在之前的分析中,我们基本明白了mybatis对接口和xml的sql文件的组装拼接的原理。但是我们执行sql又是如何实现的,或者说sql的执行到底走了哪些流程。在上次的分析中我们知道mybatis采用了动态代理的方式,而且的pagehelper分页的时候也是动态代理。那么这之间到底是怎么执行的,除此之外我们也应当考虑mybatis提供的四大拦截器的具体执行顺序。所以这是我们今天的主要工作。首先我们知道,我们通过mybatis执行sql大概是这样的。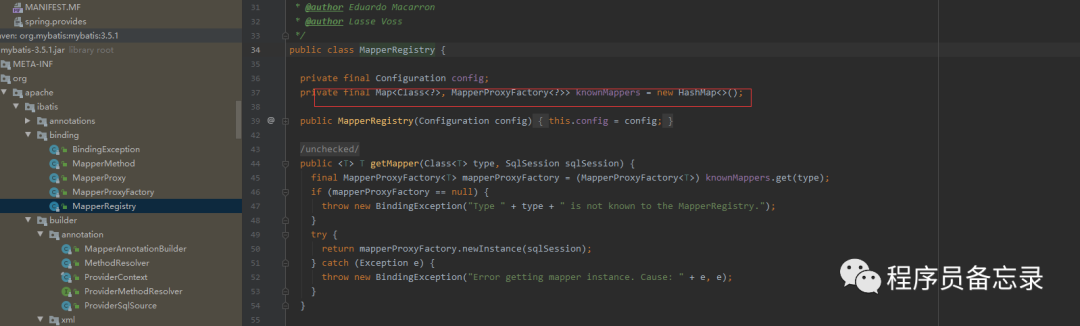 也就是说我们的sql执行肯定是通过这里的proxymapper来执行的。那么我们重点看一下这里的proxymapper。因为这里是jdk动态代理,所以我们找一下proxymapper的代码。
也就是说我们的sql执行肯定是通过这里的proxymapper来执行的。那么我们重点看一下这里的proxymapper。因为这里是jdk动态代理,所以我们找一下proxymapper的代码。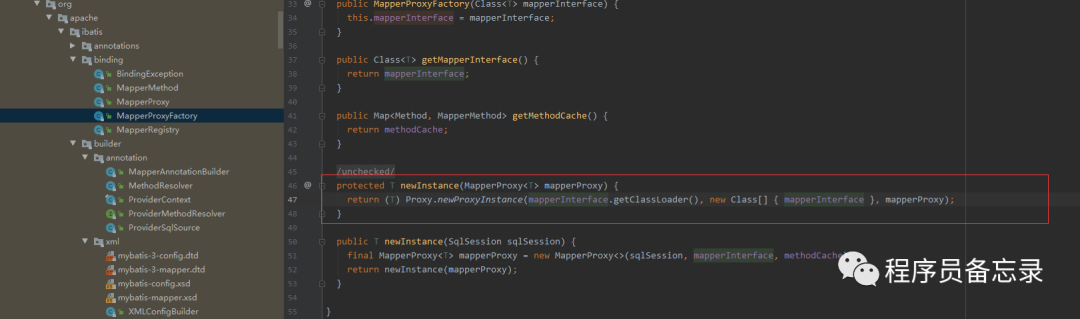 jdk动态代理,就是说我们autowried注入的是动态代理生成的对象。我们在调用的时候其实只调用了接口,但是最后执行了被代理类的方法。这块的method就是接口法发起的。
jdk动态代理,就是说我们autowried注入的是动态代理生成的对象。我们在调用的时候其实只调用了接口,但是最后执行了被代理类的方法。这块的method就是接口法发起的。 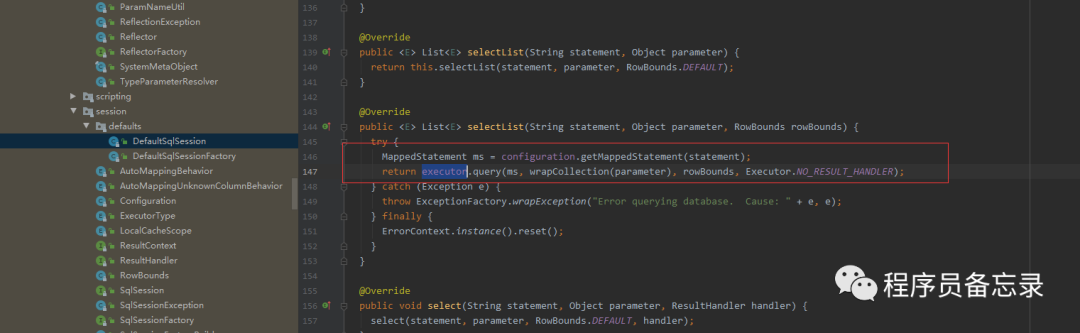 其中方法configuration.getMappedStatement是从xml文件的类中找到参数映射关系。warpcollection方法主要是对传入的参数进行map化,我们也看到这里默认collection、list、array等。也就是说我们传入这些值得时候其实是不用标记的。
其中方法configuration.getMappedStatement是从xml文件的类中找到参数映射关系。warpcollection方法主要是对传入的参数进行map化,我们也看到这里默认collection、list、array等。也就是说我们传入这些值得时候其实是不用标记的。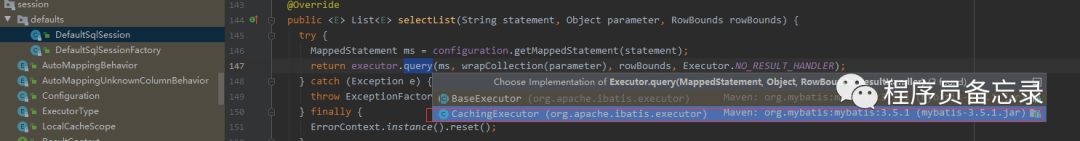
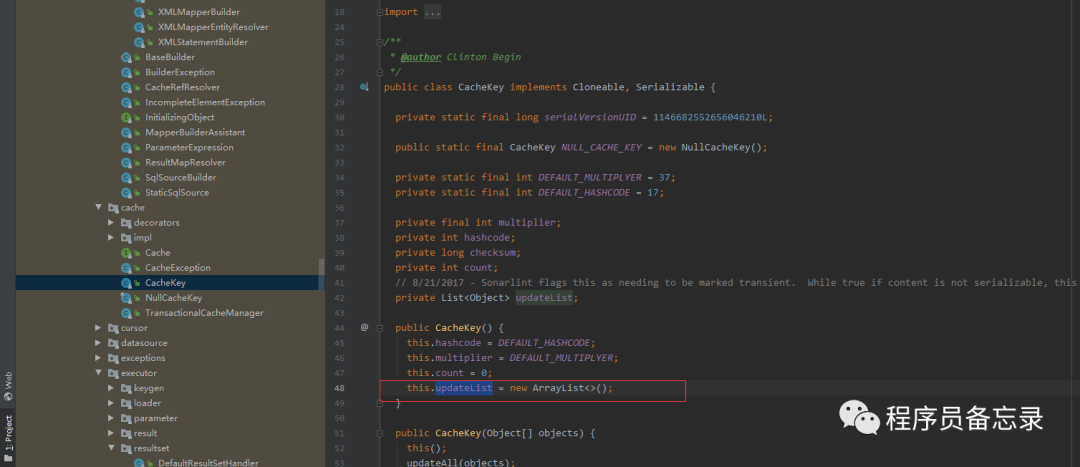
 而这里的preparestatement就是获取数据库连接的地方。
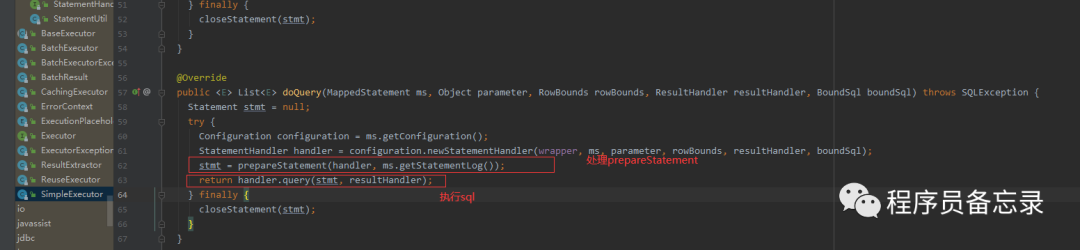
而这里的preparestatement就是获取数据库连接的地方。 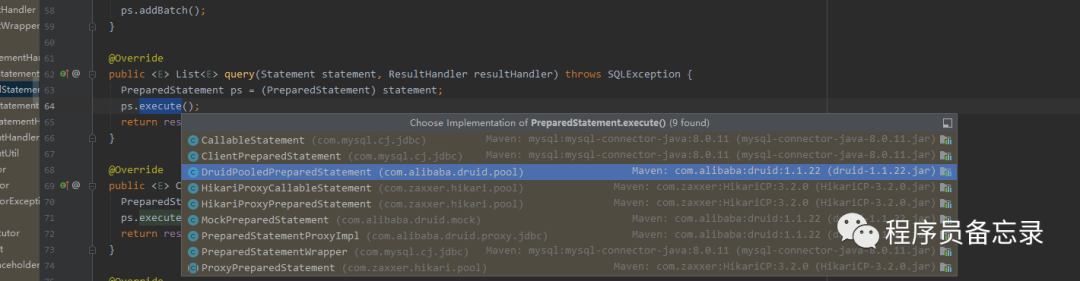 分析到这里,我们可能有点疑问,我们的executor是在哪里进行初始化的,不是说好的有拦截器么,怎么分析的过程中并没有执行?怀着这种疑问我们再来看看。我们发现executor在初始化的时候就已经创建了。
分析到这里,我们可能有点疑问,我们的executor是在哪里进行初始化的,不是说好的有拦截器么,怎么分析的过程中并没有执行?怀着这种疑问我们再来看看。我们发现executor在初始化的时候就已经创建了。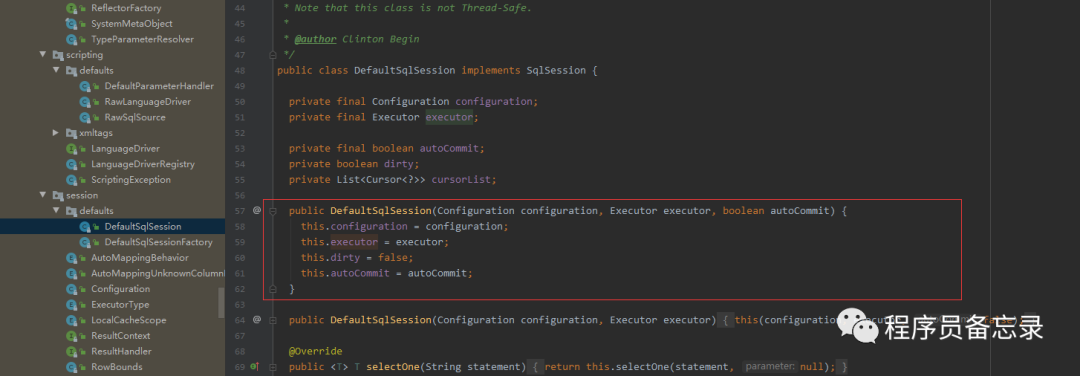 作者通过代码跟踪,发现sqlSessionFactory中具有创建的相关代码。
作者通过代码跟踪,发现sqlSessionFactory中具有创建的相关代码。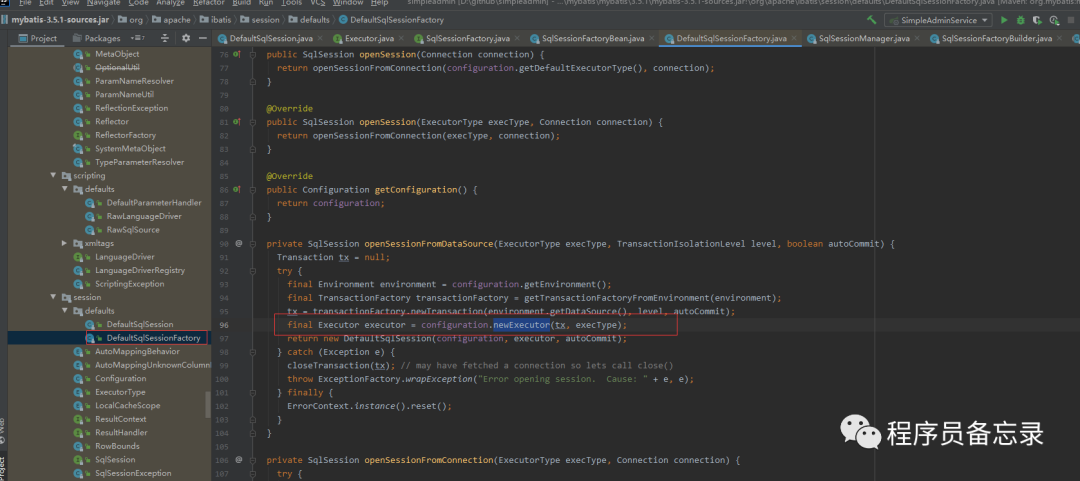 创建的细节为,具体的实现类为configuration:
创建的细节为,具体的实现类为configuration: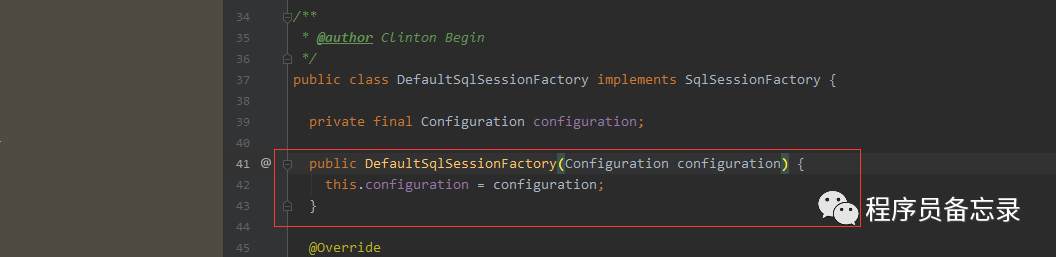
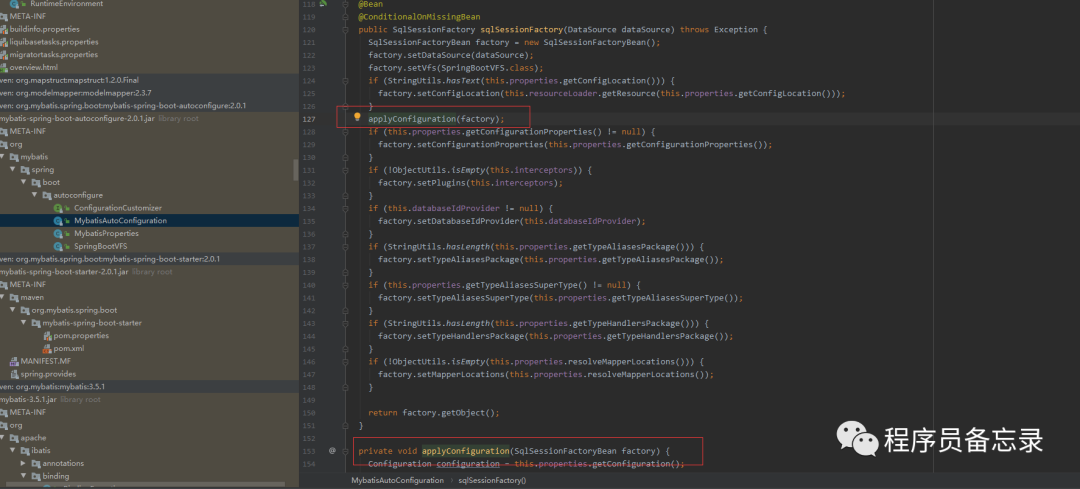 通过上述分析,我们得出的结论是我们使用注解@Autowired注入的时候是通过MapperFactoryBean注入的,而mapperFactory在初始化的时候注入了sqlsessionfactory然后初始了sqlsessiontemplate,而sqlsessiontemplate就是sqlsession的代理类。sqlsessionfactory的初始化则如上所示。sqlsessionfactory的初始化直接就已经生成了configuration,configuration在sqlsessionfactory创建的时候会进行创建 ,在之后sqlsessiontemplate调用的时候就没有后顾之忧。同时在getmapper注入sqlsession的时候其实也是注入的会话代理,同样是jdk动态代理,最终实现的是defaultsqlsession,defaultsqlsession执行方法的时候则会按照我们configuration设置的executortype来决定具体的执行器,其中的cachexecutor我们下次分析。而sqlsession的执行获取连接的部分最后就交给了数据库连接池。
通过上述分析,我们得出的结论是我们使用注解@Autowired注入的时候是通过MapperFactoryBean注入的,而mapperFactory在初始化的时候注入了sqlsessionfactory然后初始了sqlsessiontemplate,而sqlsessiontemplate就是sqlsession的代理类。sqlsessionfactory的初始化则如上所示。sqlsessionfactory的初始化直接就已经生成了configuration,configuration在sqlsessionfactory创建的时候会进行创建 ,在之后sqlsessiontemplate调用的时候就没有后顾之忧。同时在getmapper注入sqlsession的时候其实也是注入的会话代理,同样是jdk动态代理,最终实现的是defaultsqlsession,defaultsqlsession执行方法的时候则会按照我们configuration设置的executortype来决定具体的执行器,其中的cachexecutor我们下次分析。而sqlsession的执行获取连接的部分最后就交给了数据库连接池。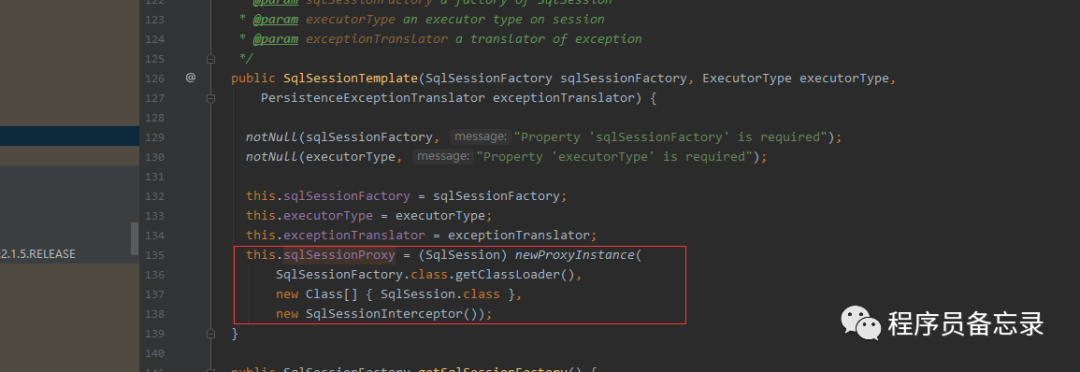
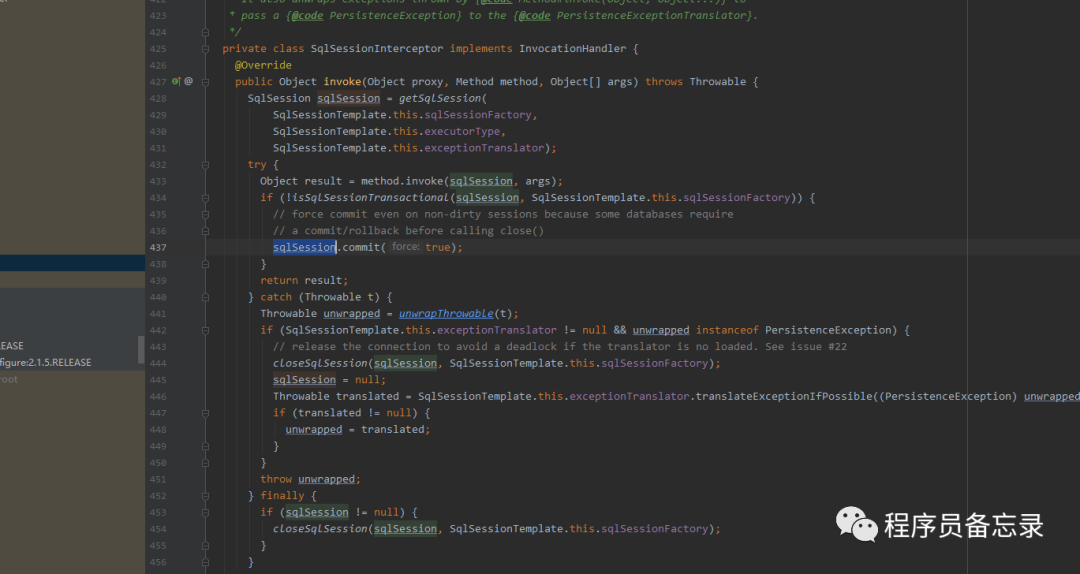
/** * 项目表 */ @Autowired private ProjectInfoPoMapper projectInfoPoMapper; /** * 添加一个项目 * @param request 添加监控项目 * @return */ @Override public ResponseResult addMonitorProject(ProjectAddRequest request) { ProjectDomain projectDomain=new ProjectDomain(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(request,projectDomain); return projectDomain.insert(projectInfoPoMapper); } /** * 添加到数据库 * @param projectInfoPoMapper * @return */ public ResponseResult insert(ProjectInfoPoMapper projectInfoPoMapper) { ProjectInfoPo po=new ProjectInfoPo(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(this,po); po.setCreateTime(new Date()); if (projectInfoPoMapper.insert(po)>0){ return ResponseResult.success(true); } return ResponseResult.error("add fail"); } 也就是说我们的sql执行肯定是通过这里的proxymapper来执行的。那么我们重点看一下这里的proxymapper。因为这里是jdk动态代理,所以我们找一下proxymapper的代码。
也就是说我们的sql执行肯定是通过这里的proxymapper来执行的。那么我们重点看一下这里的proxymapper。因为这里是jdk动态代理,所以我们找一下proxymapper的代码。 jdk动态代理,就是说我们autowried注入的是动态代理生成的对象。我们在调用的时候其实只调用了接口,但是最后执行了被代理类的方法。这块的method就是接口法发起的。
jdk动态代理,就是说我们autowried注入的是动态代理生成的对象。我们在调用的时候其实只调用了接口,但是最后执行了被代理类的方法。这块的method就是接口法发起的。 @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {//如果是Object类,那么直接诶执行。 return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); }//从缓存中获取映射的方法。 final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); }在此我们还看到这里做了一个方法的缓存 private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration())); }其中对sql的属性进行分析。 public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class mapperInterface, Method method) {//获取方法名称 final String methodName = method.getName(); final Class declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();//解析statement的映射关系 MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass, configuration); if (ms == null) { if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) { name = null; type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH; } else { throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): " + mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName); } } else {//获取sql的类型 name = ms.getId(); type = ms.getSqlCommandType(); if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) { throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name); } } }我们继续跟进sql的执行public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result;//根据类型进行执行 switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: {//拿到传入的参数 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);//执行插入操作 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);//执行更新操作 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);//执行删除操作 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT://如果返回值是空的,并且方法上有对结果的拦截 if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) {//返回的值是list result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) {//返回的值是mapper result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else {//返回值是一个 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; }可以看到上述操作对我们要执行的sql进行分类,然后去执行。我们在此大概得分析一下传入参数的解析,然后将重点放在下游调用链上。在对sql进行解析的时候,将其参数转换为map public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) { return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args); }传入参数,返回map public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) { final int paramCount = names.size(); if (args == null || paramCount == 0) { return null; } else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) { return args[names.firstKey()]; } else { final Mapparam = new ParamMap<>(); int i = 0; for (Map.Entryentry : names.entrySet()) { param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]); // add generic param names (param1, param2, ...) final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1); // ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) { param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]); } i++; } return param; } }private Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { List result;//参数转为map Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); if (method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args); result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds); } else { //通过sqlsession查询数据库 result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param); } // issue #510 Collections & arrays support if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) { if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) { return convertToArray(result); } else { return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result); } } return result; } 其中方法configuration.getMappedStatement是从xml文件的类中找到参数映射关系。warpcollection方法主要是对传入的参数进行map化,我们也看到这里默认collection、list、array等。也就是说我们传入这些值得时候其实是不用标记的。
其中方法configuration.getMappedStatement是从xml文件的类中找到参数映射关系。warpcollection方法主要是对传入的参数进行map化,我们也看到这里默认collection、list、array等。也就是说我们传入这些值得时候其实是不用标记的。 private Object wrapCollection(final Object object) { if (object instanceof Collection) { StrictMap map = new StrictMap<>(); map.put("collection", object); if (object instanceof List) { map.put("list", object); } return map; } else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) { StrictMap map = new StrictMap<>(); map.put("array", object); return map; } return object; }
@Override public Listquery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {//参数绑定处理 BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);//创建缓存 CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);//执行 return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
@Override public Listquery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); if (cache != null) { flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")//先从缓存中查询 List list = (List) tcm.getObject(cache, key); if (list == null) {//缓存中为空的,开始查库 list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);//添加到缓存中 tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 } return list; } } return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public Listquery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {//如果是刷新缓存,就清理掉本地缓存 clearLocalCache(); } List list; try { queryStack++;//尝试从缓存中查询 list = resultHandler == null ? (List) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) {//对缓存中的参数进行更新 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else {//直接查库 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; }private ListqueryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List list; localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try {//查库 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { localCache.removeObject(key); }//缓存查询结果 localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {//如果是回调,在本地参数中将参数也添加进去 localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } 而这里的preparestatement就是获取数据库连接的地方。
而这里的preparestatement就是获取数据库连接的地方。 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);//设置事务时间 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());//将传入的参数和数字关联 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } 分析到这里,我们可能有点疑问,我们的executor是在哪里进行初始化的,不是说好的有拦截器么,怎么分析的过程中并没有执行?怀着这种疑问我们再来看看。我们发现executor在初始化的时候就已经创建了。
分析到这里,我们可能有点疑问,我们的executor是在哪里进行初始化的,不是说好的有拦截器么,怎么分析的过程中并没有执行?怀着这种疑问我们再来看看。我们发现executor在初始化的时候就已经创建了。 作者通过代码跟踪,发现sqlSessionFactory中具有创建的相关代码。
作者通过代码跟踪,发现sqlSessionFactory中具有创建的相关代码。 创建的细节为,具体的实现类为configuration:
创建的细节为,具体的实现类为configuration:public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); }//添加插件,这里的插件是通过jdk代理生成的。也就是说executor最后还是动态生成的 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
 通过上述分析,我们得出的结论是我们使用注解@Autowired注入的时候是通过MapperFactoryBean注入的,而mapperFactory在初始化的时候注入了sqlsessionfactory然后初始了sqlsessiontemplate,而sqlsessiontemplate就是sqlsession的代理类。sqlsessionfactory的初始化则如上所示。sqlsessionfactory的初始化直接就已经生成了configuration,configuration在sqlsessionfactory创建的时候会进行创建 ,在之后sqlsessiontemplate调用的时候就没有后顾之忧。同时在getmapper注入sqlsession的时候其实也是注入的会话代理,同样是jdk动态代理,最终实现的是defaultsqlsession,defaultsqlsession执行方法的时候则会按照我们configuration设置的executortype来决定具体的执行器,其中的cachexecutor我们下次分析。而sqlsession的执行获取连接的部分最后就交给了数据库连接池。
通过上述分析,我们得出的结论是我们使用注解@Autowired注入的时候是通过MapperFactoryBean注入的,而mapperFactory在初始化的时候注入了sqlsessionfactory然后初始了sqlsessiontemplate,而sqlsessiontemplate就是sqlsession的代理类。sqlsessionfactory的初始化则如上所示。sqlsessionfactory的初始化直接就已经生成了configuration,configuration在sqlsessionfactory创建的时候会进行创建 ,在之后sqlsessiontemplate调用的时候就没有后顾之忧。同时在getmapper注入sqlsession的时候其实也是注入的会话代理,同样是jdk动态代理,最终实现的是defaultsqlsession,defaultsqlsession执行方法的时候则会按照我们configuration设置的executortype来决定具体的执行器,其中的cachexecutor我们下次分析。而sqlsession的执行获取连接的部分最后就交给了数据库连接池。









 本文深入探讨了Mybatis Plus如何直接执行SQL语句,详细阐述了Mybatis Plus在Sql执行过程中的工作原理,帮助读者理解其在Mybatis学习中的重要性。
本文深入探讨了Mybatis Plus如何直接执行SQL语句,详细阐述了Mybatis Plus在Sql执行过程中的工作原理,帮助读者理解其在Mybatis学习中的重要性。
















 8984
8984

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








