排序100
Problem
protal:排序100
Description
Enter an array of length n to rank him in ascending order. that is, for any adjacent two number a[i], a[i+1], a[i] ≤ \leq ≤ a[i+1]
Standard Input
The first line is an integer n, which indicates the length of the array.
Next n lines, each line an integer a[i], indicating the contents of the array.
Standard Output
The first line of the Output indicates the length of the array.
The next n lines indicate the sort result.
Constraints
1
≤
\leq
≤ n
≤
\leq
≤ 100
1
≤
\leq
≤ a[ j ]
≤
\leq
≤ 109
Sample
Input
4
4
3
1
2
Output
4
1
2
3
4
Solution
Bubble Sort
pseudocode form Aizu OJ
BubbleSort(A)
for i = 0 to A.length-1
for j = A.length-1 downto i+1
if A[j] < A[j-1]
swap A[j] and A[j-1]
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i, j;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
int temp;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = n - 1; j > i; j--)
{
if (a[j] < a[j - 1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j-1];
a[j-1] = temp;
}
}
}
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}

Insertion sort
pseudocode from wikipedia
i ← 1
while i < length(A)
j ← i
while j > 0 and A[j-1] > A[j]
swap A[j] and A[j-1]
j ← j - 1
end while
i ← i + 1
end while
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i, j, temp;
cin >> n;
cin >> a[0];
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> temp;
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (temp >= a[j])
{
a[j + 1] = temp;
break;
}
else
{
a[j + 1] = a[j];
continue;
}
}
if (j == -1)
a[0] = temp;
}
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}

Section sort
pseudocode from Aizu OJ
SelectionSort(A)
for i = 0 to A.length-1
mini = i
for j = i to A.length-1
if A[j] < A[mini]
mini = j
swap A[i] and A[mini]
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i, j;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
// Setion sort
int mini, temp;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
mini = i;
for (j = i; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[j] < a[mini])
mini = j;
}
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[mini];
a[mini] = temp;
}
// Output
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
Java
// Section Sort
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Sort100 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n, i, j;
int[] a = new int[100];
n = cin.nextInt();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = cin.nextInt();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int mini = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[mini])
mini = j;
}
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[mini];
a[mini] = temp;
}
System.out.println(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}
Shell Sort
pseudocode form Aizu OJ slightly modified
insertionSort(A, n, g)
for i = g to n-1
v = A[i]
j = i - g
while j >= 0 && A[j] > v
A[j+g] = A[j]
j = j - g
A[j+g] = v
shellSort(A, n)
m = ?
G[] = {?, ?,..., ?}
for i = 0 to m-1
insertionSort(A, n, G[i])
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i, j;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
int g, v;
for (g = n / 2; g > 0; g = g / 2)
{
for (i = g; i < n; i++)
{
v = a[i];
for (j = i - g; j >= 0 && a[j] > v; j -= g)
a[j + g] = a[j];
a[j + g] = v;
}
}
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
Merge Sort
pseudocode from Aizu OJ
Merge(A, left, mid, right)
n1 = mid - left;
n2 = right - mid;
create array L[0...n1], R[0...n2]
for i = 0 to n1-1
do L[i] = A[left + i]
for i = 0 to n2-1
do R[i] = A[mid + i]
L[n1] = SENTINEL
R[n2] = SENTINEL
i = 0;
j = 0;
for k = left to right-1
if L[i] <= R[j]
then A[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
else A[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
Merge-Sort(A, left, right){
if left+1 < right
then mid = (left + right)/2;
call Merge-Sort(A, left, mid)
call Merge-Sort(A, mid, right)
call Merge(A, left, mid, right)
cpp
// Program name: Merge Sort
// Written by: by_sknight
// Date: 2019/3/12
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
void merge(int A[], int left, int mid, int right);
void mergeSort(int A[], int left, int right);
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
mergeSort(a, 0, n); // 直接调用合并排序
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
void mergeSort(int A[], int left, int right)
{
// 当被拆分到仅剩余一个元素时, 不需要拆分
if (right - left <= 1)
return;
// 递归调用继续拆分
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSort(A, left, mid); // 拆分左边并排序左边, 注意, 不会处理下标为mid的元素
mergeSort(A, mid, right); // 拆分右边并排序右边, 会处理下标为mid的元素
merge(A, left, mid, right); // 合并两个相邻的已排序数组
return;
}
void merge(int A[], int left, int mid, int right)
{
int i, j, k;
// 统计左右数组的长度
int n1, n2;
n1 = mid - left;
n2 = right - mid;
// 分配临时空间存储左右数组内容, 并在末尾添加哨兵INT_MAX
int L[n1 + 1], R[n2 + 1];
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = A[left + i];
L[i] = INT_MAX;
for (i = 0; i < n2; i++)
R[i] = A[mid + i];
R[i] = INT_MAX;
// 比较左右数组, 较小的扔前面
i = 0, j = 0;
for (k = left; k < right; k++)
{
if (L[i] < R[j])
{
A[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
A[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
}
return;
}
reward
if you want to use INT_MAX, you need #include <climits>
Quick Sort(Simple)
pseudocode from wikipedia
function quicksort(q)
{
var list less, pivotList, greater
if length(q) ≤ 1
return q
else
{
select a pivot value pivot from q
for each x in q except the pivot element
{
if x < pivot then add x to less
if x ≥ pivot then add x to greater
}
add pivot to pivotList
return concatenate(quicksort(less), pivotList, quicksort(greater))
}
cpp
// Program name: Quick Sort (simple)
// Written by: by_sknight
// Date: 2019/3/12
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void quickSort(int A[], int length);
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
quickSort(a, n);
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
void quickSort(int A[], int length)
{
// 当待排序数组长度为1时, 视为已排序数组
if (length <= 1)
return;
int i;
int pivot = A[0]; // 就以首元素作为基准值
// 开辟额外的空间存储基准值两边的值
int less[length], greater[length], lessNum = 0, greaterNum = 0;
for (i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
if (A[i] < pivot)
{
less[lessNum] = A[i];
lessNum++;
}
else
{
greater[greaterNum] = A[i];
greaterNum++;
}
} // 分配完毕
quickSort(less, lessNum);
quickSort(greater, greaterNum);
// 将小于基准, 基准, 大于基准的所有数组装起来
for (i = 0; i < lessNum; i++)
A[i] = less[i];
A[lessNum] = pivot;
for (i = 0; i < greaterNum; i++)
A[lessNum + 1 + i] = greater[i];
return;
}
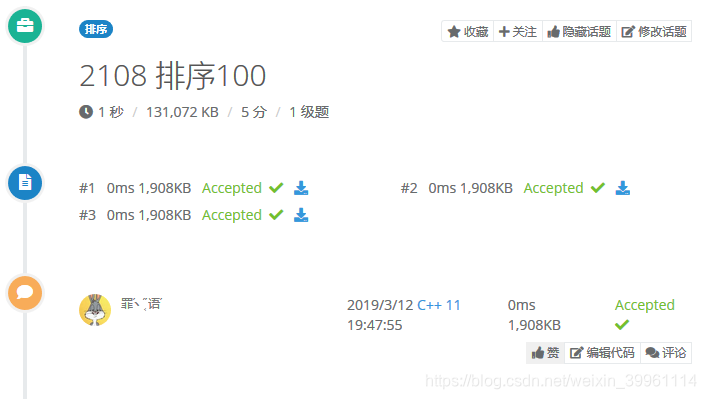
Quick Sort (in-place)
pseudocode from wikipedia
function partition(a, left, right, pivotIndex)
{
pivotValue := a[pivotIndex]
swap(a[pivotIndex], a[right]) // 把pivot移到結尾
storeIndex := left
for i from left to right-1
{
if a[i] < pivotValue
{
swap(a[storeIndex], a[i])
storeIndex := storeIndex + 1
}
}
swap(a[right], a[storeIndex]) // 把pivot移到它最後的地方
return storeIndex
}
procedure quicksort(a, left, right)
if right > left
select a pivot value a[pivotIndex]
pivotNewIndex := partition(a, left, right, pivotIndex)
quicksort(a, left, pivotNewIndex-1)
quicksort(a, pivotNewIndex+1, right)
cpp
// program name: quick sort (in-place)
// Written by: by_sknight
// Date: 2019/3/13
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void qsort(int A[], int left, int right);
void swap(int &a, int &b);
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
qsort(a, 0, n);
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
void qsort(int A[], int left, int right)
{
if (right - left <= 1)
return;
int i, sotreIndex;
int pivot = A[right - 1];
for (i = left, sotreIndex = left; i < right - 1; i++)
{
if (A[i] < pivot)
{
swap(A[i], A[sotreIndex]);
sotreIndex++;
}
}
swap(A[right - 1], A[sotreIndex]);
qsort(A, left, sotreIndex);
qsort(A, sotreIndex + 1, right);
}
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
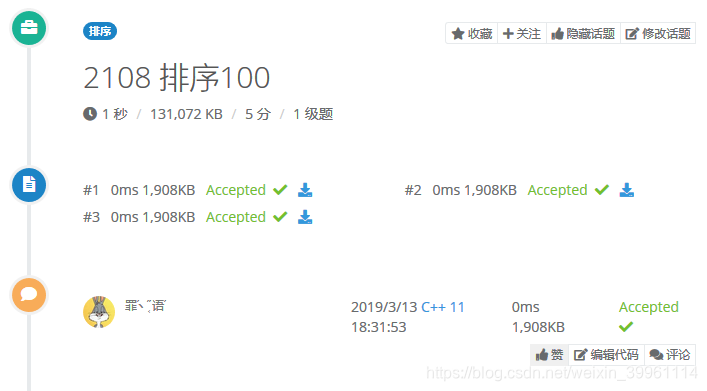
Heap Sort
pseudocode from 《编程珠玑》第2版 修订版
void siftup(n)
pre n > 0 && heap(1, n-1)
post heap(1, n)
i = n
loop
/* invariant: heap(1, n) except perhaps
between i and its parent */
if i == 1
break
p = i / 2
if x[p] <= x[i]
break
swap(p, i)
i = p
void siftdown(n)
pre heap(2, n) && n >= 0
post heap(1, n)
i = 1
loop
/* invatiant: heap(1, n) except perhaps between
i and its (0, 1 or 2) children */
c = 2*i
if c > n
break
/* c is the left child of i */
if c+1 <= n
/* c+1 is the right child of i */
if x[c+1] < x[c]
c++
/* c is the lesser child of i */
if x[i] <= x[c]
break
swap(c, i)
i = c
cpp
// Program name: Heap sort
// Written by: by_sknight
// Date: 2019/3/13
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int &a, int &b);
int main(void)
{
int n, a[100], i, j, heapSize;
cin >> n;
cin >> a[0];
heapSize = 1;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
heapSize++;
// sift up
j = i;
while (j != 0 && a[(j-1)/2] < a[j]) // 当存在父节点且父节点小于子节点
{
swap(a[j], a[(j-1)/2]);
j = (j - 1) / 2;
}
}
// 此时大根堆已经创建完毕
while (heapSize != 1)
{
swap(a[0], a[heapSize-1]);
heapSize--;
// sift down
i = 0;
while (2*i+1 < heapSize) // 当存在子节点
{
if (2*i+2 < heapSize) // 存在左右子节点, 选择最大的交换, 如果子节点小于该节点, 则该堆已排序
{
if (a[2*i+1] >= a[2*i+2] && a[2*i+1] > a[i])
{
swap(a[2*i+1], a[i]);
i = 2*i+1;
}
else if (a[2*i+1] < a[2*i+2] && a[2*i+2] > a[i])
{
swap(a[2*i+2], a[i]);
i = 2*i+2;
}
else
break;
}
else // 只有左子节点
{
if (a[2*i+1] > a[i]) // 左子节点更大时交换
{
swap(a[2*i+1], a[i]);
i = 2*i+1;
}
else // 该堆已排序
break;
}
}
}
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
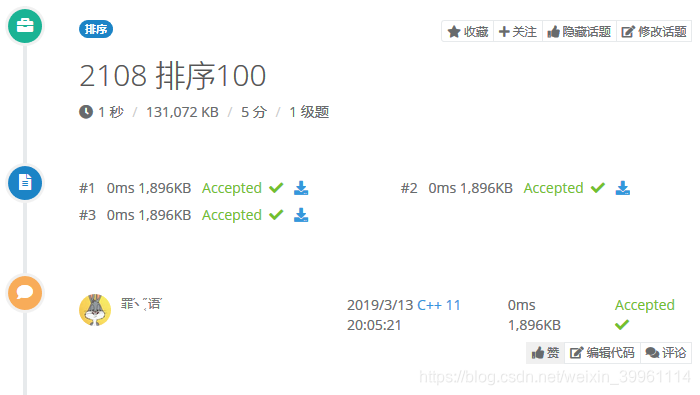
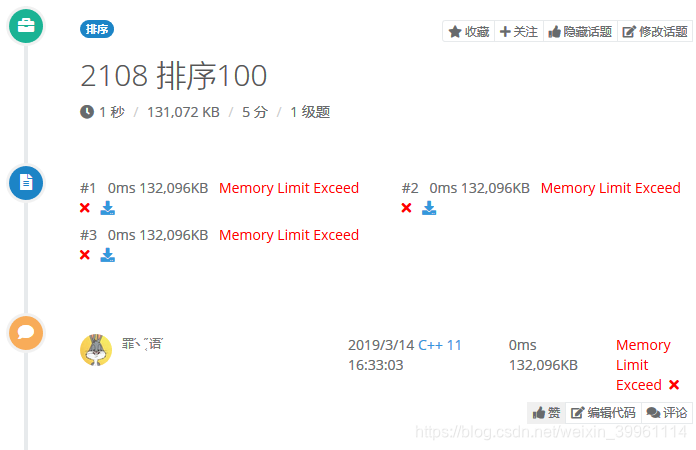
Count Sort
description
Count Sorting is suitable for arrays with small data ranges and high densities, so the submission of this question did not pass.
cpp
// program name: countSort
// Written by: by_sknight
// Date: 2018/3/14
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int n, *arr, *count, i, j, max = 0;
cin >> n;
arr = new int[n];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> arr[i];
if (arr[i] > max)
max = arr[i];
}
count = new int[max + 1];
// 初始化计数数组
for (i = 0; i < max + 1; i++)
count[i] = 0;
// 统计数量
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[arr[i]]++;
// 按照从小到大的顺序存到原数组
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++)
{
while (count[j] == 0)
j++;
arr[i] = j;
count[j]--;
}
cout << n << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}





 这篇博客介绍了排序100问题,包括输入输出格式和约束条件,并详细探讨了八种不同的排序算法:冒泡排序、插入排序、部分排序、希尔排序、归并排序、简单快速排序、原地快速排序和堆排序。每种算法都提供了伪代码和对应的C++实现。此外,还提及了计数排序,但由于其适用范围限制,该问题未采用。
这篇博客介绍了排序100问题,包括输入输出格式和约束条件,并详细探讨了八种不同的排序算法:冒泡排序、插入排序、部分排序、希尔排序、归并排序、简单快速排序、原地快速排序和堆排序。每种算法都提供了伪代码和对应的C++实现。此外,还提及了计数排序,但由于其适用范围限制,该问题未采用。
















 715
715

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








