建立和设置Cookie的过程
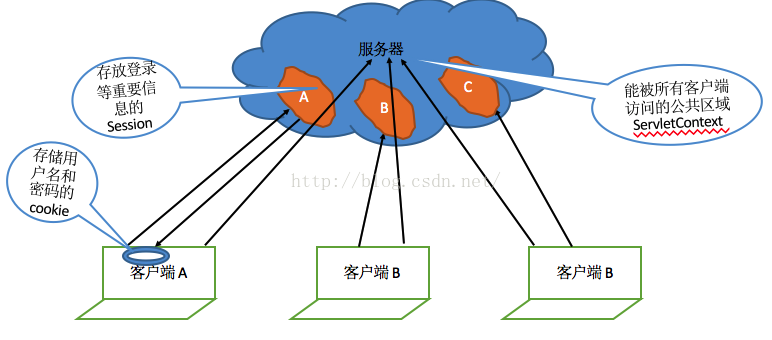
什么是Cookie
- Cookie是一小块嵌到Http请求和响应中的数据.
- Web服务器将cookie嵌入响应的头部,而浏览器的同一客户端则在以后的请求中都将在部携带同样的cookie
- Cookie由浏览器存在客户端,常为一个文本文件
- Cookie中添加与会话相关的内容,实现会话跟踪Cookie包含可选的注释、版本号及最长生命周期(如商城,超过30分钟,cookie失效。)
- Cooke的争议:可能暴露隐私,如你的账号名、密码每次保存在客户端,自动登录
为什么要使用cookie
- HTTP协议是无状态协议,客户端每一次访问都是一次新的连接
- 容器认为每一次连接都是新的客户,因此每一个客户端需要一个能够唯一标识自身的数据
如何在Servlet中建立Cookie
-
从Request请求体中提取所有Cookies
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); -
从Cookies数组中找到需要修改数据的Cookie
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){ if(cookie.getName().equals("cookieName") || cookie.getValue().equals("cookieValue")){ codes... } } -
若Cookie不存在则建立Cookie,并将Cookie放入Response体头部
if(cookie == null){ cookie = new Cookie("cookieName", "cookieValue"); cookie.setPath(request.getContextPath()); cookie.setMaxAge(-1);//表示当浏览器关闭时删除该cookie response.addCookie(cookie) }
以下是示例代码
public class CartServlet extends HttpServlet {
private Cookie cookie = null;
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); // 本句必须在获取输出流前
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();// 获取请求体中所有cookie
for(Cookie cookie : cookies){
if(cookie.getName().equals("visitTime")){
int visitTime = Integer.parseInt(cookie.getValue()) + 1;
cookie.setValue(Integer.toString(visitTime));
response.addCookie(cookie);//注意将修改后的cookie重新添加
this.cookie = cookie;
break;
}
}
if(this.cookie == null){
this.cookie = new Cookie("visitTime", "1");
this.cookie.setPath(request.getContextPath());
this.cookie.setMaxAge(-1);
response.addCookie(this.cookie);
}
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.println("<html>");
pw.println(
"<p>你购买了</p>"
+ request.getParameter("apple") + " 苹果"
+ "<br/>" + request.getParameter("banana") + " 香蕉"
+ "<br/>" + request.getParameter("grape") + " 葡萄"
);
pw.println("<p>这是你第 " + this.cookie.getValue() + " 次访问本页");
pw.println("</html>");
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}
Session建立和设置的过程
什么是Session
- 是一个基于Cookie或URL改写的高级会话状态跟踪接口。HttpSession接口,提供很多的方法,来自动进行会话跟踪,确保信息持续跨越多个用户连接
- 客户端需要接收、记忆和回送 Session的会话标识号,Session可以且通常是借助Cookie来传递会话标识号
如何理解Session
可以将Session看作一个Map<String, ObjectL>容器

Session的跟踪机制
-
Servlet API规范中定义了一个HttpSession接口,HttpSession接口定义了各种管理和操作会话状态的方法。
-
HttpSession对象是保持会话状态信息的存储结构,一个客户端在WEB服务器端对应一个各自的HttpSession对象。
-
WEB服务器并不会在客户端开始访问它时就创建HttpSession对象,只有客户端访问某个能与客户端开启会话的Servlet程序时,WEB应用程序才会创建一个与该客户端对应的HttpSession对象。
-
WEB服务器为HttpSession对象分配一个独一无二的会话标识号,然后在响应消息中将这个会话标识号传递给客户端。客户端需要记住会话标识号,并在后续的每次访问请求中都把这个会话标识号传送给WEB服务器,WEB服务器端程序依据回传的会话标识号就知道这次请求是哪个客户端发出的,从而选择与之对应的HttpSession对象
如何使用Session
-
获取Session
HttpSession session = request.getSession(); -
向Session添加/修改、获取、删除Attribute
//添加 第二个参数是Object型,可以进行强制转换 session.setAttribute(String name, Object val); //获取 HashMap hs = (HashMap)session.getAttribute(String name); //删除 session.removeAttribute(String name); -
Session的超时管理
有三种方式进行Session的销毁
-
在DD(Deployment Descriptor)中设置超时或setMaxInteractiveInterval()函数设置超时
<session-config> <session-timeout>15</session-timeout> </session-conifg> -
调用invalidate()销毁Session
-
web应用崩溃或反部署
-
示例代码
public class CartServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final String CART = "cart";
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
HashMap cart = (HashMap) session.getAttribute(CART);
//若cart不存在则将cart添加至session
if(cart == null){
cart = new HashMap();
cart.put("apple_count", "0");
cart.put("banana_count", "0");
cart.put("grape_count", "0");
session.setAttribute("cart", cart);
}
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String apple = request.getParameter("apple");
String banana = request.getParameter("banana");
String grape = request.getParameter("grape");
String apple_new = Integer.parseInt(apple) + Integer.parseInt(cart.get("apple_count") + "") + "";
String banana_new = Integer.parseInt(banana) + Integer.parseInt(cart.get("banana_count") + "") + "";
String grape_new = Integer.parseInt(grape) + Integer.parseInt(cart.get("grape_count") + "") + "";
cart.put("apple_count", apple_new);
cart.put("banana_count", banana_new);
cart.put("grape_count", grape_new);
//不要忘记将修改后的属性设置到session
session.setAttribute("cart", cart);
out.println("<html><head><title>购物车内容:</title></head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<h1>你的购物车里有<h1>");
out.println(apple_new + "斤苹果" + banana_new + "斤香蕉" + grape_new + "斤葡萄");
out.println("<hr>");
out.println("<a href=\""+response.encodeRedirectURL("index.jsp")+"\">回到水果店</a>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
out.close();
}
}
网站在线人数以及历史访问人数统计
什么是ServletContext
ServletContext 是一种服务器机制,ServletContext对象实现数据共享。WEB容器在启动时,它会为每个WEB应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表当前web应用。
为什么要使用ServletContext
- ServletContext保存所有客户端都能访问的数据
- 网站计数器
- 网站在线用户显示
- 简单的聊天系统,显示在线人数等
怎么使用ServletContext
- 获取ServletContext
ServletContext sc = (*).getServletContext();
- 插入/修改、删除、查找ServletContext中的属性
//与Session类似
sc.setAttribute(String name, Object var);
sc.getAttribute(String name);
sc.removeAttribute(String name);
- 从web.xml文件中读入Context-param
<!-- 假定web.xml中有如下Context-param -->
<!-- web.xml 中servlet上下文只能保存为String类型 -->
<context-param>
<param-name></param-name>
</context-param>
sc.getInitParameter(String name);
使用各种事件监听器
三种监听器
- ServletContextListener
- HttpSessionListener
- HttpSessionAttributeListener
三种监听事件
- ServletContextEvent
- HttpSessionEvent
- HttpSessionBindingEvent
常重写的7种监听方法
示例代码
@WebListener()
public class Listener implements ServletContextListener,
HttpSessionListener, HttpSessionAttributeListener {
// Public constructor is required by servlet spec
public Listener() {
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// ServletContextListener implementation
// -------------------------------------------------------
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
/* This method is called when the servlet context is
initialized(when the Web application is deployed).
You can initialize servlet context related data here.
*/
com.web.Util.File file = new File();
String name = (String) sce.getServletContext().getInitParameter("CounterFilePath");
String path = sce.getServletContext().getRealPath(name);
String history = file.readFile(path);
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("History", history);
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("Online", "0");
System.out.println("Attribute History Created -" + history + " Attribute Online Created");
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
/* This method is invoked when the Servlet Context
(the Web application) is undeployed or
Application Server shuts down.
*/
//将历史数重新写入count.txt文件
String history = (String) sce.getServletContext().getAttribute("History");
com.web.Util.File file = new File();
String name = (String) sce.getServletContext().getInitParameter("CounterFilePath");
String path = sce.getServletContext().getRealPath(name);
file.writeFile(path, history);
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// HttpSessionListener implementation
// -------------------------------------------------------
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
/* Session is created. */
System.out.println("New Session Created");
//当前online数加一
String online = (String) se.getSession().getServletContext().getAttribute("Online");
se.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("Online", Integer.parseInt(online) + 1 + "");
//历史人数加一
String history = (String) se.getSession().getServletContext().getAttribute("History");
se.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("History", Integer.parseInt(history) + 1 + "");
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
/* Session is destroyed. */
System.out.println("Session Destroyed");
//当前online数减一
String online = (String) se.getSession().getServletContext().getAttribute("Online");
se.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("Online", Integer.parseInt(online) - 1 + "");
}
// -------------------------------------------------------
// HttpSessionAttributeListener implementation
// -------------------------------------------------------
public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent sbe) {
/* This method is called when an attribute
is added to a session.
*/
}
public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent sbe) {
/* This method is called when an attribute
is removed from a session.
*/
}
public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent sbe) {
/* This method is invoked when an attibute
is replaced in a session.
*/
}
}








 本文详细介绍了Cookie、Session和ServletContext在JavaEE中的使用。讲解了Cookie的原理、设置过程以及可能涉及的隐私问题;Session的概念、会话跟踪机制以及管理方法;ServletContext的作用、数据共享方式以及如何利用监听器进行管理。通过示例代码加深理解。
本文详细介绍了Cookie、Session和ServletContext在JavaEE中的使用。讲解了Cookie的原理、设置过程以及可能涉及的隐私问题;Session的概念、会话跟踪机制以及管理方法;ServletContext的作用、数据共享方式以及如何利用监听器进行管理。通过示例代码加深理解。
















 445
445

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








