题目链接
Mr. Frog recently studied how to add two fractions up, and he came up with an evil idea to trouble you by asking you to calculate the result of the formula below:
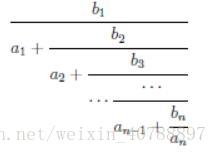
As a talent, can you figure out the answer correctly?
Input
The first line contains only one integer T, which indicates the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains only one integer n (n≤8).
The second line contains n integers: a1,a2,⋯an(1≤ai≤10a1,a2,⋯an(1≤ai≤10).
The third line contains n integers: b1,b2,⋯,bn(1≤bi≤10)b1,b2,⋯,bn(1≤bi≤10).
Output
For each case, print a line “Case #x: p q”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and p/q indicates the answer.
You should promise that p/q is irreducible.
Sample Input
1
2
1 1
2 3
Sample Output
Case #1: 1 2
Hint
Here are the details for the first sample:
2/(1+3/1) = 1/2
题目就是让你求一个如图所示的分数的分子和分母。其实也没啥好办法啊,就是模拟呗,我们平时怎么算的分数还是怎么算啊。刚开始我想的是直接用递归来算出分母的值,发现一只wa,emmm,后来想了想,确实,这样做的话总会有精度损失的,所以还是模拟吧。还有就是,他要求不能再约分,所以还要有一个求最大公约数的函数。具体的话,还是看代码吧,其实主要的就是涉及了分子分母之间的转化。
AC代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[10], b[10];
int n;
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
return y == 0 ? x : gcd(y, x % y);
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
for(int T = 1; T <= t; T++)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
int x, y;
x = b[n], y = a[n];
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
{
int temp = a[i] * y + x;
x = y; y = temp;
x *= b[i];
}
int _gcd = gcd(x, y);
printf("Case #%d: %d %d\n", T, x / _gcd, y / _gcd);
}
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了一个关于分数加法的编程挑战,需要计算特殊形式的分数并确保结果为最简形式。文章提供了完整的AC代码实现,包括输入输出示例、算法思路和最大公约数的计算方法。
本文介绍了一个关于分数加法的编程挑战,需要计算特殊形式的分数并确保结果为最简形式。文章提供了完整的AC代码实现,包括输入输出示例、算法思路和最大公约数的计算方法。
















 209
209

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








