数据结构篇之数组
由于c原声数组的缺点,如内存不能动态更新,apr实现了自己的数组数据结构,apr数组更像是队列的变形,只支持pop和push,不支持随机访问。apr数组是整个apr数据结构的基础,几乎所有的数据结构都使用了apr数组。
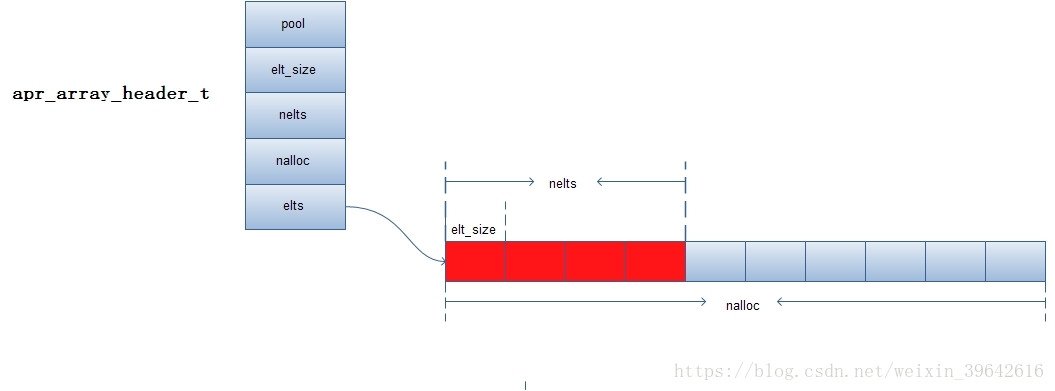
结构声明
/** @see apr_array_header_t */
typedef struct apr_array_header_t apr_array_header_t;
/** An opaque array type */
struct apr_array_header_t {
/** The pool the array is allocated out of */
apr_pool_t *pool;
/** 每个元素的大小,固定大小 */
int elt_size;
/** 已经使用的元素个数 */
int nelts;
/** 分配的元素个数,动态变化 */
int nalloc;
/** 指向元素存储空间的指针 */
char *elts;
};
数据结构图
- Nginx的数组只存储比较小的数据
- 数组的元素长度在创建数组的时候就固定死了。但是数组个数,会自动扩容。
- apr数组更像是队列的变形,只支持pop和push,不支持随机访问
具体函数实现
创建一个数组
指定分配内存的pool,元素大小和个数
static void make_array_core(apr_array_header_t *res, apr_pool_t *p,
int nelts, int elt_size, int clear)
{
/*
* Assure sanity if someone asks for
* array of zero elts.
*/
if (nelts < 1) {
nelts = 1;
}
// 分配存储元素的内存空间
if (clear) {
res->elts = apr_pcalloc(p, nelts * elt_size);
}
else {
res->elts = apr_palloc(p, nelts * elt_size);
}
res->pool = p;
res->elt_size = elt_size;
// 元素个数为0
res->nelts = 0; /* No active elements yet... */
res->nalloc = nelts; /* ...but this many allocated */
}
APR_DECLARE(apr_array_header_t *) apr_array_make(apr_pool_t *p,
int nelts, int elt_size)
{
apr_array_header_t *res;
res = (apr_array_header_t *) apr_palloc(p, sizeof(apr_array_header_t));
make_array_core(res, p, nelts, elt_size, 1);
return res;
}
push元素
APR_DECLARE(void *) apr_array_push(apr_array_header_t *arr)
{
// 如果空间不够则重新分配空间
if (arr->nelts == arr->nalloc) {
// 原大小的两倍
int new_size = (arr->nalloc <= 0) ? 1 : arr->nalloc * 2;
char *new_data;
new_data = apr_palloc(arr->pool, arr->elt_size * new_size);
// 复制旧数据到新的内存空间
memcpy(new_data, arr->elts, arr->nalloc * arr->elt_size);
memset(new_data + arr->nalloc * arr->elt_size, 0,
arr->elt_size * (new_size - arr->nalloc));
arr->elts = new_data;
arr->nalloc = new_size;
}
// 元素个数加 1
++arr->nelts;
// 返回对应的内存地址
return arr->elts + (arr->elt_size * (arr->nelts - 1));
}
pop元素
APR_DECLARE(void *) apr_array_pop(apr_array_header_t *arr)
{
if (apr_is_empty_array(arr)) {
return NULL;
}
// 返回最后的一个元素地址,元素个数减 1
return arr->elts + (arr->elt_size * (--arr->nelts));
}
复制数组
APR_DECLARE(apr_array_header_t *) apr_array_copy(apr_pool_t *p,
const apr_array_header_t *arr)
{
//创建一个数组
apr_array_header_t *res =
(apr_array_header_t *) apr_palloc(p, sizeof(apr_array_header_t));
make_array_core(res, p, arr->nalloc, arr->elt_size, 0);
// 复制元素
memcpy(res->elts, arr->elts, arr->elt_size * arr->nelts);
res->nelts = arr->nelts;
// 没有使用的空间置 0
memset(res->elts + res->elt_size * res->nelts, 0,
res->elt_size * (res->nalloc - res->nelts));
return res;
}
合并数组
APR_DECLARE(void) apr_array_cat(apr_array_header_t *dst,
const apr_array_header_t *src)
{
int elt_size = dst->elt_size;
// dst和src元素个数 > dst已分配的元素个数则需要重新
// 分配内存空间
if (dst->nelts + src->nelts > dst->nalloc) {
int new_size = (dst->nalloc <= 0) ? 1 : dst->nalloc * 2;
char *new_data;
while (dst->nelts + src->nelts > new_size) {
new_size *= 2;
}
// 分配内存和复制数据
new_data = apr_pcalloc(dst->pool, elt_size * new_size);
memcpy(new_data, dst->elts, dst->nalloc * elt_size);
dst->elts = new_data;
dst->nalloc = new_size;
}
// 复制src到dst
memcpy(dst->elts + dst->nelts * elt_size, src->elts,
elt_size * src->nelts);
dst->nelts += src->nelts;
}








 本文深入解析APR数组数据结构,探讨其在内存管理和元素操作上的独特设计,包括创建、push、pop及复制等功能,适用于需要高效内存利用和快速元素访问的应用场景。
本文深入解析APR数组数据结构,探讨其在内存管理和元素操作上的独特设计,包括创建、push、pop及复制等功能,适用于需要高效内存利用和快速元素访问的应用场景。
















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








