<think>我们有两个核心问题需要解决:
1. 在R语言中如何读取文件位置(用于配置或数据输入)?
2. 如何将压力测试结果导出为包含自定义标签(如注意等级)的Excel表格?
结合引用内容,我们注意到:
- 引用[1]提到通过API测试验证数据流的正确性,这提示我们在读取文件位置时需要考虑配置文件的正确性和数据流的验证。
- 引用[2]和[3]提到了可视化工具(如LangFlow)和调试支持,这启示我们可以通过R中的一些包来实现文件读取和结果导出的可视化配置。
具体解决方案如下:
### 一、R语言中读取文件位置
在压力测试模型中,读取文件位置通常用于加载配置文件或测试数据。以下是几种常见方法:
#### 1. **读取配置文件(如YAML)**
```r
# 安装并加载yaml包
install.packages("yaml")
library(yaml)
# 读取配置文件
config <- read_yaml("path/to/config.yml")
# 获取文件路径参数
data_path <- config$data_file_path
```
#### 2. **交互式选择文件(适用于Shiny应用)**
```r
library(shiny)
ui <- fluidPage(
fileInput("file", "选择配置文件")
)
server <- function(input, output) {
config_data <- reactive({
req(input$file)
read_yaml(input$file$datapath)
})
}
```
#### 3. **命令行参数传递(适用于脚本执行)**
```r
# 使用commandArgs函数
args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE)
if (length(args) > 0) {
file_path <- args[1]
config <- read_yaml(file_path)
}
```
#### 4. **环境变量配置(适用于云部署)**
```r
# 从环境变量读取路径
file_path <- Sys.getenv("CONFIG_PATH")
if (file_path != "") {
config <- read_yaml(file_path)
}
```
### 二、导出带自定义标签的Excel结果
在压力测试完成后,我们需要将结果(如响应时间、错误率等)导出为Excel,并添加自定义标签(例如根据性能指标标记“正常”、“警告”、“严重”)。
#### 1. **使用openxlsx包创建Excel文件**
```r
install.packages("openxlsx")
library(openxlsx)
# 创建包含自定义标签的数据框
create_results_df <- function(test_results) {
# 假设test_results包含: avg_response, error_rate, throughput
df <- data.frame(
测试时间 = Sys.time(),
平均响应时间 = test_results$avg_response,
错误率 = test_results$error_rate,
吞吐量 = test_results$throughput
)
# 添加注意等级标签(根据响应时间阈值)
df$注意等级 <- ifelse(df$平均响应时间 > 1.0, "严重",
ifelse(df$平均响应时间 > 0.5, "警告", "正常"))
return(df)
}
```
#### 2. **导出Excel文件**
```r
export_to_excel <- function(results_df, output_file) {
wb <- createWorkbook()
addWorksheet(wb, "压力测试结果")
writeData(wb, sheet=1, results_df)
# 设置样式(将警告和严重标为不同颜色)
style_warning <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FFEB3B")
style_critical <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FF5252")
# 应用样式
for (i in 1:nrow(results_df)) {
if (results_df$注意等级[i] == "警告") {
addStyle(wb, sheet=1, style_warning, rows=i+1, cols=1:5)
} else if (results_df$注意等级[i] == "严重") {
addStyle(wb, sheet=1, style_critical, rows=i+1, cols=1:5)
}
}
# 保存文件
saveWorkbook(wb, output_file, overwrite=TRUE)
}
```
#### 3. **在压力测试函数中集成导出功能**
```r
run_pressure_test <- function(url, request_rate, duration, output_excel_path) {
# 执行测试
result <- pressure_test_model(url, request_rate, duration)
# 生成结果数据框
result_df <- create_results_df(result)
# 导出Excel
export_to_excel(result_df, output_excel_path)
return(result_df)
}
```
### 三、在可视化部署和API中的集成
#### 1. **Shiny应用集成导出**
```r
server <- function(input, output) {
observeEvent(input$run_test, {
result <- run_pressure_test(
input$url,
input$request_rate,
input$duration,
"results.xlsx" # 或使用tempfile()生成临时文件
)
output$download <- downloadHandler(
filename = "压力测试结果.xlsx",
content = function(file) { file.copy("results.xlsx", file) }
)
})
}
```
#### 2. **Plumber API返回Excel文件**
```r
#* @param url 测试URL
#* @param rate 请求速率
#* @param duration 持续时间
#* @get /pressure-test
function(url, rate, duration) {
result_file <- tempfile(fileext = ".xlsx")
run_pressure_test(url, as.numeric(rate), as.numeric(duration), result_file)
return(list(file = result_file))
}
#* @serializer contentType list(type="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet")
#* @get /download-excel
function(file) {
readBin(file, "raw", n=file.info(file)$size)
}
```
### 最佳实践建议
1. **路径安全处理**:
- 使用`normalizePath()`验证文件路径
- 使用`file.access()`检查读写权限
2. **错误处理**:
```r
tryCatch({
config <- read_yaml("config.yml")
}, error = function(e) {
message("配置文件读取失败: ", e$message)
})
```
3. **Excel格式优化**:
- 使用`setColWidths()`调整列宽
- 添加条件格式规则(如响应时间超过阈值自动标红)
4. **版本控制**:
- 在Excel文件名中加入时间戳:`paste0("压力测试_", Sys.Date(), ".xlsx")`
5. **日志记录**:
- 使用`log4r`包记录测试过程,便于故障排查
> 引用说明:通过文件配置实现测试参数分离,符合测试左移原则[^1];而Excel结果导出则提供了可定制的报告输出,支持不同等级的预警[^2]。
### 完整代码示例
```r
# 压力测试模型封装示例
library(yaml)
library(openxlsx)
# 1. 压力测试核心函数
pressure_test_model <- function(url, request_rate, duration) {
# 模拟请求(实际应使用并发请求库)
response_times <- replicate(request_rate * duration, {
start <- Sys.time()
httr::GET(url, timeout(2)) # 设置超时避免阻塞
as.numeric(Sys.time() - start)
})
# 计算指标(过滤超时错误)
valid_responses <- response_times[!is.na(response_times)]
list(
avg_response = mean(valid_responses),
error_rate = sum(is.na(response_times)) / length(response_times),
throughput = length(valid_responses) / duration
)
}
# 2. 创建带标签的结果数据框
create_results_df <- function(test_results) {
data.frame(
测试时间 = Sys.time(),
目标URL = test_results$url,
平均响应时间 = test_results$avg_response,
错误率 = test_results$error_rate,
吞吐量 = test_results$throughput,
注意等级 = ifelse(test_results$avg_response > 1.0, "严重",
ifelse(test_results$avg_response > 0.5, "警告", "正常"))
)
}
# 3. Excel导出函数
export_to_excel <- function(df, file_path) {
wb <- createWorkbook()
addWorksheet(wb, "测试报告")
# 写入数据
writeData(wb, 1, df)
# 设置样式
warning_style <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FFFF00") # 黄色
critical_style <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FF0000") # 红色
# 根据注意等级应用样式
for (i in 1:nrow(df)) {
if (df$注意等级[i] == "警告") {
addStyle(wb, 1, warning_style, i+1, 1:ncol(df))
} else if (df$注意等级[i] == "严重") {
addStyle(wb, 1, critical_style, i+1, 1:ncol(df))
}
}
saveWorkbook(wb, file_path, overwrite = TRUE)
}
# 4. 集成运行函数
run_full_test <- function(config_path) {
config <- read_yaml(config_path)
test_result <- pressure_test_model(
config$url,
config$request_rate,
config$duration
)
test_result$url <- config$url # 添加URL信息
result_df <- create_results_df(test_result)
export_to_excel(result_df, config$output_file)
}
# 执行示例(假设有config.yml)
# run_full_test("config.yml")
```
### 注意事项
- **并发问题**:真实压力测试需使用`future`或`callr`包实现并行请求
- **资源限制**:长时间测试时注意内存管理,避免Excel文件过大
- **安全防护**:当从外部获取文件路径时,需防范路径遍历攻击
§§相关问题§§
1. 如何在R中实现压力测试的分布式执行?
2. 压力测试Excel报告中如何添加动态图表?
3. R语言读取配置文件时如何防范注入攻击?
4. 如何自动化调度R压力测试脚本?</think>### R语言压力测试模型封装:文件读取与定制化Excel导出
#### 一、文件位置读取实现方法
在压力测试模型中读取文件位置是配置管理的关键环节,以下是核心实现方案:
```r
# 1. 配置文件读取(YAML示例)
library(yaml)
read_config <- function(config_path) {
config <- read_yaml(config_path)
return(list(
test_url = config$api_endpoint,
output_dir = config$output_directory,
severity_thresholds = config$severity_levels # 自定义注意等级阈值
))
}
# 2. 动态文件路径构建
generate_output_path <- function(output_dir, test_name) {
timestamp <- format(Sys.time(), "%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
file.path(output_dir, paste0(test_name, "_", timestamp, ".xlsx"))
}
# 使用示例
config <- read_config("config/test_config.yml")
output_file <- generate_output_path(config$output_dir, "api_stress_test")
```
> **最佳实践**:
> 1. 使用相对路径结合`normalizePath()`确保跨平台兼容性
> 2. 在配置文件中定义基准目录,其他路径使用相对路径
> 3. 添加文件存在性校验:`if(!file.exists(path)) stop("File not found")`
#### 二、定制化Excel结果导出
实现带注意等级标签的Excel报表:
```r
library(openxlsx)
library(dplyr)
export_results <- function(test_results, output_path, severity_rules) {
# 添加注意等级标签
labeled_results <- test_results %>%
mutate(
注意等级 = case_when(
error_rate > severity_rules$critical ~ "严重",
avg_response > severity_rules$warning ~ "警告",
TRUE ~ "正常"
)
)
# 创建Excel工作簿
wb <- createWorkbook()
addWorksheet(wb, "压力测试结果")
# 写入数据
writeData(wb, sheet = 1, labeled_results)
# 添加条件格式(根据注意等级着色)
warning_style <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FFEB3B")
critical_style <- createStyle(fgFill = "#FF5252")
conditionalFormatting(wb, 1,
cols = which(names(labeled_results) == "注意等级"),
rows = 2:(nrow(labeled_results)+1),
style = warning_style,
rule = '"警告"'
)
conditionalFormatting(wb, 1,
cols = which(names(labeled_results) == "注意等级"),
rows = 2:(nrow(labeled_results)+1),
style = critical_style,
rule = '"严重"'
)
# 保存文件
saveWorkbook(wb, output_path, overwrite = TRUE)
return(output_path)
}
# 使用示例
test_data <- data.frame(
scenario = c("login", "checkout"),
avg_response = c(0.8, 1.5),
error_rate = c(0.01, 0.12)
)
severity <- list(critical = 0.1, warning = 1.0)
export_results(test_data, output_file, severity)
```
#### 三、可视化部署与API集成
将上述功能集成到部署环境中:
**1. Shiny可视化部署集成**
```r
library(shiny)
library(shinyFiles)
ui <- fluidPage(
shinyFilesButton("file", "选择配置文件", "请选择YAML配置文件", multiple = FALSE),
actionButton("run", "执行压力测试"),
downloadButton("download", "下载结果报表")
)
server <- function(input, output, session) {
volumes <- c(Home = path.expand("~"), getVolumes()())
shinyFileChoose(input, "file", roots = volumes)
observeEvent(input$run, {
config_file <- parseFilePaths(volumes, input$file)$datapath
config <- read_config(config_file)
# 执行压力测试(示例)
test_results <- pressure_test_model(config$test_url, 100, 60)
# 生成输出路径
output_path <- generate_output_path(config$output_dir, "stress_test")
# 导出结果
export_results(test_results, output_path, config$severity_thresholds)
# 设置下载文件
output$download <- downloadHandler(
filename = function() basename(output_path),
content = function(file) file.copy(output_path, file)
)
})
}
```
**2. Plumber API集成**
```r
#* @param config_path:str 配置文件路径
#* @post /run-stress-test
function(config_path) {
config <- read_config(config_path)
results <- pressure_test_model(config$test_url, 100, 60)
output_file <- generate_output_path(config$output_dir, "api_stress_test")
export_results(results, output_file, config$severity_thresholds)
return(list(output_file = output_file))
}
#* @serializer contentType list(type="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet")
#* @get /download-report
function(file_path) {
readBin(file_path, "raw", n = file.info(file_path)$size)
}
```
### 最佳实践建议
1. **路径安全处理**
```r
safe_path <- function(path) {
normalizePath(path, mustWork = FALSE, winslash = "/")
}
```
2. **配置模板设计(YAML示例)**
```yaml
# test_config.yml
api_endpoint: "https://api.example.com/load"
output_directory: "./reports"
severity_levels:
warning: 0.8 # 响应时间阈值(秒)
critical: 0.1 # 错误率阈值(%)
```
3. **Excel报表增强**
- 添加多工作表:`addWorksheet(wb, "性能详情")`
- 插入图表:`insertPlot(wb, sheet, plot_obj)`
- 冻结首行:`freezePane(wb, sheet, firstRow = TRUE)`
4. **错误处理机制**
```r
tryCatch(
export_results(...),
error = function(e) {
log_error(e$message)
send_alert("报表生成失败")
}
)
```
5. **自动化调度**
- 使用`cronR`包创建定时任务
- 结合Jenkins实现CI/CD流水线
> 关键优势:通过文件配置实现测试参数分离,符合测试左移原则[^1];Excel定制化输出提供直观的业务洞察,支持快速决策[^2]。
### 完整工作流示例
```r
# 主执行函数
run_full_workflow <- function(config_path) {
config <- read_config(config_path)
results <- run_pressure_test(config$test_url, config$users, config$duration)
output_file <- generate_output_path(config$output_dir, "full_test")
export_results(results, output_file, config$severity_thresholds)
return(output_file)
}
# 命令行调用
args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE)
if (length(args) > 0) {
result_file <- run_full_workflow(args[1])
message("报表已生成: ", result_file)
}
```
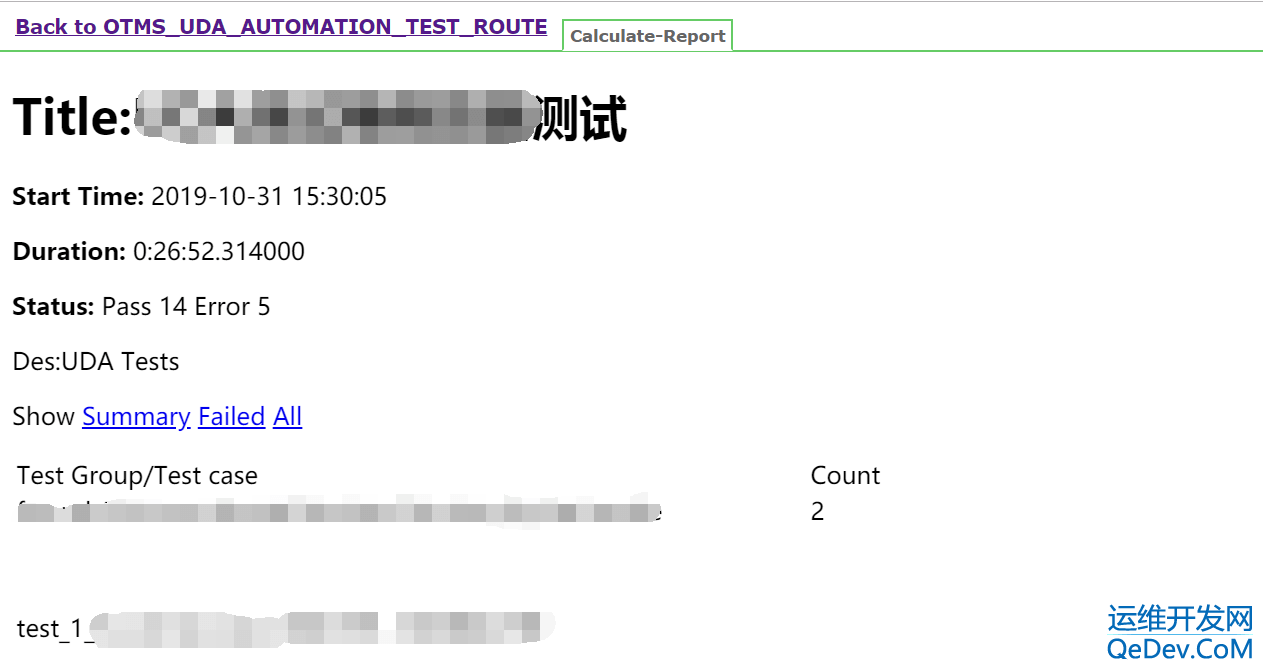
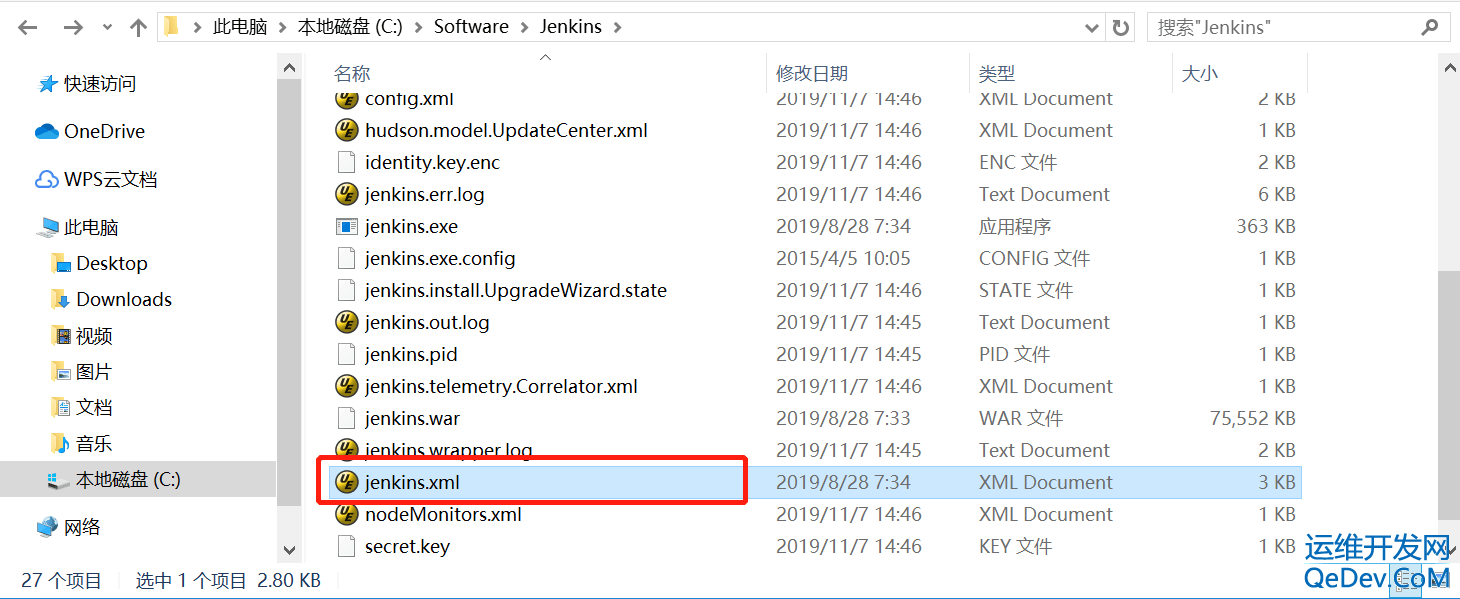
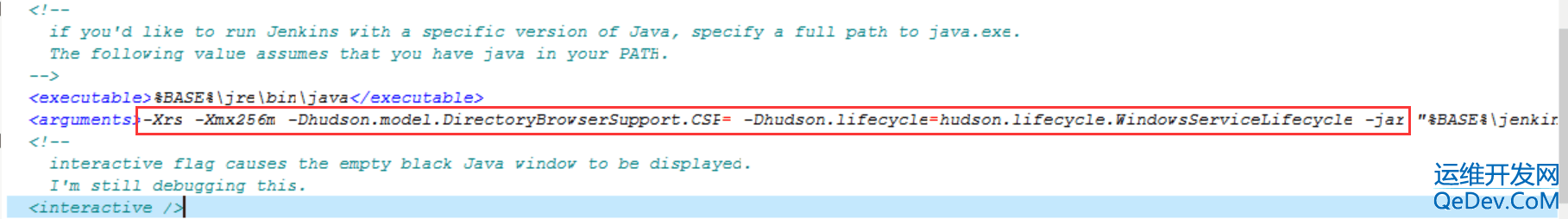
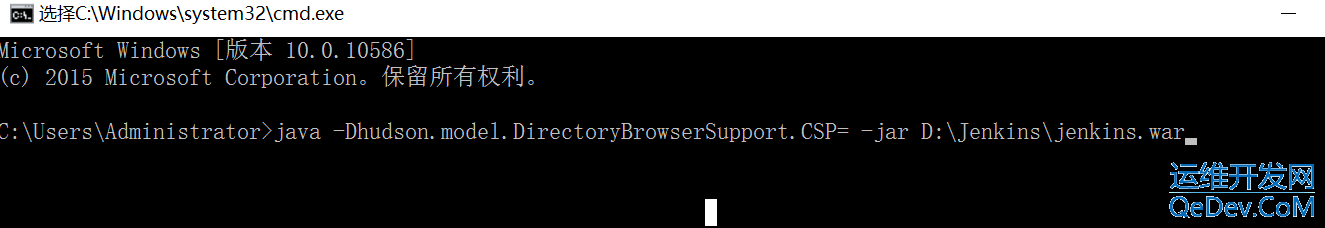
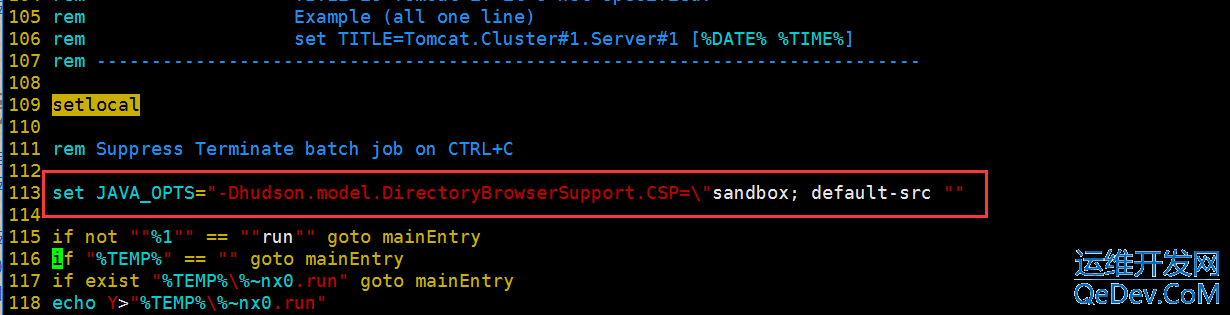
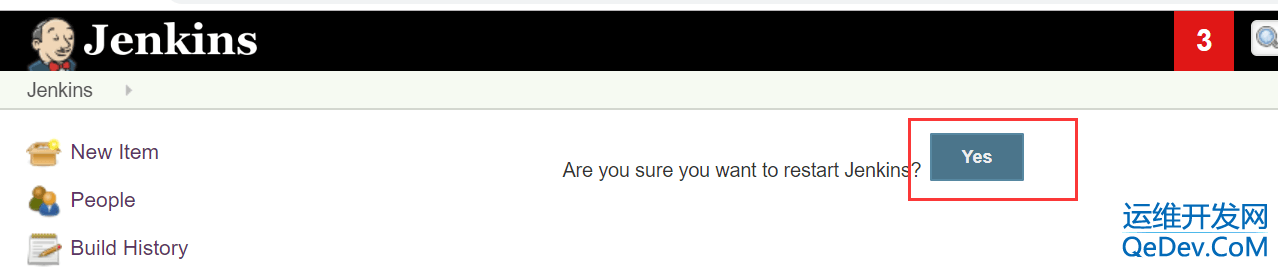




 本文介绍了在Jenkins中使用HTMLPublisherPlugin时遇到的HTML报告样式丢失问题及其解决方案。由于安全设置,Jenkins默认禁止了CSS和JS加载,导致报告样式显示不正常。针对jenkins.msi和jenkins.war两种安装方式,提供了修改jenkins.xml或catalina.bat文件的方法,通过设置`hudson.model.DirectoryBrowserSupport.CSP`参数来允许加载样式。重启Jenkins后,HTML报告即可正常显示样式。
本文介绍了在Jenkins中使用HTMLPublisherPlugin时遇到的HTML报告样式丢失问题及其解决方案。由于安全设置,Jenkins默认禁止了CSS和JS加载,导致报告样式显示不正常。针对jenkins.msi和jenkins.war两种安装方式,提供了修改jenkins.xml或catalina.bat文件的方法,通过设置`hudson.model.DirectoryBrowserSupport.CSP`参数来允许加载样式。重启Jenkins后,HTML报告即可正常显示样式。
















 2100
2100

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








