
spring是一个轻量级的企业开发一站式解决方案框架。spring使用简单的POJO来进行开发,每一个被spring管理的java对象,被称为bean。而spring提供了ioc容器来创建和维护bean之间的依赖关系。
IOC与DI
插自官网的一段介绍:

在spring中,IOC(控制反转)与DI(依赖注入)是同等的概念。控制反转是通过依赖注入来实现的。所谓的依赖注入是指,被spring管理的bean,他们初始化以及之间依赖关系,由spring容器来生产bean,以及管理维护他们之间存在的依赖,以达到解耦的目的。简单的说,spring的ioc容器负责创建bean,并且将bean注入到另一个存在依赖关系的bean中。
spring可以通过xml配置,以及注解方式。无论哪一种方式,springioc容器都对它们进行解析,然后bean初始化,配置,依赖管理。现在大部分公司都是使用注解方式。
注解配置
声明bean的注解
- @Controller:用于springmvc的表现层。
- @Service:用于业务层,也就是我们写的service
- @Repository:用于数据访问层,就是我们写的dao
- @Component:本身没有实际的意思,只是标注为bean。也就是我们如果将一个Java对象交给spring容器管理,除了以上三种外,还可以使用这种通用的组件
除了以上四种,还存在@Configuration与@Bean结合使用的方式。
注入bean的注解
- @Autowired:常用,应用于属性或者属性的setter方法。属于spring提供的注解
- @Inject:JSR-330提供的注解,不常用
- @Resource:JSR-250提供的注解,常用
声明bean的注解与注入bean的注解结合使用案例:
一,引入依赖:
org.springframework spring-context 5.0.5.RELEASE二,创建HelloRepository:
@Repository public class HelloRepository { public void sayHello(String content){ System.out.println(" sayHello : " + content); } }@Repository表示将HelloRepository的实例化交给spring容器管理
HelloService:
@Service public class HelloService { @Autowired private HelloRepository helloRepository; public void sayHello(String content){ helloRepository.sayHello(content); } }@Service表示将HelloService交给spring容器管理@Autowired表示将HelloRepository依赖给注入进来,也就是将上边创建好的HelloRepository给注入。
三,创建AppConfig:
@ComponentScan("com.spring.*") public class AppConfig { }@ComponentScan("com.spring.*")表示以com.spring为根包向下扫描,将扫到@Controller,@Service,@Repository,@Component注解的类,都交给spring容器管理注册为bean
四,使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器:
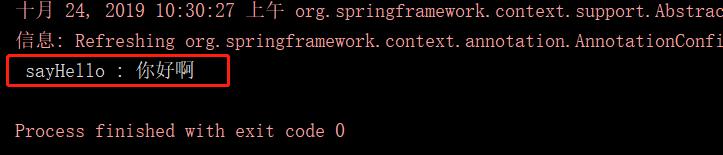
public class SpringDemoMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); HelloService bean = ac.getBean(HelloService.class); bean.sayHello("你好啊"); } }运行后输出:
我们还可使用@Configuration与@Bean结合方式创建bean
一,将@Service,@Repository去掉,修改AppConfig类:
@ComponentScan("com.spring.*") @Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean public HelloService helloService(){ return new HelloService(); } @Bean public HelloRepository helloRepository(){ return new HelloRepository(); } }@Configuration:表示这个是个配置类@Bean:表示当前声明方法返回一个bean,交给spring管理。
二,运行SpringDemoMain的main方法,输出:
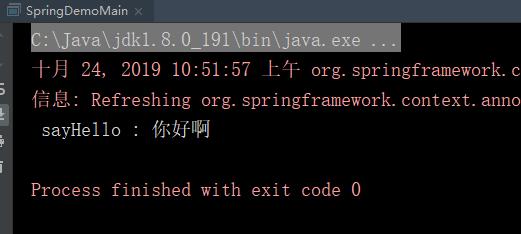
效果是一样的。springioc容器自动帮我们创建并且维护各个bean之间的依赖关系。
beab的Scope
scope在spring中描述如何新建bean的实例,准确的说是描述bean的作用域。scope有以下几个常用的值
- singleton:默认配置。单例模式,表示一个spring容器中只能有一个bean的实例
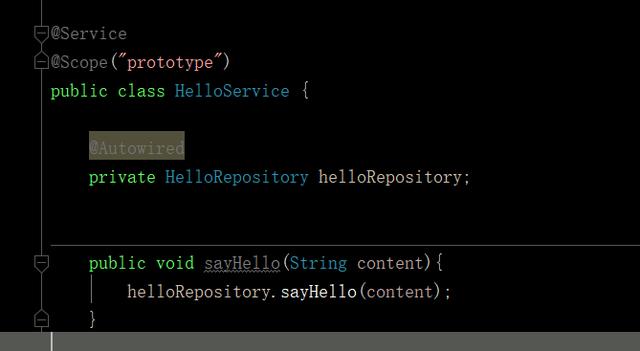
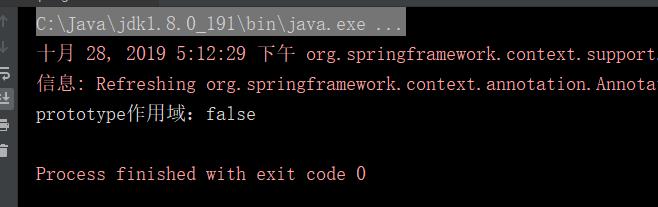
- prototype:允许每次使用的时候,都新建一个新的bean
- request:表示web项目中,每次http request都新建一个bean
- session:表示web项目中,每次http session都新建一个bean
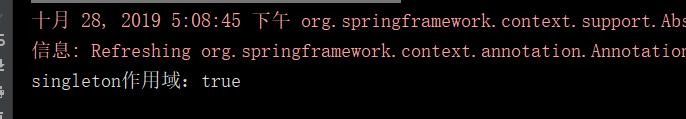
1,看singleton例子:
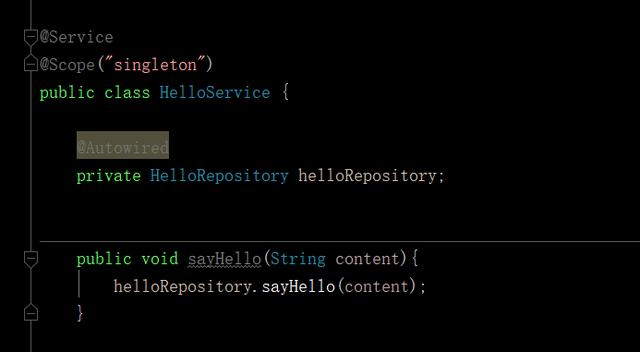
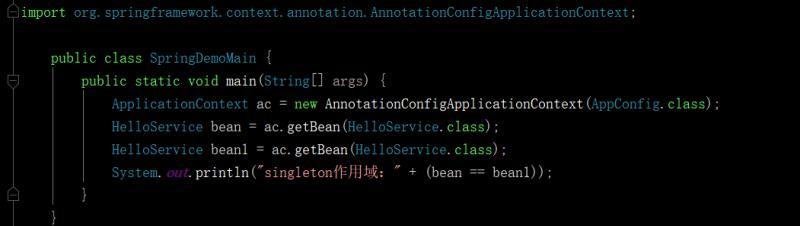
最后输出:
2,看prototype例子:
最后输出:
beab的生命周期回调
在某些业务下,我们也许会有这样的需求,在bean创建或者销毁做一些有必要的任务。spring提供了对bean生命周期操作的支持:
- @PostConstruct ,@PreDestroy方式
1)@PostConstruct表示bean构造器完成之后执行的方法。使用方式如下:
@PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("PostConstruct.............."); }2)@PreDestroy表示bean销毁之前执行。使用方式如下:
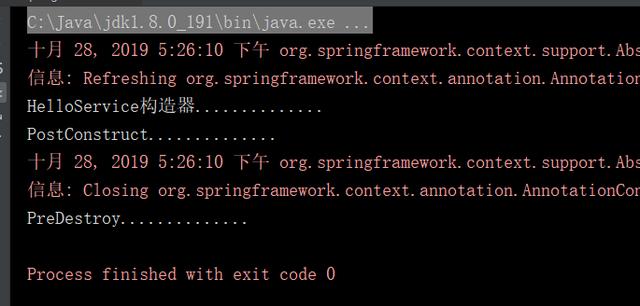
@PreDestroy public void destroy(){ System.out.println("PreDestroy.............."); }以上代码的例子:
最后输出:
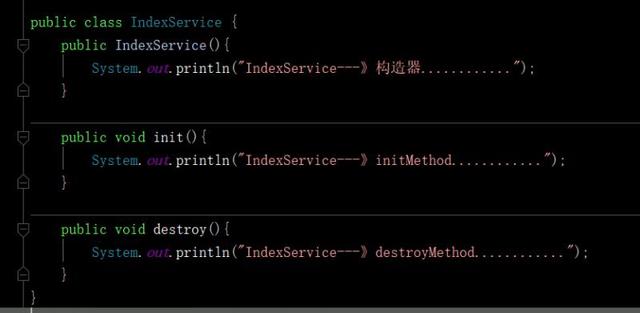
- @bean的initMethod和destroyMethod方式
1)initMethod:指定bean的initMethod方法在构造器之后执行
2)destroyMethod:指定bean的destroyMethod方法在销毁之前执行
例子:
IndexService.class
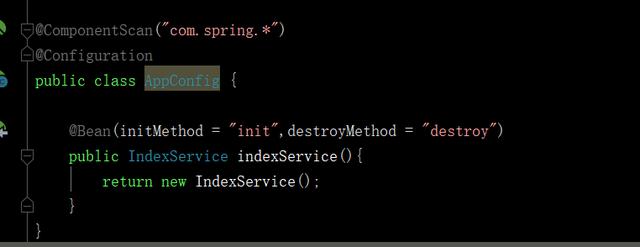
AppConfig.class
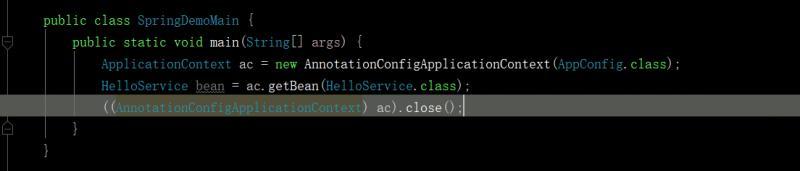
public class SpringDemoMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); IndexService bean = ac.getBean(IndexService.class); ((AnnotationConfigApplicationContext) ac).close(); } }最后输出:
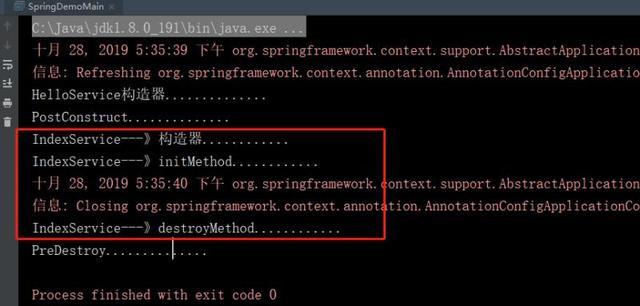
spring事件(Application Event)
spring的事件为bean与bean之间提供了消息通信的支持。当一个bean完成一个任务之后,希望另一个bean能做出响应的任务,那么就能使用spring事件机制完成。
使用spring事件需要完成三个步骤即可
1)自定义事件,继承ApplicationEvent
public class IndexEvent extends ApplicationEvent { public String msg; public IndexEvent(Object source,String msg) { super(source); this.msg = msg; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } public void myIndexEvent(){ System.out.println("myIndexEvent。。。。。。。。。。。。" + msg); } }2)自定义事件监听器,实现ApplicationListener。注意要把创建的监听器交给容器管理
@Component public class IndexListener implements ApplicationListener { public void onApplicationEvent(IndexEvent indexEvent) { System.out.println("监听器监听事件............"); indexEvent.myIndexEvent(); } }注意加上@Component
3)使用spring容器发布事件
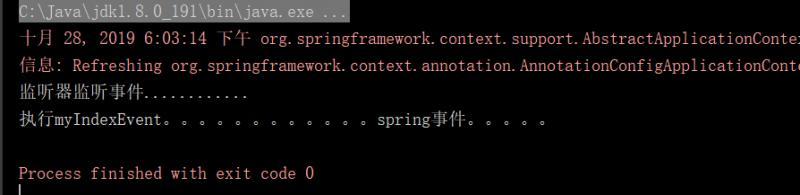
public class SpringDemoMain { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); IndexService bean = ac.getBean(IndexService.class); ac.publishEvent(new IndexEvent(bean,"spring事件。。。。。")); } }最后输出:
本人水平有限,难免有错误或遗漏之处,望大家指正和谅解,提出宝贵意见,愿与之交流。




 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的IOC(控制反转)和DI(依赖注入)概念,以及它们如何通过注解实现。讲解了@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component等注解的作用,以及@Autowired、@Inject和@Resource等注入注解的使用。文章还提到了bean的scope、生命周期回调方法以及spring事件的应用。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的IOC(控制反转)和DI(依赖注入)概念,以及它们如何通过注解实现。讲解了@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component等注解的作用,以及@Autowired、@Inject和@Resource等注入注解的使用。文章还提到了bean的scope、生命周期回调方法以及spring事件的应用。
















 965
965

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








