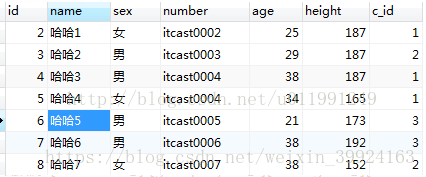
——数据库是mysql,使用的数据库表名称是my_student.
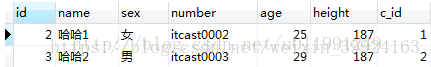
表的完整数据信息是:
select完整的语法语句为:
Select [select选项] 字段列表[字段别名]/* from 数据源 [where 字句] [group by子句 ][having 子句][order by 子句][limit 子句];- [select选项]:all(所有,默认), distinct(去重) 。其中distinct针对的是查询结果的整条记录而言的。
select distinct(sex) from my_student; 
select DISTINCT(sex),name from my_student; //select distinct sex,name from my_student 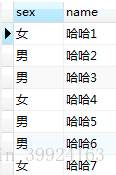
2. [where字句]:where是唯一一个从磁盘开始拿数据的时候就开始进行判断的条件,从磁盘取出一条记录,开始进行where判断,判断结果如果成立,那么取出结果保存到内存,否则放弃。
select * from my_student where name='哈哈1';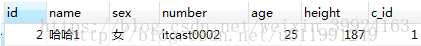
3. [group子句]:分组子句,group by子句主要的作用是分组,从而进行统计操作,而不是为了展示(展示的时候,只会展示分组记录的第一条记录),分组时,一般会结合使用count()、max()、min()、avg()、sum()函数。
- 单字段分组:my_student表以c_id进行分组,然后显示分组后的每组的c_id名称、每组的总数、每组的最高、最低、平均身高和每组的年龄总和。
select c_id, count(*), max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) group by c_id;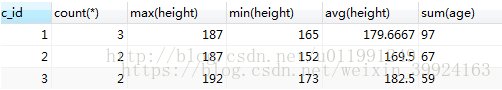
- 多字段分组:对整个表先按照c_id进行分组,然后在此分组的基础之上,然后每组再按照sex,进行分组。
select c_id,sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age)from my_student group by c_id ,sex;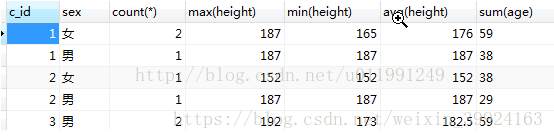
- 多字段分组(加上显示每组的某一字段的所有数据):
selectc_id,sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) ,GROUP_CONCAT(name)from my_student group by c_id ,sex;
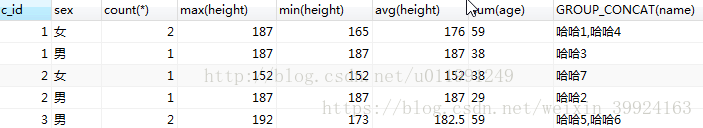
4. [having语句]:having的作用和where相似,而且where能做的事,having基本上都能做,但是having能做where很多做不了的事情。主要是因为where只能在磁盘上提取数据对数据进行操作;而在内存中对数据进行group by分组后再进行的操作只能用having了。
select c_id,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) from my_studentgroup by c_id having COUNT(*) >= 3;
5. [order by子句] 对数据进行排序操作,根据某个字段进行升序或者降序排序。(进行多字段排序的时候,先根据某一字段进行潘旭,然后在排序好的内部再按照某字段进行排序)
- 单个字段的排序
select * from my_student order by c_id;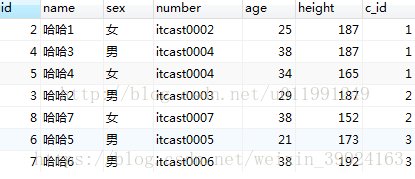
- 多字段排序
select * from my_student order by c_id,sex;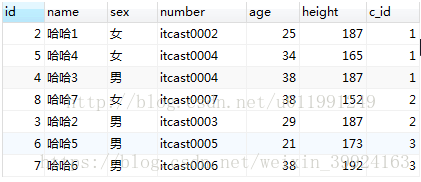
6. [limit子句]限制结果的数量 Limit 偏移量 记录条数;
select * from my_student limit 2;
7. 删除语句。
delete用于删除表中的行,用法:
delete from 表名称 where 列名称 = 值删除表中的名字为“哈哈5”这一行
delete from my_student were name="哈哈5”删除所有行:
即在不删除表的情况下,删除所有行,这意味着表的结构、属性和索引都是完整的。
delete from tablename
//delete *from tablename——数据库是mysql,使用的数据库表名称是my_student.
表的完整数据信息是:

select完整的语法语句为:
Select [select选项] 字段列表[字段别名]/* from 数据源 [where 字句] [group by子句 ][having 子句][order by 子句][limit 子句];- [select选项]:all(所有,默认), distinct(去重) 。其中distinct针对的是查询结果的整条记录而言的。
select distinct(sex) from my_student; 
select DISTINCT(sex),name from my_student; //select distinct sex,name from my_student 
2. [where字句]:where是唯一一个从磁盘开始拿数据的时候就开始进行判断的条件,从磁盘取出一条记录,开始进行where判断,判断结果如果成立,那么取出结果保存到内存,否则放弃。
select * from my_student where name='哈哈1';
3. [group子句]:分组子句,group by子句主要的作用是分组,从而进行统计操作,而不是为了展示(展示的时候,只会展示分组记录的第一条记录),分组时,一般会结合使用count()、max()、min()、avg()、sum()函数。
- 单字段分组:my_student表以c_id进行分组,然后显示分组后的每组的c_id名称、每组的总数、每组的最高、最低、平均身高和每组的年龄总和。
select c_id, count(*), max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) group by c_id;
- 多字段分组:对整个表先按照c_id进行分组,然后在此分组的基础之上,然后每组再按照sex,进行分组。
select c_id,sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age)from my_student group by c_id ,sex;
- 多字段分组(加上显示每组的某一字段的所有数据):
selectc_id,sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) ,GROUP_CONCAT(name)from my_student group by c_id ,sex;

4. [having语句]:having的作用和where相似,而且where能做的事,having基本上都能做,但是having能做where很多做不了的事情。主要是因为where只能在磁盘上提取数据对数据进行操作;而在内存中对数据进行group by分组后再进行的操作只能用having了。
select c_id,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(height),sum(age) from my_studentgroup by c_id having COUNT(*) >= 3;
5. [order by子句] 对数据进行排序操作,根据某个字段进行升序或者降序排序。(进行多字段排序的时候,先根据某一字段进行潘旭,然后在排序好的内部再按照某字段进行排序)
- 单个字段的排序
select * from my_student order by c_id;
- 多字段排序
select * from my_student order by c_id,sex;
6. [limit子句]限制结果的数量 Limit 偏移量 记录条数;
select * from my_student limit 2;

7. 删除语句。
delete用于删除表中的行,用法:
delete from 表名称 where 列名称 = 值删除表中的名字为“哈哈5”这一行
delete from my_student were name="哈哈5”删除所有行:
即在不删除表的情况下,删除所有行,这意味着表的结构、属性和索引都是完整的。
delete from tablename
//delete *from tablename



 本文详细介绍了MySQL数据库中SELECT语句的各种用法,包括去重、条件筛选、分组统计、排序及结果限制等,帮助读者掌握高效的数据查询技能。
本文详细介绍了MySQL数据库中SELECT语句的各种用法,包括去重、条件筛选、分组统计、排序及结果限制等,帮助读者掌握高效的数据查询技能。
















 46万+
46万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








