前言
最近任务需求,特殊模式下任务管理界面 不能打开某个APK
任务分析
任务管理界面下单个task的onClick或者onTouch
首先找到Recents 源码 位于systemui 中

这里我们直接打开RecentsActivity.java 文件

在RecentsActivity 的oncreate中发现setContentView为recents资源文件

这里我们看到代码及注释,说明是一个自定义view - RecentsView
我们可以看到RecentsView是继承 FrameLayout的一个自定义View
RecentsView 中 有三个view 一个TaskStackView 两个Textview

public RecentsView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
setWillNotDraw(false);
SystemServicesProxy ssp = Recents.getSystemServices();
mTransitionHelper = new RecentsTransitionHelper(getContext());
mDividerSize = ssp.getDockedDividerSize(context);
mTouchHandler = new RecentsViewTouchHandler(this);
mFlingAnimationUtils = new FlingAnimationUtils(context, 0.3f);
mScrimAlpha = Recents.getConfiguration().isGridEnabled
? GRID_LAYOUT_SCRIM_ALPHA : DEFAULT_SCRIM_ALPHA;
mBackgroundScrim = new ColorDrawable(
Color.argb((int) (mScrimAlpha * 255), 0, 0, 0)).mutate();
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
if (RecentsDebugFlags.Static.EnableStackActionButton) {
mStackActionButton = (TextView) inflater.inflate(R.layout.recents_stack_action_button,
this, false);
mStackActionButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
EventBus.getDefault().send(new DismissAllTaskViewsEvent());
}
});
addView(mStackActionButton);
}
mEmptyView = (TextView) inflater.inflate(R.layout.recents_empty, this, false);
addView(mEmptyView);
}
mStackActionButton即全部清除按钮,mEmptyView 即当TaskStack(Task的集合) 数量为空时显示的TextView,因此我们平时见到的APP的任务管理应该是在TaskStackView中的
然后分析TaskStackView 发现

TaskStackViewTouchHandler 这个应该是和Touch事件有关,因此我们进入 TaskStackViewTouchHandler中

可以看到上面的注释 说明它是 处理TaskStackView 触摸事件的类
TaskStackViewTouchHandler 中有onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent 看到它都调用到了 handleTouchEvent

下面是整个handleTouchEvent的代码
private boolean handleTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// Short circuit if we have no children
if (mSv.getTaskViews().size() == 0) {
return false;
}
final TaskStackLayoutAlgorithm layoutAlgorithm = mSv.mLayoutAlgorithm;
int action = ev.getAction();
switch (action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
// Stop the current scroll if it is still flinging
mScroller.stopScroller();
mScroller.stopBoundScrollAnimation();
mScroller.resetDeltaScroll();
cancelNonDismissTaskAnimations();
mSv.cancelDeferredTaskViewLayoutAnimation();
// Save the touch down info
mDownX = (int) ev.getX();
mDownY = (int) ev.getY();
mLastY = mDownY;
mDownScrollP = mScroller.getStackScroll();
mActivePointerId = ev.getPointerId(0);
mActiveTaskView = findViewAtPoint(mDownX, mDownY);
Log.e("zhuwww"," mActiveTaskView \n");
// Initialize the velocity tracker
initOrResetVelocityTracker();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN: {
final int index = ev.getActionIndex();
mActivePointerId = ev.getPointerId(index);
mDownX = (int) ev.getX(index);
mDownY = (int) ev.getY(index);
mLastY = mDownY;
mDownScrollP = mScroller.getStackScroll();
mScroller.resetDeltaScroll();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
int activePointerIndex = ev.findPointerIndex(mActivePointerId);
int y = (int) ev.getY(activePointerIndex);
int x = (int) ev.getX(activePointerIndex);
if (!mIsScrolling) {
int yDiff = Math.abs(y - mDownY);
int xDiff = Math.abs(x - mDownX);
if (Math.abs(y - mDownY) > mScrollTouchSlop && yDiff > xDiff) {
mIsScrolling = true;
float stackScroll = mScroller.getStackScroll();
List taskViews = mSv.getTaskViews();
for (int i = taskViews.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
layoutAlgorithm.addUnfocusedTaskOverride(taskViews.get(i).getTask(),
stackScroll);
}
layoutAlgorithm.setFocusState(TaskStackLayoutAlgorithm.STATE_UNFOCUSED);
// Disallow parents from intercepting touch events
final ViewParent parent = mSv.getParent();
if (parent != null) {
parent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
}
MetricsLogger.action(mSv.getContext(), MetricsEvent.OVERVIEW_SCROLL);
mLastY = mDownY = y;
}
}
if (mIsScrolling) {
// If we just move linearly on the screen, then that would map to 1/arclength
// of the curve, so just move the scroll proportional to that
float deltaP = layoutAlgorithm.getDeltaPForY(mDownY, y);
// Modulate the overscroll to prevent users from pulling the stack too far
float minScrollP = layoutAlgorithm.mMinScrollP;
float maxScrollP = layoutAlgorithm.mMaxScrollP;
float curScrollP = mDownScrollP + deltaP;
if (curScrollP < minScrollP || curScrollP > maxScrollP) {
float clampedScrollP = Utilities.clamp(curScrollP, minScrollP, maxScrollP);
float overscrollP = (curScrollP - clampedScrollP);
float overscrollX = Math.abs(overscrollP) / MAX_OVERSCROLL;
float interpX = OVERSCROLL_INTERP.getInterpolation(overscrollX);
curScrollP = clampedScrollP + Math.signum(overscrollP) *
(interpX * MAX_OVERSCROLL);
}
mDownScrollP += mScroller.setDeltaStackScroll(mDownScrollP,
curScrollP - mDownScrollP);
mStackViewScrolledEvent.updateY(y - mLastY);
EventBus.getDefault().send(mStackViewScrolledEvent);
}
mLastY = y;
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP: {
int pointerIndex = ev.getActionIndex();
int pointerId = ev.getPointerId(pointerIndex);
if (pointerId == mActivePointerId) {
// Select a new active pointer id and reset the motion state
final int newPointerIndex = (pointerIndex == 0) ? 1 : 0;
mActivePointerId = ev.getPointerId(newPointerIndex);
mDownX = (int) ev.getX(pointerIndex);
mDownY = (int) ev.getY(pointerIndex);
mLastY = mDownY;
mDownScrollP = mScroller.getStackScroll();
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaximumVelocity);
int activePointerIndex = ev.findPointerIndex(mActivePointerId);
int y = (int) ev.getY(activePointerIndex);
int velocity = (int) mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(mActivePointerId);
if (mIsScrolling) {
if (mScroller.isScrollOutOfBounds()) {
mScroller.animateBoundScroll();
} else if (Math.abs(velocity) > mMinimumVelocity) {
float minY = mDownY + layoutAlgorithm.getYForDeltaP(mDownScrollP,
layoutAlgorithm.mMaxScrollP);
float maxY = mDownY + layoutAlgorithm.getYForDeltaP(mDownScrollP,
layoutAlgorithm.mMinScrollP);
mScroller.fling(mDownScrollP, mDownY, y, velocity, (int) minY, (int) maxY,
mOverscrollSize);
mSv.invalidate();
}
// Reset the focused task after the user has scrolled, but we have no scrolling
// in grid layout and therefore we don't want to reset the focus there.
if (!mSv.mTouchExplorationEnabled && !mSv.useGridLayout()) {
mSv.resetFocusedTask(mSv.getFocusedTask());
}
} else if (mActiveTaskView == null) {
// This tap didn't start on a task.
maybeHideRecentsFromBackgroundTap((int) ev.getX(), (int) ev.getY());
}
mActivePointerId = INACTIVE_POINTER_ID;
mIsScrolling = false;
recycleVelocityTracker();
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: {
mActivePointerId = INACTIVE_POINTER_ID;
mIsScrolling = false;
recycleVelocityTracker();
break;
}
}
return mIsScrolling;
}
分析发现,在handleTouchEvent 中 当MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN时 通过mActiveTaskView = findViewAtPoint(mDownX, mDownY);得到了一个TaskView
findViewAtPoint实现
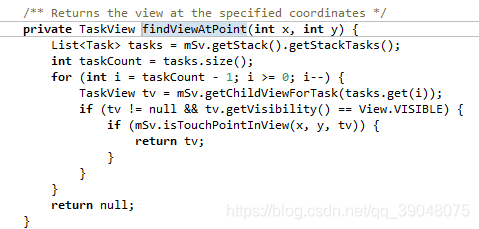
这里我们直接进入TaskView.java中查看 看到这里有实现点击事件的代码,这里我们加个Log打印,验证点击视图时是否经过这里
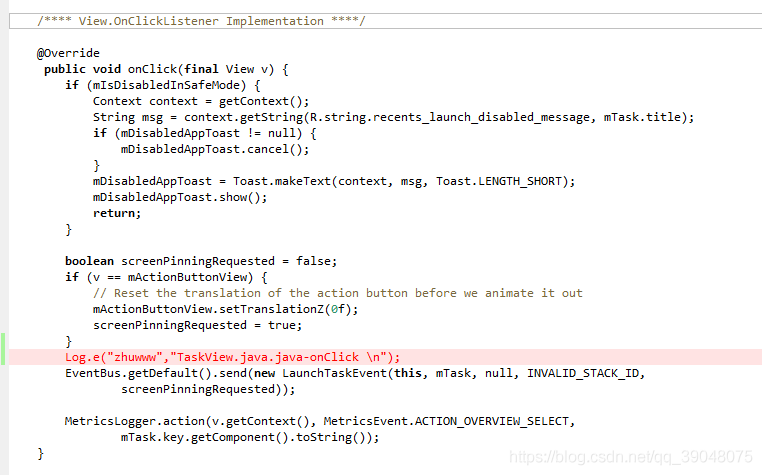
通过打印验证
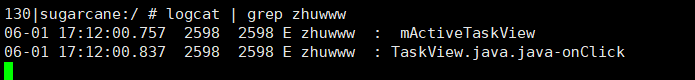
的确是走的这个地方,那么我们这里可以看到主要是通过eventBus发送了一个LaunchTaskEvent事件
EventBus.getDefault().send(new LaunchTaskEvent(this, mTask, null, INVALID_STACK_ID,
screenPinningRequested));
LaunchTaskEvent源码
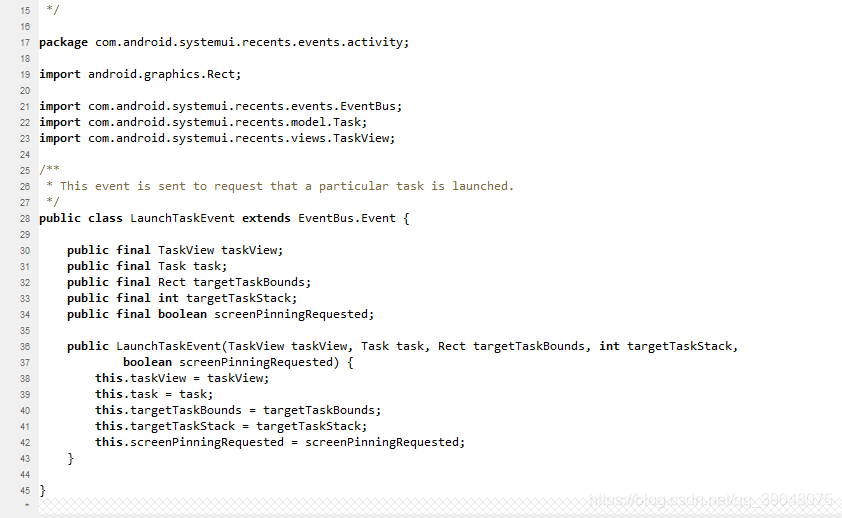
因此我们直接在recents中搜索哪个地方的方法用到了LaunchTaskEvent
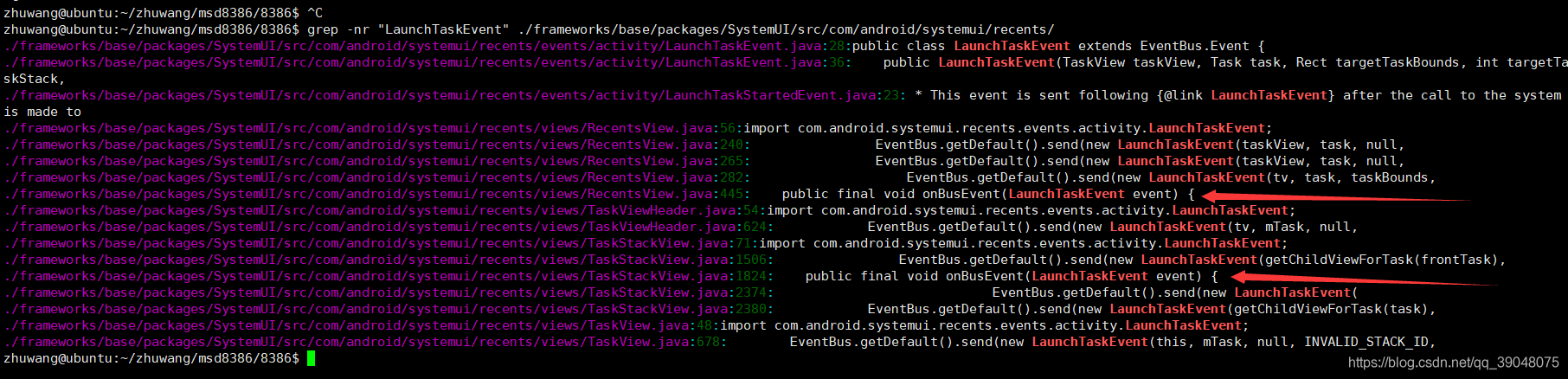
这里看到只在TaskStackView和RecentsView中有使用到LaunchTaskEvent,其余的都是eventBus发送事件,所以我们就不用管了
然后下面看TaskStackView中的实现,很明显不是的,因此我们可以先确定是在RecentsView中的方法中

如下图所示,这个我们看它用的方法,通过mTransitionHelper去launchTaskFromRecents。这里从字面意思应该不难看出,地方已经找对了 launchTaskFromRecents即从recents中运行一个task。
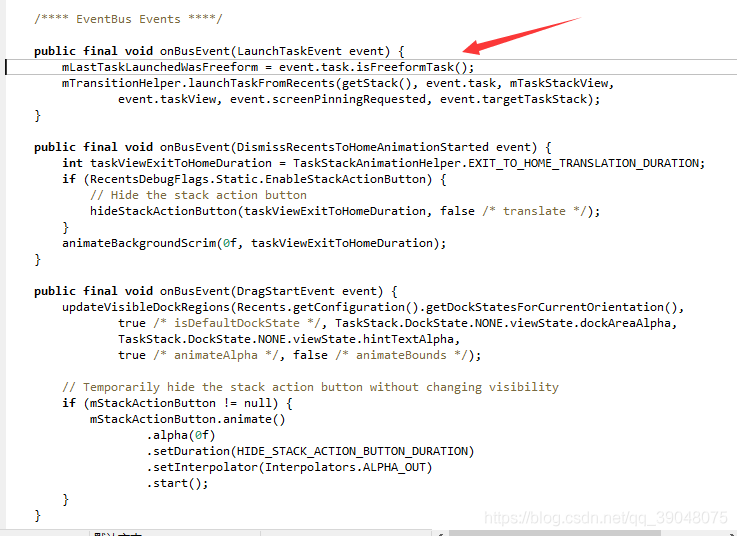
然后我们在launchTaskFromRecents方法中发现有一个startTaskActivity方法
public void launchTaskFromRecents(final TaskStack stack, @Nullable final Task task,
final TaskStackView stackView, final TaskView taskView,
final boolean screenPinningRequested, final int destinationStack) {
final ActivityOptions.OnAnimationStartedListener animStartedListener;
final AppTransitionAnimationSpecsFuture transitionFuture;
if (taskView != null) {
// Fetch window rect here already in order not to be blocked on lock contention in WM
// when the future calls it.
final Rect windowRect = Recents.getSystemServices().getWindowRect();
transitionFuture = getAppTransitionFuture(
() -> composeAnimationSpecs(task, stackView, destinationStack, windowRect));
animStartedListener = () -> {
// If we are launching into another task, cancel the previous task's
// window transition
EventBus.getDefault().send(new CancelEnterRecentsWindowAnimationEvent(task));
EventBus.getDefault().send(new ExitRecentsWindowFirstAnimationFrameEvent());
stackView.cancelAllTaskViewAnimations();
if (screenPinningRequested) {
// Request screen pinning after the animation runs
mStartScreenPinningRunnable.taskId = task.key.id;
mHandler.postDelayed(mStartScreenPinningRunnable, 350);
}
};
} else {
// This is only the case if the task is not on screen (scrolled offscreen for example)
transitionFuture = null;
animStartedListener = () -> {
// If we are launching into another task, cancel the previous task's
// window transition
EventBus.getDefault().send(new CancelEnterRecentsWindowAnimationEvent(task));
EventBus.getDefault().send(new ExitRecentsWindowFirstAnimationFrameEvent());
stackView.cancelAllTaskViewAnimations();
};
}
final ActivityOptions opts = ActivityOptions.makeMultiThumbFutureAspectScaleAnimation(mContext,
mHandler, transitionFuture != null ? transitionFuture.future : null,
animStartedListener, true /* scaleUp */);
if (taskView == null) {
// If there is no task view, then we do not need to worry about animating out occluding
// task views, and we can launch immediately
startTaskActivity(stack, task, taskView, opts, transitionFuture, destinationStack);
} else {
LaunchTaskStartedEvent launchStartedEvent = new LaunchTaskStartedEvent(taskView,
screenPinningRequested);
if (task.group != null && !task.group.isFrontMostTask(task)) {
launchStartedEvent.addPostAnimationCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
startTaskActivity(stack, task, taskView, opts, transitionFuture,
destinationStack);
}
});
EventBus.getDefault().send(launchStartedEvent);
} else {
EventBus.getDefault().send(launchStartedEvent);
startTaskActivity(stack, task, taskView, opts, transitionFuture, destinationStack);
}
}
Recents.getSystemServices().sendCloseSystemWindows(
StatusBar.SYSTEM_DIALOG_REASON_HOME_KEY);
}
关键代码 ssp.startActivityFromRecents 从Recents 中启动activity
private void startTaskActivity(TaskStack stack, Task task, @Nullable TaskView taskView,
ActivityOptions opts, AppTransitionAnimationSpecsFuture transitionFuture,
int destinationStack) {
SystemServicesProxy ssp = Recents.getSystemServices();
ssp.startActivityFromRecents(mContext, task.key, task.title, opts, destinationStack,
succeeded -> {
if (succeeded) {
// Keep track of the index of the task launch
int taskIndexFromFront = 0;
int taskIndex = stack.indexOfStackTask(task);
if (taskIndex > -1) {
taskIndexFromFront = stack.getTaskCount() - taskIndex - 1;
}
EventBus.getDefault().send(new LaunchTaskSucceededEvent(taskIndexFromFront));
} else {
// Dismiss the task if we fail to launch it
if (taskView != null) {
taskView.dismissTask();
}
// Keep track of failed launches
EventBus.getDefault().send(new LaunchTaskFailedEvent());
}
});
if (transitionFuture != null) {
mHandler.post(transitionFuture::precacheSpecs);
}
}
至此,已经找到了任务管理中启动task的地方,我们这里只需要在RecentsView.java的onBusEvent方法中拦截即可
比如任务管理中不能打开相册
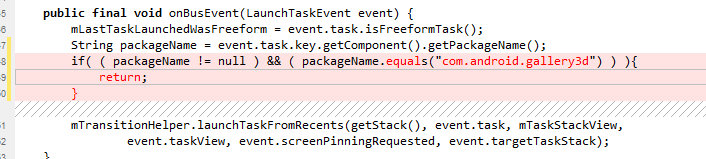
全文结束,欢迎点赞




 本文深入解析Android 8.0中SystemUI的Recents任务启动过程,从RecentsActivity.java开始,逐步剖析RecentsView、TaskStackViewTouchHandler,揭示任务管理界面点击任务时的处理逻辑,最终定位到启动任务的关键代码ssp.startActivityFromRecents。
本文深入解析Android 8.0中SystemUI的Recents任务启动过程,从RecentsActivity.java开始,逐步剖析RecentsView、TaskStackViewTouchHandler,揭示任务管理界面点击任务时的处理逻辑,最终定位到启动任务的关键代码ssp.startActivityFromRecents。
















 1466
1466

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








