跑跑镇最近发生了一件大事,镇子郊外突然发现了一座金矿,这个爆炸性的新闻让镇上三位无业游民甲、乙、丙情绪价值瞬间拉满,终于可以告别每日泡面裹腹的艰难岁月了。不久,三位阶级兄弟摇身一变,成为了有稳定收入来源的黄金矿工,阶层直接从无产阶级跨越到了高级蓝领。新发现的金矿被跑跑镇收为国有资产,新成立的国营公司金矿跳动要开始开工前的准备工作了。公司在金矿附近选定了一块区域,命名为藏经阁。接着,在藏经阁内放置不同大小不同数量的箱子用来存放矿工们挖出来的金子,每种尺寸的箱子需要集中连续放置在一起,同时每种尺寸的箱子对于在藏经阁的放置位置有自己的要求和调性,如下图所示:
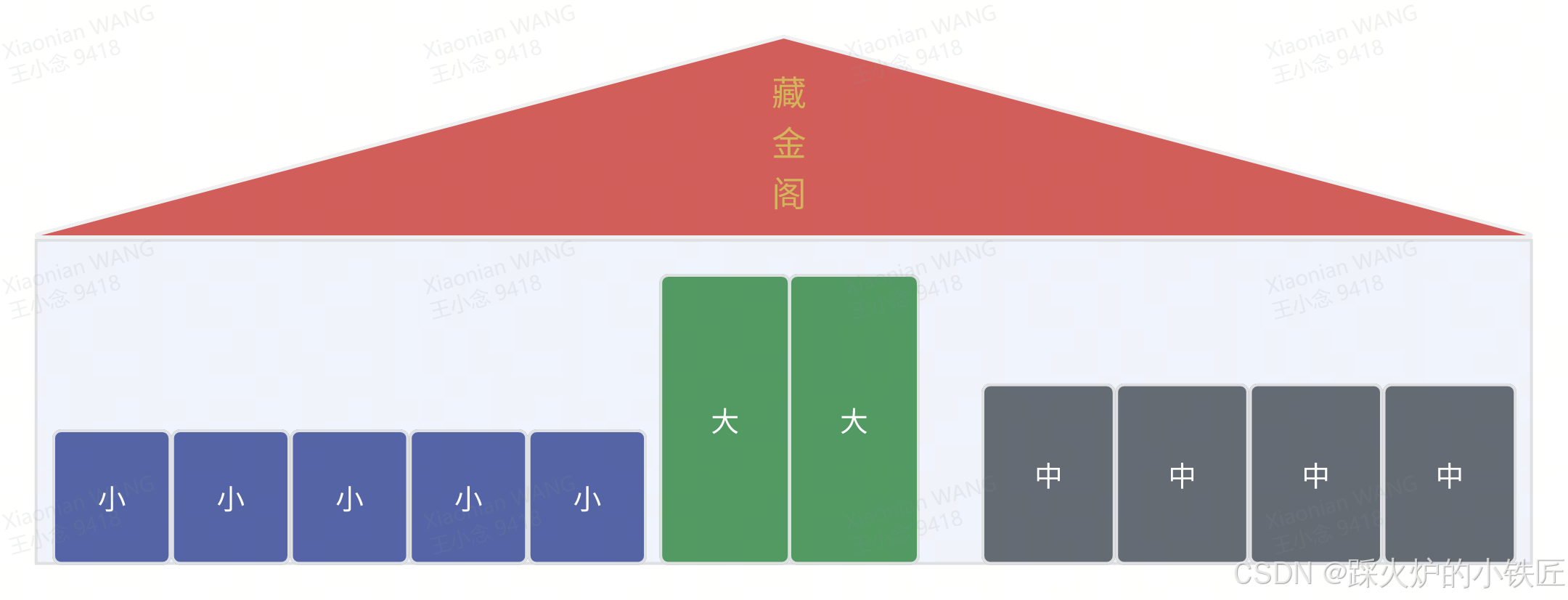
图1
公司首先会为每位矿工安排一次入职体检和心理调查问卷考试,主要考察每位矿工的身体素质和内卷程度,以此确定每位矿工每次挖矿的上限数量。每位矿工每次挖矿的数量不得大于这个规定值,防止身体超负荷运转造成不好的后果,带来失控的舆情。每次挖好矿后,矿工们需要在藏经阁找到一个合适大小的箱子将挖到的金子装进去。箱子的大小及对应的数量是公司根据大模型精准获取的。
所有的准备工作就绪后,为了满足不同尺寸箱子放置的选址要求并最终确认其地址,公司指派在内部有着火眼金睛美誉的悟空作为选址勘测员,并为悟空配备一辆地形车提高工作效率。出发前,悟空被告知了藏经阁的起始位置和大小,并被授予了三个锦囊,每个锦囊以天机相授,分别描述了每种箱子的尺寸、数目及对放置地址的要求。最后,悟空出发了,带着天机,带着任务,势在必得。
按照公司给的地址信息,悟空顺利找到了藏经阁的起始位置。悟空的目标是开车从起始位置出发,在到达藏经阁终点之前,不走回头路,沿途确定每个箱子的放置位置,边玩边把大事给办成了。现在开始作业,大致过程如下:
- 在起始位置图2 Start打开小锦囊,小尺寸箱子的尺寸M、数目N及放置位置要求一目了然,天机如此,so easy!现在出发了,开着开着,位置A正好满足要求,于是悟空将位置A标记为小箱子存放的起始位置,并从该位置开始,计算连续放置N个小尺寸箱子所需要的空间,即M × N,如果A + M × N的长度超过了藏经阁的终点位置,此次任务失败终止,因为藏经阁空间有限,放不下这么多个小箱子。
- 如果1中小尺寸箱子放置位置确认成功,悟空开车继续前进,开过M × N距离后,来到了位置B。在位置B上重复1中类似的步骤,拿出大锦囊并最终确定大尺寸箱子的起始位置C。
- 中尺寸箱子的放置位置最终也可以得到,记为E。
打开锦囊的顺序由公司在悟空出发时告知。
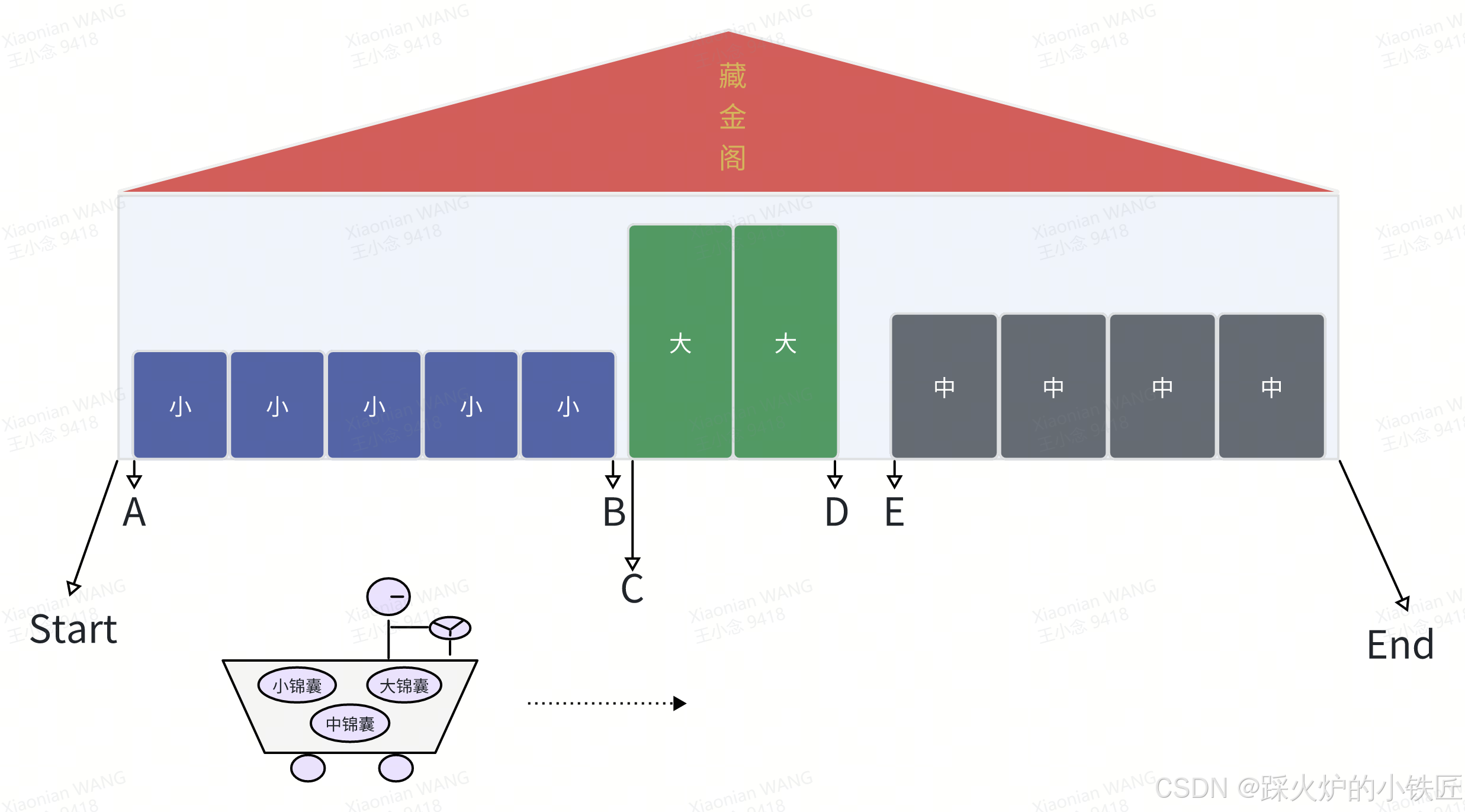
图 2
任务完成,3.75的绩效众望所归给到了悟空。
冰羚中BumpAllocator的作用类似开着小车给不同尺寸箱子寻找放置位置的悟空,用比较专业的话表述为,BumpAllocator的作用为在一段指定的内存空间上为特定对象指定构造的内存地址。
下面为实现代码分析:
class BumpAllocator final
{
public:
/// @brief c'tor
/// @param[in] startAddress of the memory this allocator manages
/// @param[in] length of the memory this allocator manages
BumpAllocator(void* const startAddress, const uint64_t length) noexcept; (4)
BumpAllocator(const BumpAllocator&) = delete;
BumpAllocator(BumpAllocator&&) noexcept = default;
BumpAllocator& operator=(const BumpAllocator&) noexcept = delete;
BumpAllocator& operator=(BumpAllocator&&) noexcept = default;
~BumpAllocator() noexcept = default;
/// @brief allocates on the memory supplied with the ctor
/// @param[in] size of the memory to allocate, must be greater than 0
/// @param[in] alignment of the memory to allocate
/// @return an expected containing a pointer to the memory if allocation was successful, otherwise
/// BumpAllocatorError
expected<void*, BumpAllocatorError> allocate(const uint64_t size, const uint64_t alignment) noexcept;
/// @brief mark the memory as unused
void deallocate() noexcept;
private:
uint64_t m_startAddress{0U}; (1)
uint64_t m_length{0U}; (2)
uint64_t m_currentPosition{0U}; (3)
};
(1)(2)(3)为BumpAllocator的私有成员变量,
其中:
m_startAddress
内存块的起始地址,对应藏经阁的起始位置,图2中Start
m_length
内存块的长度,对应藏经阁的大小,图2中(End - Start)
m_currentPosition
重新寻找空闲内存的相对位置,参考点为m_startAddress,对应悟空驾驶小车的出发位置和重新出发位置(图2中的Start - Start、B - Start、D - Start)
(4):BumpAllocator的构造函数,用内存块的起始地址和大小初始化BumpAllocator,赋值给对应的成员变量
allocate是BumpAllocator的核心函数,作用为根据对象的大小和地址对齐要求,在内存块中寻找符合要求的内存地址,在该地址可以构造该类型的对象。类似图2中A、C、E的寻找过程。
expected<void*, BumpAllocatorError> BumpAllocator::allocate(const uint64_t size, const uint64_t alignment) noexcept
{
if (size == 0)
{
IOX_LOG(WARN, "Cannot allocate memory of size 0.");
return err(BumpAllocatorError::REQUESTED_ZERO_SIZED_MEMORY);
}
const uint64_t currentAddress{m_startAddress + m_currentPosition}; (1)
uint64_t alignedPosition{align(currentAddress, alignment)}; (2)
alignedPosition -= m_startAddress;
void* allocation{nullptr};
const uint64_t nextPosition{alignedPosition + size};
if (m_length >= nextPosition) (3)
{
// AXIVION Next Construct AutosarC++19_03-A5.2.4 : required for low level memory management
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(cppcoreguidelines-pro-type-reinterpret-cast, performance-no-int-to-ptr)
allocation = reinterpret_cast<void*>(m_startAddress + alignedPosition);(4)
m_currentPosition = nextPosition; (5)
}
else
{
IOX_LOG(WARN,
"Trying to allocate additional " << size << " bytes in the memory of capacity " << m_length
<< " when there are already " << alignedPosition
<< " aligned bytes in use.\n Only " << m_length - alignedPosition
<< " bytes left.");
return err(BumpAllocatorError::OUT_OF_MEMORY);
}
return ok(allocation);
}
(1): 确定内存搜寻的起始位置
(2):确定满足地址对齐要求的地址
(3):确保在分配的地址上构造大小为size的对象不超过内存块的末端地址
(4):返回满足地址对齐要求和size大小的内存地址
(5):更新内存搜索的起始位置

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








