接上篇文章:类的本质和底层实现,我们今天说一下类的缓存!
- 先看一下上篇中类的结构图:

- 在图中,我们看到 cache_t cache ,这是一个结构体,就是我们要说的缓存!那么我们的类在缓存里面存了些什么东西呢?
接下来我们探索一下
- 当然先来看一看cache_t结构:
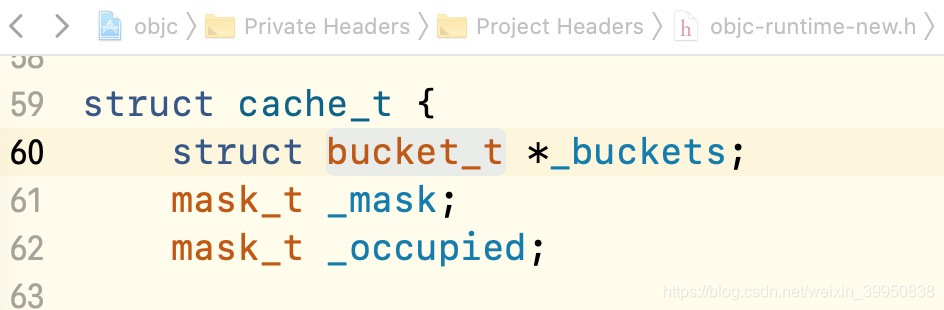
- 在 cache_t 中有两种类型, bucket_t 和 mask_t ,我们在看一下这两个是怎么定义的:
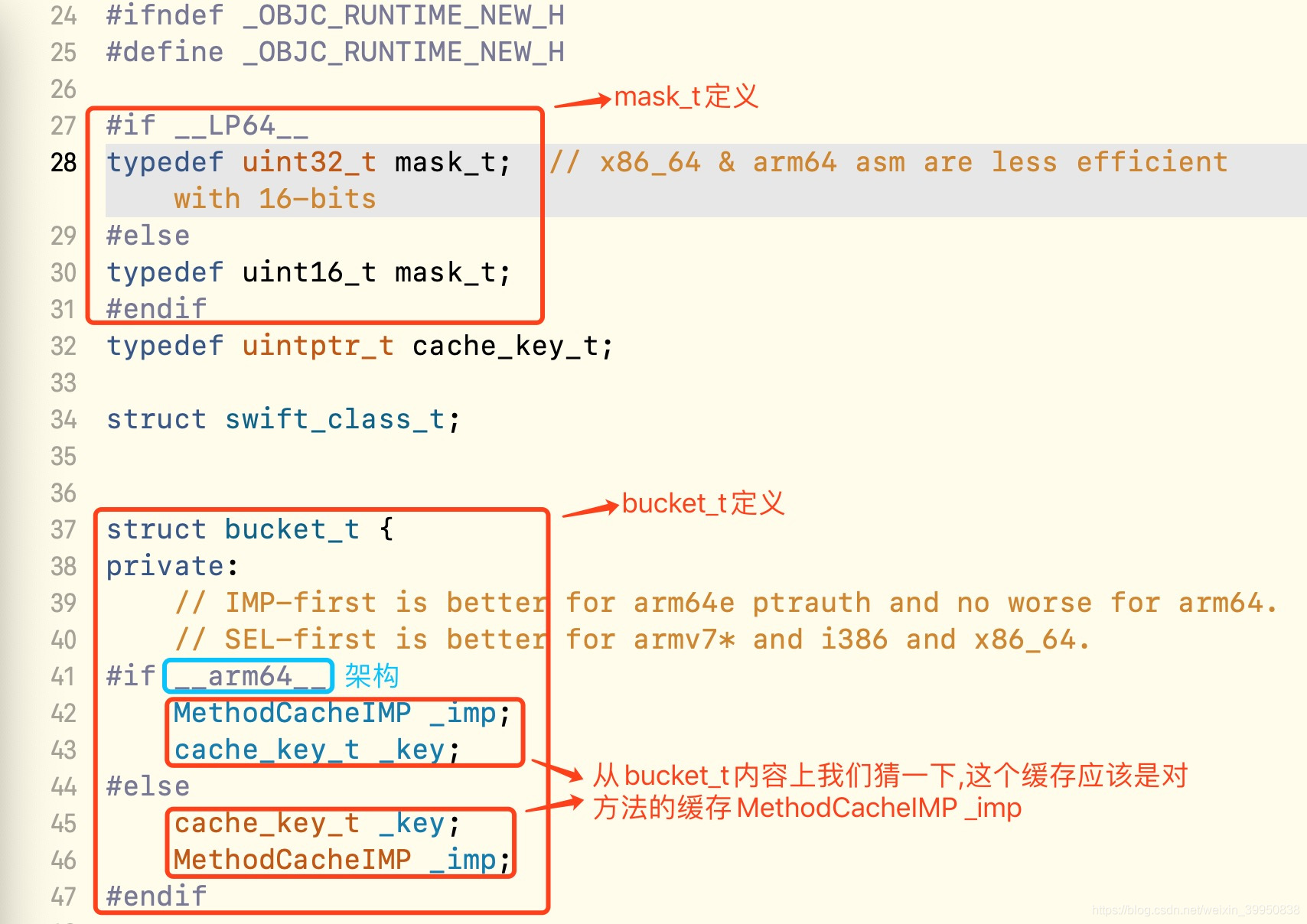

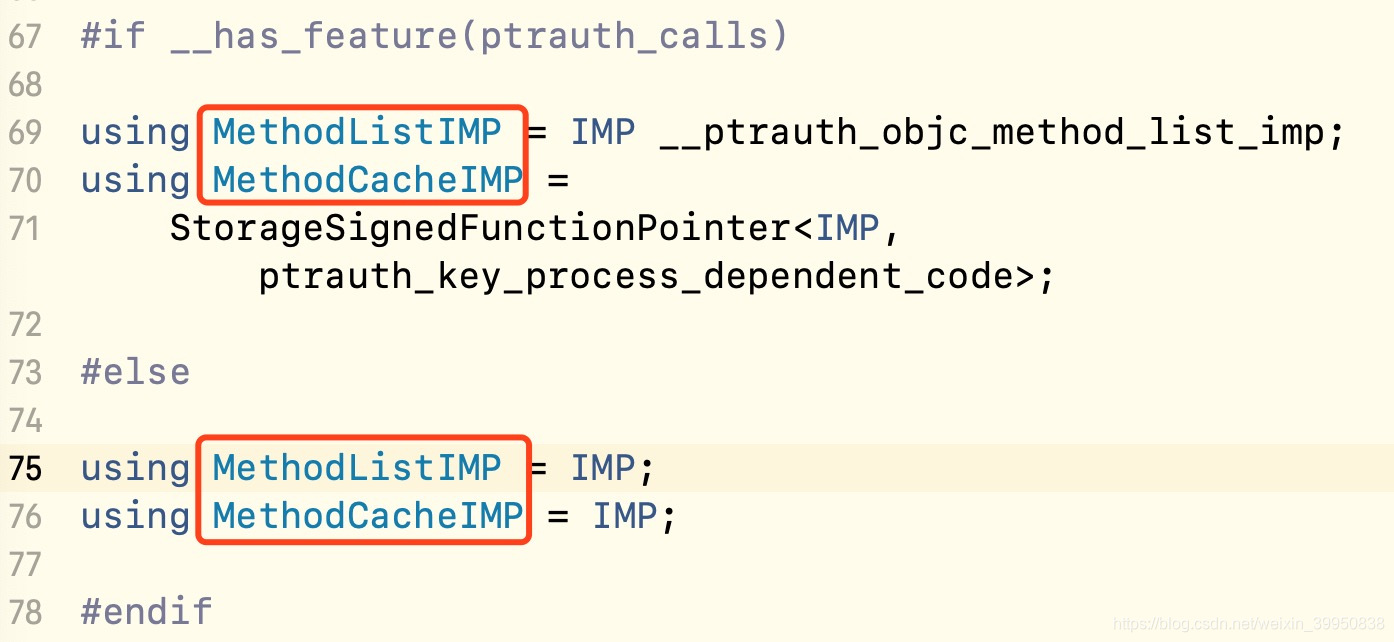
- 从上面的图中,我们看到,根据架构,不同里面存的是_imp和_key,这里面缓存的应该是方法!
- 在iOS Runtime详解—源码分析中,我们知道,消息发送过程中,首先调用的是快速查找的方法,就是从缓存中去找sel对应的imp,找到直接返回!另外一种方法,就是从类、父类、元类、根元类、再到NSObject中查找sel对应的imp,找到之后进行cache_fill,也就是填充到缓存中的操作,并且返回imp!如果这些都找不到就会进行动态方法决议进行消息转发的流程!
下面我们来验证一下cache_t是不是缓存了这些方法:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
WMPerson *person = [[WMPerson alloc] init];
Class pClass = [WMPerson class];
[person look];
[person say];
[person walk];
[person run];
[WMPerson jump];//类方法
NSLog(@"%@ - %p",person,pClass);
}
return 0;
}
/*
断点在[person walk];然后我们lldb打印:
*/
(lldb) x/4gx pClass
0x100002498: 0x001d800100002471 0x0000000100b37140
0x1000024a8: 0x0000000100ff9bf0 0x0000000300000003
(lldb) p (cache_t *)0x1000024a8 //0x1000024a8 cache_t的内存首地址
(cache_t *) $1 = 0x00000001000024a8
(lldb) p *$1
(cache_t) $2 = {
_buckets = 0x0000000100ff9bf0
_mask = 3
_occupied = 3
}
(lldb) p $2._buckets
(bucket_t *) $3 = 0x0000000100ff9bf0
(lldb) p *$3
(bucket_t) $4 = {
_key = 140734683087864
_imp = 0x00000001000019a0 (LGTest`-[WMPerson look] at WMPerson.m:12)
}
/*
我们打印到bucket_t获取到了缓存
(bucket_t) $4 = {
_key = 140734683087864
_imp = 0x00000001000019a0 (LGTest`-[WMPerson look] at WMPerson.m:12)
}
但是还是没有看到其他方法的缓存!
断点走到[person run]所在行
重新进行打印
*/
(lldb) p (cache_t *)0x1000024a8
(cache_t *) $6 = 0x00000001000024a8
(lldb) p *$6
(cache_t) $7 = {
_buckets = 0x0000000102200270
_mask = 7
_occupied = 1
}
(lldb) p $7._buckets
(bucket_t *) $8 = 0x0000000102200270
(lldb) p *$8
(bucket_t) $9 = {
_key = 0
_imp = 0x0000000000000000
}
/*
我们看到结果:
cache_t结构体中只有改变_mask : 3 -> 7 _occupied : 3 -> 1
(cache_t) $7 = {
_buckets = 0x0000000102200270
_mask = 7
_occupied = 1
}
但是打印的bucket_t:
(bucket_t) $9 = {
_key = 0
_imp = 0x0000000000000000
}
变为了空!
*/
我们知道了我们的类在调用方法之后是做了缓存的,但是具体的一个缓存的原理我们还是不知道的,那么要知道原理,就要先知道有关cache缓存的一个流程,我们搜索cache慢慢查找(比较笨,因为我也不知道在哪)或者通过汇编


-
在这个方法处添加断点,运行objc项目,我们确实猜的没错,程序被断在这里!
void cache_fill(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver) { //首先来到这个方法cache_fill缓存填充 #if !DEBUG_TASK_THREADS //这个宏定义调试使用 mutex_locker_t lock(cacheUpdateLock); //跳转到下面的方法进行缓存的设置 cache_fill_nolock(cls, sel, imp, receiver); #else _collecting_in_critical(); return; #endif } static void cache_fill_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver) { cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked(); // Never cache before +initialize is done if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;//如果cls不存在,那就没有cache缓存,就没必要在查找,直接返回 // Make sure the entry wasn't added to the cache by some other thread // before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock. //确保在获取cacheUpdateLock之前,imp没有被其他线程添加到缓存中. //再次检查获取缓存 if (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return; //根据cls获取对应的缓存cache_t数组 cache_t *cache = getCache(cls); cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);//cache_key_t类型为unsigned long // Use the cache as-is if it is less than 3/4 full //如果缓存不足3/4,则按原样使用缓存 //occupied() + 1 这里加一,是因为系统没有防止内存溢出 //没有将缓存大小设置到100%,在赋值的时候进行了减一! mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1; mask_t capacity = cache->capacity(); if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache()) { // 如果cache是空,则给初始化值4 //INIT_CACHE_SIZE : 4 //enum { //INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 2, //INIT_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2) //}; cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE); } else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3) { // Cache is less than 3/4 full. Use it as-is. //缓存小于3/4,不进行扩容. } else { // Cache is too full. Expand it. //缓存已满,扩容! cache->expand(); } // Scan for the first unused slot and insert there. // There is guaranteed to be an empty slot because the // minimum size is 4 and we resized at 3/4 full. //这里说明此时插入缓存是肯定不会内存溢出的 //因为我们判断的是申请内存大小的3/4 //此时缓存扩容前的调用方法,之前缓存的方法已经被清空 //缓存里面只有一个方法 bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver); if (bucket->key() == 0) cache->incrementOccupied(); bucket->set(key, imp); } mask_t cache_t::capacity() { return mask() ? mask()+1 : 0; } void cache_t::expand() { cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked(); uint32_t oldCapacity = capacity();//获取旧的缓存大小 //缓存扩大到原来的两倍!!!! uint32_t newCapacity = oldCapacity ? oldCapacity*2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; if ((uint32_t)(mask_t)newCapacity != newCapacity) { // mask overflow - can't grow further // fixme this wastes one bit of mask newCapacity = oldCapacity; } reallocate(oldCapacity, newCapacity); } /* 扩容设置 */ void cache_t::reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity) { //扩容时,若果cache不是空: //bool cache_t::canBeFreed(){return !isConstantEmptyCache();} //则需要释放旧的缓存 bool freeOld = canBeFreed(); bucket_t *oldBuckets = buckets(); bucket_t *newBuckets = allocateBuckets(newCapacity);//创建新的bucket assert(newCapacity > 0); assert((uintptr_t)(mask_t)(newCapacity-1) == newCapacity-1); //newCapacity - 1是为了防止大小超过百分之百 //我们看到了这里的减1! setBucketsAndMask(newBuckets, newCapacity - 1); //释放旧的缓存 if (freeOld) { cache_collect_free(oldBuckets, oldCapacity); cache_collect(false); } } bucket_t * cache_t::find(cache_key_t k, id receiver) { assert(k != 0); bucket_t *b = buckets();//获取buckets数组 mask_t m = mask(); // 通过cache_hash哈希函数和参数cache_key_t&mask_t //计算出开始查找的位置, //begin用来记录查询起始索引 mask_t begin = cache_hash(k, m); // begin 赋值给 i,用于切换索引 mask_t i = begin; do { if (b[i].key() == 0 || b[i].key() == k) { //用索引i从散列表取值 //如果取出来的bucket_t的key = k,则查询成功,返回该bucket_t, //如果key = 0,说明在索引i的位置上还没有缓存过方法 //同样需要返回该bucket_t,用于中止缓存查询. return &b[i]; } } while ((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin); // while条件判断相当于 i = i-1,回到上面do循环里面 //相当于查找散列表上一个单元格里面的元素,再次进行key值 k的比较, //当i=0时,也就是i指向散列表最首个元素索引的时候重新将mask赋值给i,使其指向散列表最后一个元素,重新开始反向遍历散列表, //其实就相当于绕圈,把散列表头尾连起来 //从begin值开始,递减索引值,当走过一圈之后,必然会重新回到begin值 //如果此时还没有找到key对应的bucket_t,或者是空的bucket_t,则循环结束 //说明查找失败,调用bad_cache方法. Class cls = (Class)((uintptr_t)this - offsetof(objc_class, cache)); cache_t::bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)k, cls); } /** 上面步骤中,我们如果没有缓存,首先开辟缓存控件,开辟缓存控件大小为4 当我们调用方法过程中,如果缓存内容大于缓存的3/4,就会开启扩容:expand() 将内存容量扩大为原来的2倍,并且将之前的缓存清空(为了快) 当扩容操作完成后,会进行一项操作,就是将扩容前调用的方法存到缓存中 这个存储的顺序并不是按照数组那样顺序存储,而是根据哈希算法生成的索引进行缓存 */
下面我们通过代码断点去验证这个过程:

-
打印:
(lldb) x/4gx pClass 0x1000013f8: 0x001d8001000013d1 0x0000000100b36140 0x100001408: 0x0000000100f502a0 0x0000000100000007 (lldb) p (cache_t *)0x100001408 (cache_t *) $1 = 0x0000000100001408 (lldb) p *$1 (cache_t) $2 = { _buckets = 0x0000000100f502a0 _mask = 7 _occupied = 1 } (lldb) p $2._buckets (bucket_t *) $4 = 0x0000000100f502a0 (lldb) p $4[0] //正好存在了索引0的位置 (bucket_t) $6 = { _key = 4294971016 _imp = 0x0000000100000b10 (LGTest`-[WMPerson walk] at WMPerson.m:20) } (lldb) p $4[1] //下面1-7均为空,之前的缓存被清空,扩容之后只缓存了walk方法,其他均为0 (bucket_t) $5 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[2] (bucket_t) $7 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[3] (bucket_t) $8 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[4] (bucket_t) $9 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[5] (bucket_t) $10 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[6] (bucket_t) $11 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[7] (bucket_t) $12 = { _key = 0 _imp = 0x0000000000000000 } (lldb) p $4[8] //此处打印野指针了 (bucket_t) $13 = { _key = 1 _imp = 0x0000000100f502a0 (0x0000000100f502a0) }
类的缓存缓存了调用过程中的一些方法,并且在缓存过程中动态的改变缓存大小,并清空扩容前的缓存数据(为了快,如果保存之前的,需要哈希值的一个映射过程,比较慢),缓存最新调用的方法!





 本文深入探讨iOS Runtime中类的缓存机制,解析cache_t结构体如何存储方法的_imp和_key,以及缓存填充、扩容和哈希算法在动态调整缓存大小中的作用。
本文深入探讨iOS Runtime中类的缓存机制,解析cache_t结构体如何存储方法的_imp和_key,以及缓存填充、扩容和哈希算法在动态调整缓存大小中的作用。
















 1314
1314

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








