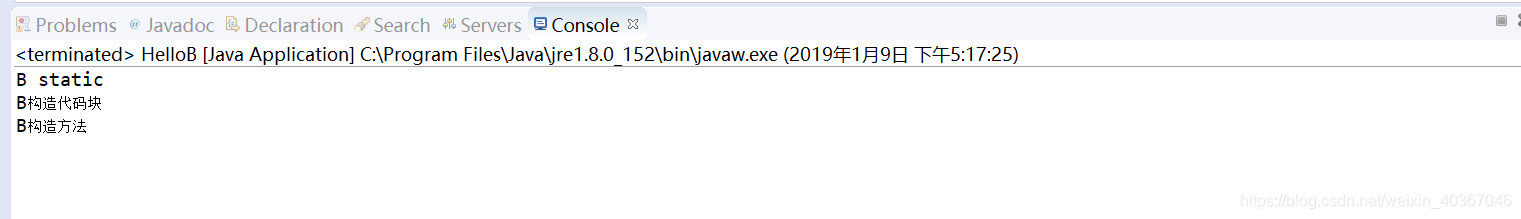
(1)如果只有一个类,执行顺序:
静态初始化代码块、构造代码块、构造方法
代码举例:
public class HelloB {
public HelloB() {
System.out.println("B构造方法");
}
{
System.out.println("B构造代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("B static");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloB();
}
}
运行结果:
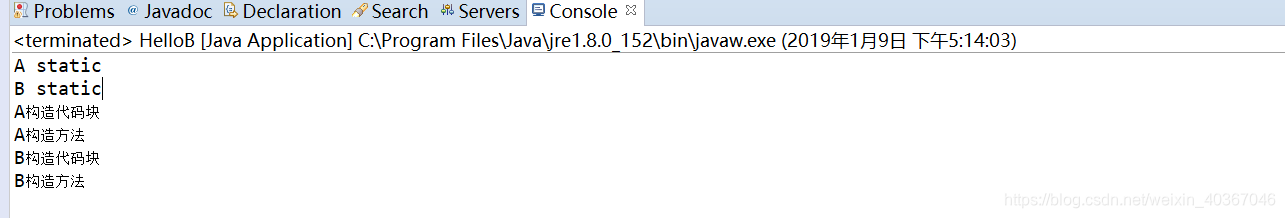
(2)如果有父类和子类,执行顺序:
1.父类静态初始化代码块、子类静态初始化代码块
2.父类构造代码块、父类构造方法
3.子类构造代码块、子类构造方法
代码举例:
public class HelloB extends HelloA {
public HelloB() {
System.out.println("B构造方法");
}
{
System.out.println("B构造代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("B static");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new HelloB();
}
}
class HelloA {
public HelloA() {
System.out.println("A构造方法");
}
{
System.out.println("A构造代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("A static");
}
}
运行结果:





 本文详细解析了Java中类的构造顺序,包括静态初始化代码块、构造代码块和构造方法的执行顺序,以及当存在父类和子类时的构造顺序。通过具体的代码示例展示了不同构造部分的执行流程。
本文详细解析了Java中类的构造顺序,包括静态初始化代码块、构造代码块和构造方法的执行顺序,以及当存在父类和子类时的构造顺序。通过具体的代码示例展示了不同构造部分的执行流程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








