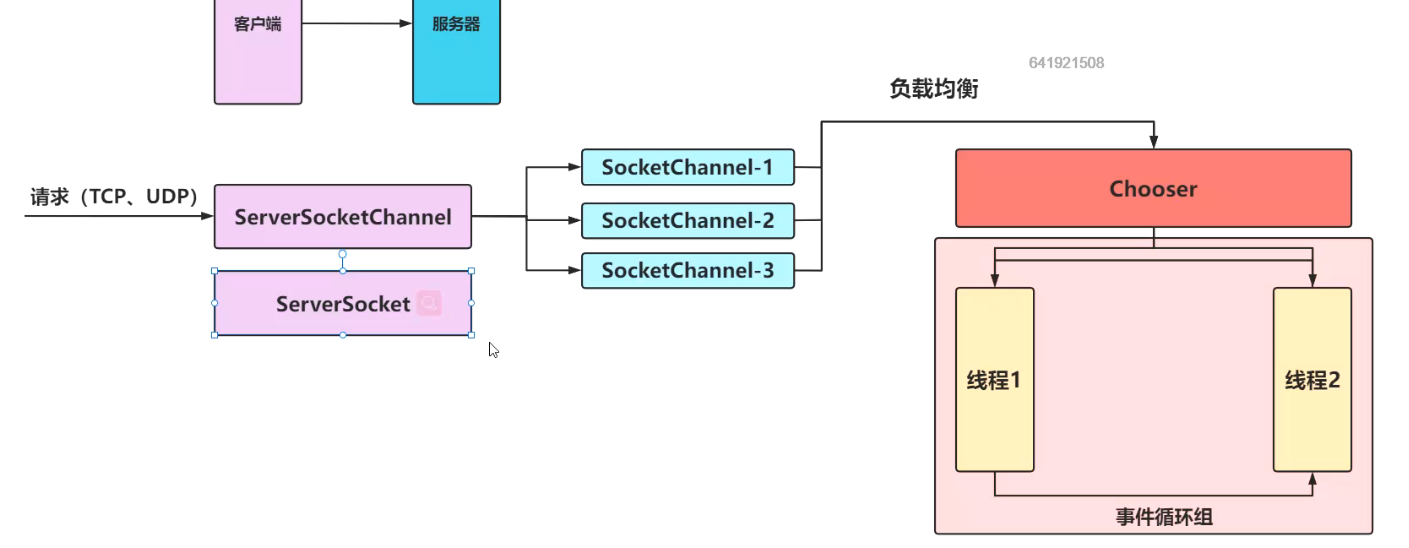
这里的ServerSocketChannel为什么不用ServerSocket?

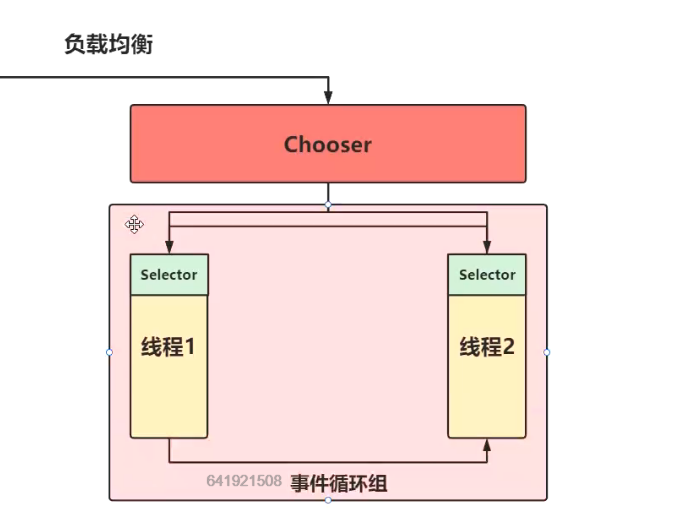
Selector:
如何异步执行?
1.Future接口
2.通过Future获取任务执行结果即可
Future弊端:使用Future获得异步执行结果时,要么调用阻塞方法get(),要么轮询看isDone()是否为true,这两种方法都不是很好,因为主线程也会被迫等待。
如何解决?使用观察者模式,当执行完成时,自动在执行线程中回调callback
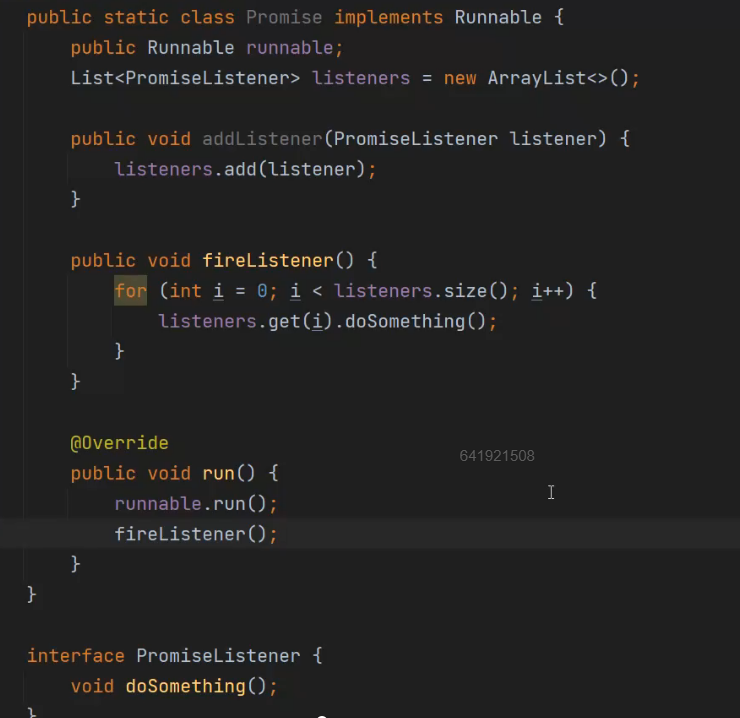
当然在FutureTask中Java已经帮我们实现了,
/**
* Removes and signals all waiting threads, invokes done(), and
* nulls out callable.
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
protected void done() { }
在Netty中就有一个接口Promise来完成这个事情,这时将Promise与Runnable组合即可。
public interface Promise<V> extends Future<V> {
Promise<V> setSuccess(V var1);
boolean trySuccess(V var1);
Promise<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> var1);
Promise<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... var1);
Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
}
public class DefaultPromise<V> extends AbstractFuture<V> implements Promise<V> {
@Override
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Object result = this.result;
if (!isDone0(result)) {
await();
result = this.result;
}
if (result == SUCCESS || result == UNCANCELLABLE) {
return null;
}
Throwable cause = cause0(result);
if (cause == null) {
return (V) result;
}
if (cause instanceof CancellationException) {
throw (CancellationException) cause;
}
throw new ExecutionException(cause);
}
@Override
public Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException {
if (isDone()) {
return this;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException(toString());
}
checkDeadLock();
synchronized (this) {
while (!isDone()) {
incWaiters();
try {
wait();//如果没完成就等待
} finally {
decWaiters();
}
}
}
return this;
}
//触发监听器
@Override
public boolean trySuccess(V result) {
return setSuccess0(result);
}
private boolean setSuccess0(V result) {
return setValue0(result == null ? SUCCESS : result);
}
private boolean setValue0(Object objResult) {
if (RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, null, objResult) ||
RESULT_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, UNCANCELLABLE, objResult)) {
if (checkNotifyWaiters()) {
notifyListeners();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
事件循环组的线程应该有哪些特性?
1.负载均衡
2.周期性调度的工作
内存池的设计:
1.内存种类:DirectByteBuffer、HeapByteBuffer,我想要减少内存分配造成的损耗,那么Netty自己管理内存行不?
操作系统的内存分配策略
首次适应算法(first-fit):从空闲分区表的第一个表目起查找该表,把最先能够满足要求的空闲区分配给作业,这种方法的目的在于减少查找时间。
最佳适应算法(best-fit):从全部空闲区中找出能满足作业要求的,且大小最小的空闲分区,这种方法能使碎片尽量小。
最差适应算法(worst-fit):它从全部空闲区中找出能满足作业要求的、且大小最大的空闲分区,从而使链表中的节点大小趋于均匀。
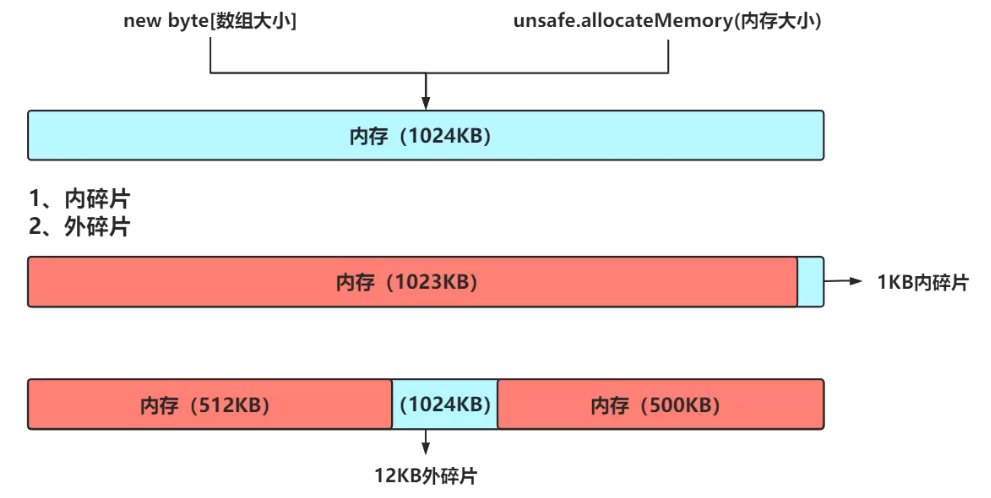
怎么减少外碎片呢?
伙伴算法,将内存拆分成一棵满二叉树。
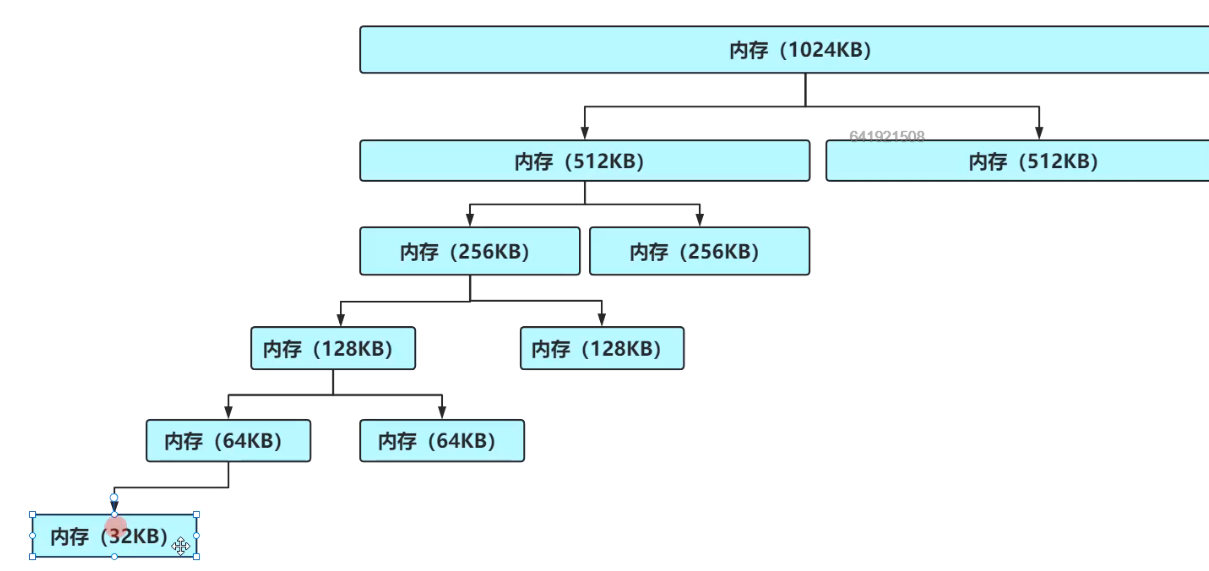
如图,如果分配了8KB,那么同级叶子节点还有8KB可用空间,下一次如果再分配8KB,那么可以直接分配右边的8KB,如果两块空间释放掉以后,它俩又合并为16KB的可用空间,这样按整分配,就减少了外碎片的发生。
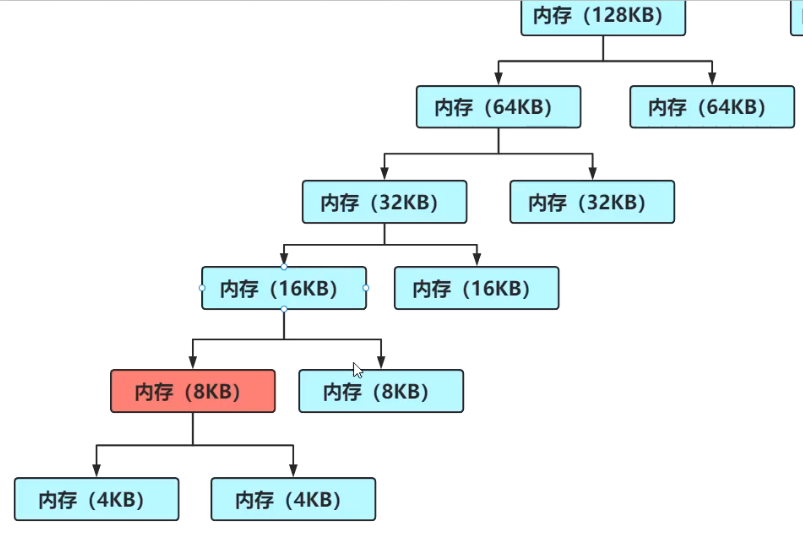
这种算法是不能避免外碎片的发生的,
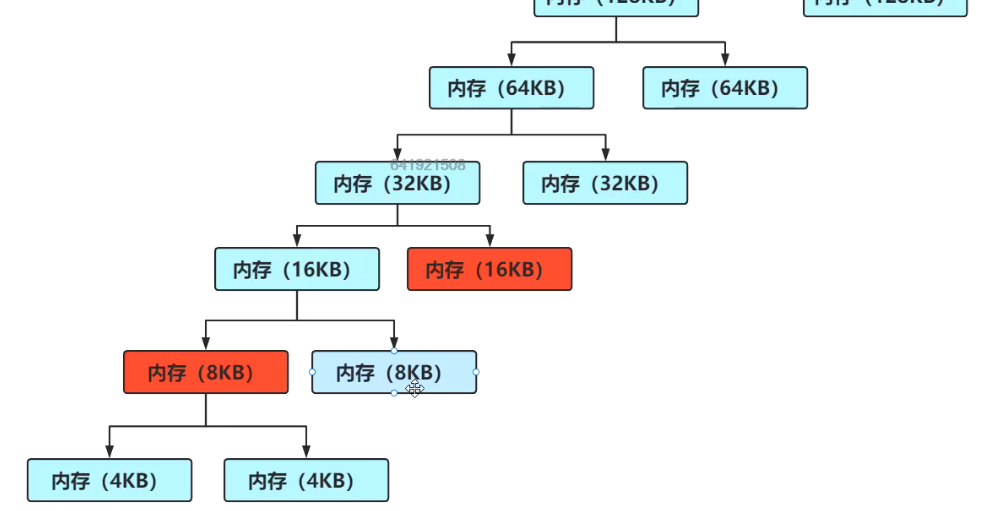
如图,已经分配了8KB,和一个16KB,此时还想分配16KB,那么就不能在左边的32KB中去分配,因为它还剩下8KB可用,这8KB就是外碎片。
怎么减少内碎片呢?
slab算法,如果想要分配1KB,那么将8KB拆分成8个1KB,如果想要分配2KB,那么拆分成4个2KB
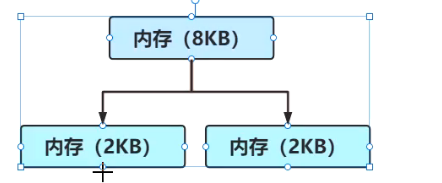
如果要分配3KB,那么只能拆分成2个3KB和一个2KB,这就会产生2KB的内碎片。
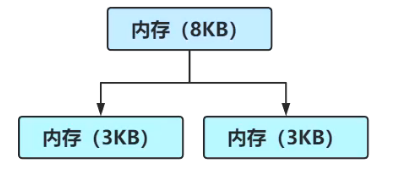
在Netty中,叶子节点的最小值是8KB,既能切分的足够多,也能最大限度的减少内碎片。
高并发下锁优化:
1、锁细粒度化
可以分配多个1024KB的内存块
2、无锁化
将内存分配在线程本地缓存中(ThreadLocal)
有多个1024KB的内存块,我怎么更加合理的减少外碎片?我是从使用率高的内存块中分配,还是从使用率低的分配?
public class PooledByteBufAllocator extends AbstractByteBufAllocator implements ByteBufAllocatorMetricProvider {
static {
//默认叶子节点是8KB
int defaultPageSize = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.allocator.pageSize", 8192);
//二叉树的树高2^11
int defaultMaxOrder = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.allocator.maxOrder", 11);
private final PoolArena<byte[]>[] heapArenas;
private final PoolArena<ByteBuffer>[] directArenas;
}
//preferDirect要不要分配直接内存
public PooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, int nHeapArena,
int nDirectArena, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int tinyCacheSize,
int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize,
boolean useCacheForAllThreads) {
this(preferDirect, nHeapArena, nDirectArena, pageSize, maxOrder,
tinyCacheSize, smallCacheSize, normalCacheSize,
useCacheForAllThreads, DEFAULT_DIRECT_MEMORY_CACHE_ALIGNMENT);
}
public PooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, int nHeapArena, int nDirectArena, int pageSize, int maxOrder,
int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize,
boolean useCacheForAllThreads, int directMemoryCacheAlignment) {
super(preferDirect);
threadCache = new PoolThreadLocalCache(useCacheForAllThreads);
}
final class PoolThreadLocalCache extends FastThreadLocal<PoolThreadCache> {
@Override
protected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() {
//找到持有线程数最少的Arena(内存区域,相当于一个1024块,netty中一个PoolArena是16M)
final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas);
final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = leastUsedArena(directArenas);
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// No caching so just use 0 as sizes.
return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
}
private <T> PoolArena<T> leastUsedArena(PoolArena<T>[] arenas) {
if (arenas == null || arenas.length == 0) {
return null;
}
PoolArena<T> minArena = arenas[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arenas.length; i++) {
PoolArena<T> arena = arenas[i];
if (arena.numThreadCaches.get() < minArena.numThreadCaches.get()) {
minArena = arena;
}
}
return minArena;
}
}
}
@Override
protected ByteBuf newHeapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get();
PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = cache.heapArena;
final ByteBuf buf;
if (heapArena != null) {
buf = heapArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ?
new UnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) :
new UnpooledHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);
}
abstract class PoolArena<T> implements PoolArenaMetric {
protected PoolArena(PooledByteBufAllocator parent, int pageSize,
int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int cacheAlignment) {
//将每个PoolChunk计算出使用率,放入对应的List
q100 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize);
q075 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize);
q050 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize);
q025 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize);
q000 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize);
qInit = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize);
q100.prevList(q075);
q075.prevList(q050);
q050.prevList(q025);
q025.prevList(q000);
q000.prevList(null);
qInit.prevList(qInit);
List<PoolChunkListMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolChunkListMetric>(6);
metrics.add(qInit);
metrics.add(q000);
metrics.add(q025);
metrics.add(q050);
metrics.add(q075);
metrics.add(q100);
chunkListMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics);
}
PooledByteBuf<T> allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
PooledByteBuf<T> buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity);
allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity);
return buf;
}
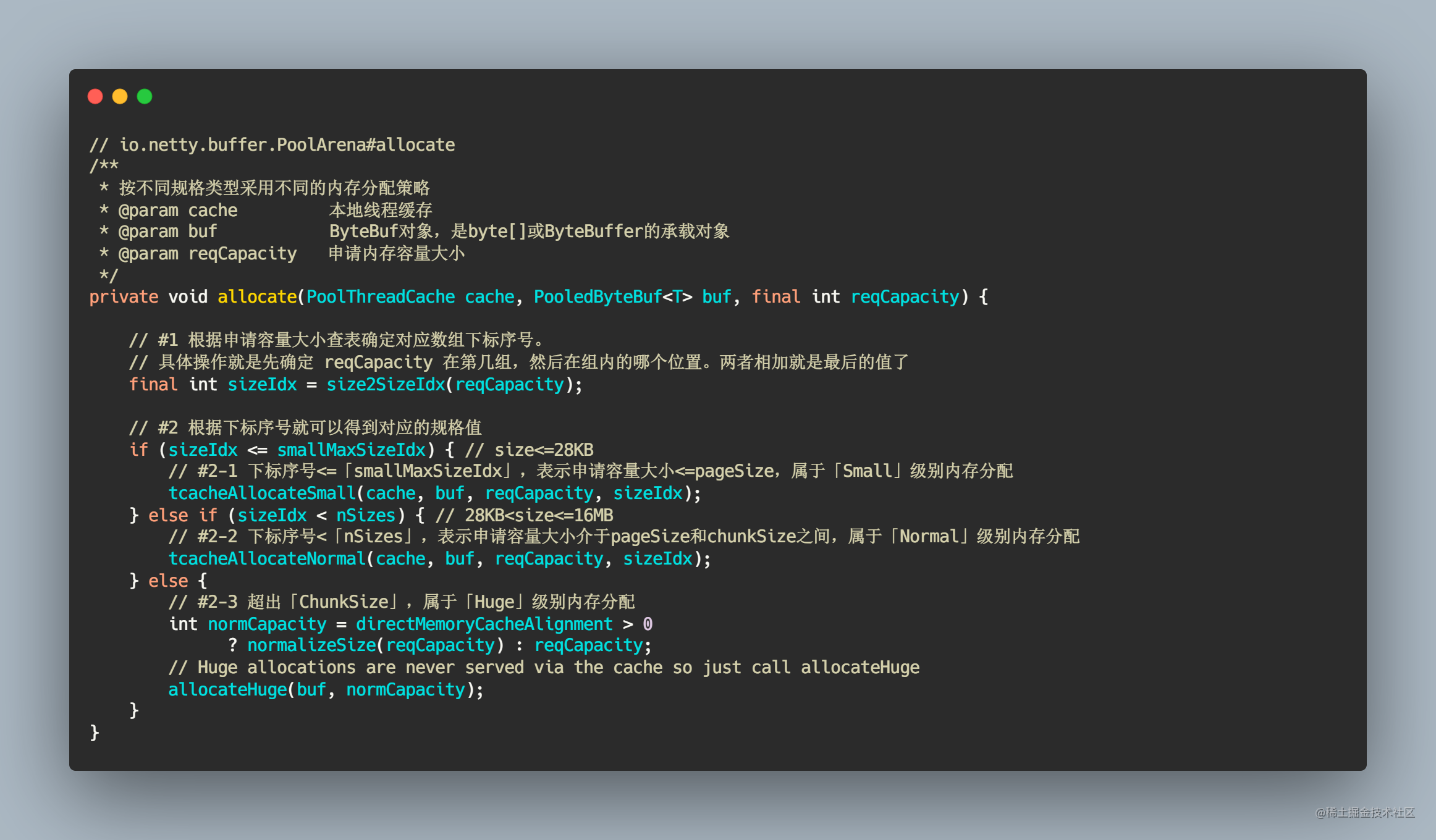
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity) {
final int sizeIdx = size2SizeIdx(reqCapacity);
if (sizeIdx <= smallMaxSizeIdx) {
//分配小页内存,使用slab算法
tcacheAllocateSmall(cache, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx);
} else if (sizeIdx < nSizes) {
tcacheAllocateNormal(cache, buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx);
} else {
int normCapacity = directMemoryCacheAlignment > 0
? normalizeSize(reqCapacity) : reqCapacity;
// 分配大页内存
allocateHuge(buf, normCapacity);
}
}
private void allocateHuge(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity) {
//一个PoolChunk代表一个大页内存
PoolChunk<T> chunk = newUnpooledChunk(reqCapacity);
activeBytesHuge.add(chunk.chunkSize());
buf.initUnpooled(chunk, reqCapacity);
allocationsHuge.increment();
}
//
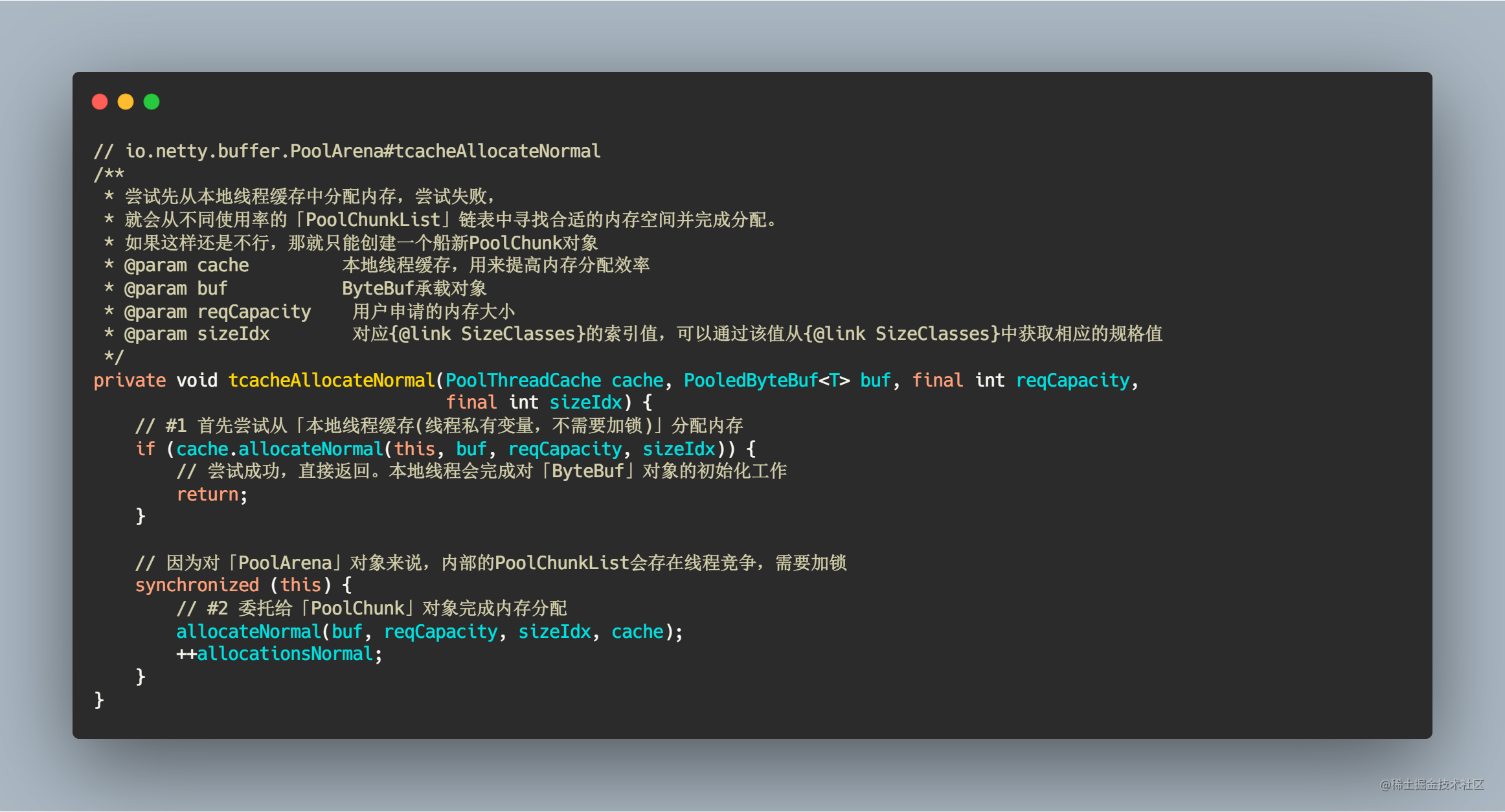
/**
* 先从「PoolChunkList」链表中选取某一个「PoolChunk」进行内存分配,如果实在找不到合适的「PoolChunk」对象,
* 那就只能新建一个全新的「PoolChunk」对象,在完成内存分配后需要添加到对应的PoolChunkList链表中。
* 内部有多个「PoolChunkList」链表,q050、q025表示内部的「PoolChunk」最低的使用率。
* Netty 会先从q050开始分配,并非从q000开始。
* 这是因为如果从q000开始分配内存的话会导致有大部分的PoolChunk面临频繁的创建和销毁,造成内存分配的性能降低。
*
* @param buf ByeBuf承载对象
* @param reqCapacity 用户所需要真实的内存大小
* @param sizeIdx 对应{@link SizeClasses}的索引值,可以通过该值从{@link SizeClasses}中获取相应的规格值
* @param threadCache 本地线程缓存,这个缓存主要是为了初始化PooledByteBuf时填充对象内部的缓存变量
*/
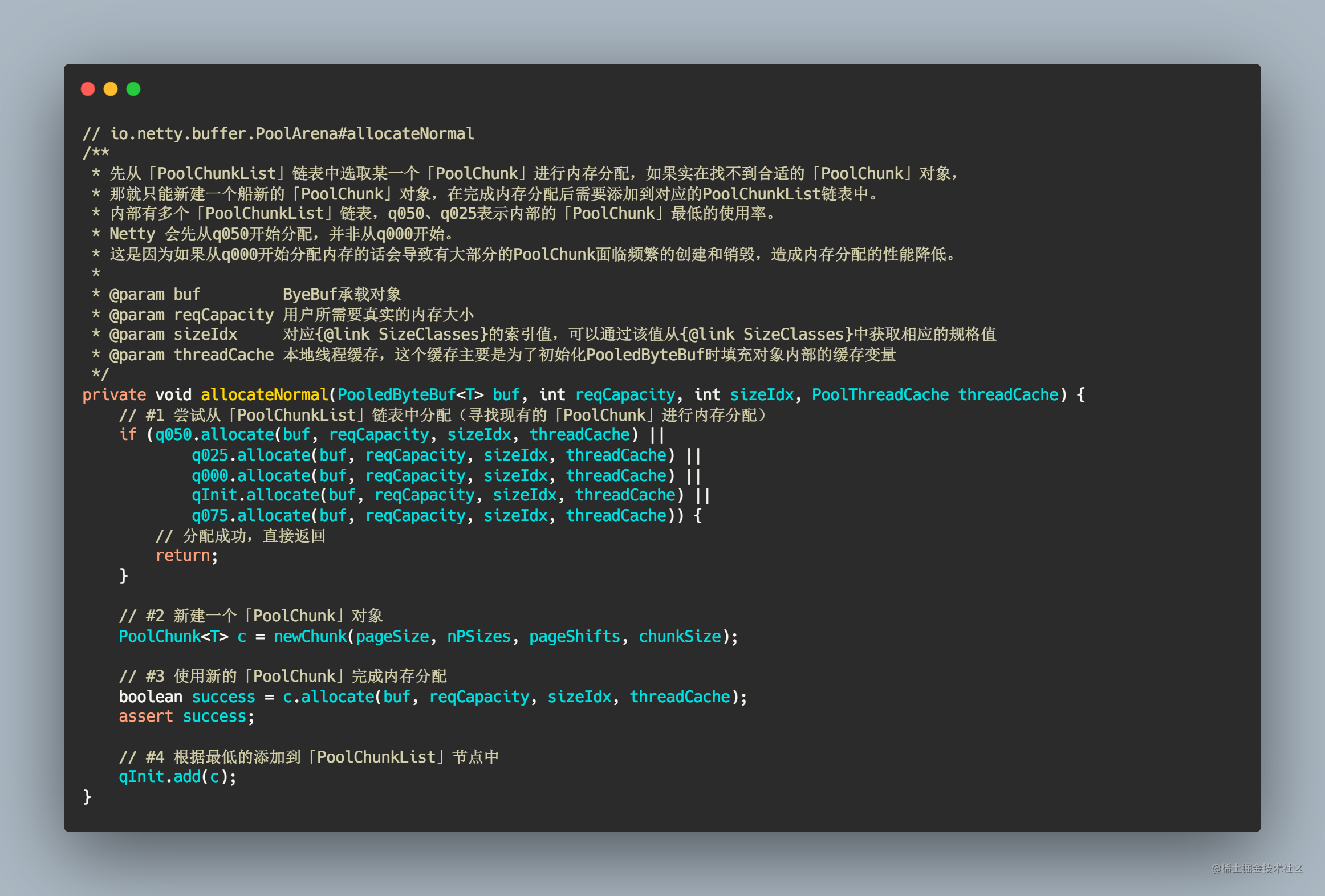
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int sizeIdx, PoolThreadCache threadCache) {
// #1 尝试从「PoolChunkList」链表中分配(寻找现有的「PoolChunk」进行内存分配)
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache) ||
q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache)) {
// 分配成功,直接返回
return;
}
// #2 新建一个「PoolChunk」对象
PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, nPSizes, pageShifts, chunkSize);
// #3 使用新的「PoolChunk」完成内存分配
boolean success = c.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, sizeIdx, threadCache);
assert success;
// #4 根据最低的添加到「PoolChunkList」节点中
qInit.add(c);
}
}







 本文探讨了Java中的ServerSocketChannel和Selector在异步编程中的应用,以及Future和Promise接口的使用及其局限。重点介绍了Netty中的Promise机制如何解决Future的不足,并讨论了内存管理,包括内存池设计、内存分配策略(如首次适应、最佳适应和最差适应)以及如何减少外内碎片。此外,还涉及了高并发场景下的锁优化和内存分配策略优化技巧。
本文探讨了Java中的ServerSocketChannel和Selector在异步编程中的应用,以及Future和Promise接口的使用及其局限。重点介绍了Netty中的Promise机制如何解决Future的不足,并讨论了内存管理,包括内存池设计、内存分配策略(如首次适应、最佳适应和最差适应)以及如何减少外内碎片。此外,还涉及了高并发场景下的锁优化和内存分配策略优化技巧。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








