

在这一篇文章里,小编说到UDP是不可靠的,故,我们要自己写一套协议,来使UDP实现可靠性传输,这里,小编和小编的小伙伴一起,写了一个协议,实现了通过UDP来传输文件,下面就来和大家讲讲我们的思路和具体实现
在最开始的时候,我和我的伙伴想了许多的UDP协议,刚开始的时候想的特别复杂,好在,后来有位非常优秀的学长,跟我们提出了许多宝贵的建议,给我们提供了很多思路,这样,我们在后面所涉及的UDP可靠性传输才有了一个较为完全的方案。
以下便是我们的大致方案:
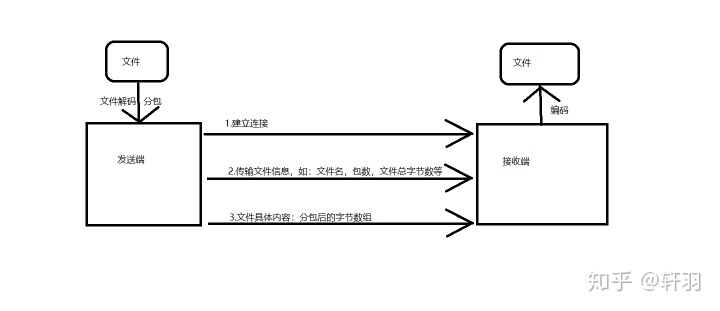
1.数据包的规定:
我们知道,在Android中要实现通信,需要DatagramPacket类
而且,在后面,会有不同类型的包,同时考虑服务器接收多方发的文件的情况,所以我们对DatagramPacket类中的字节数组做如下规定:
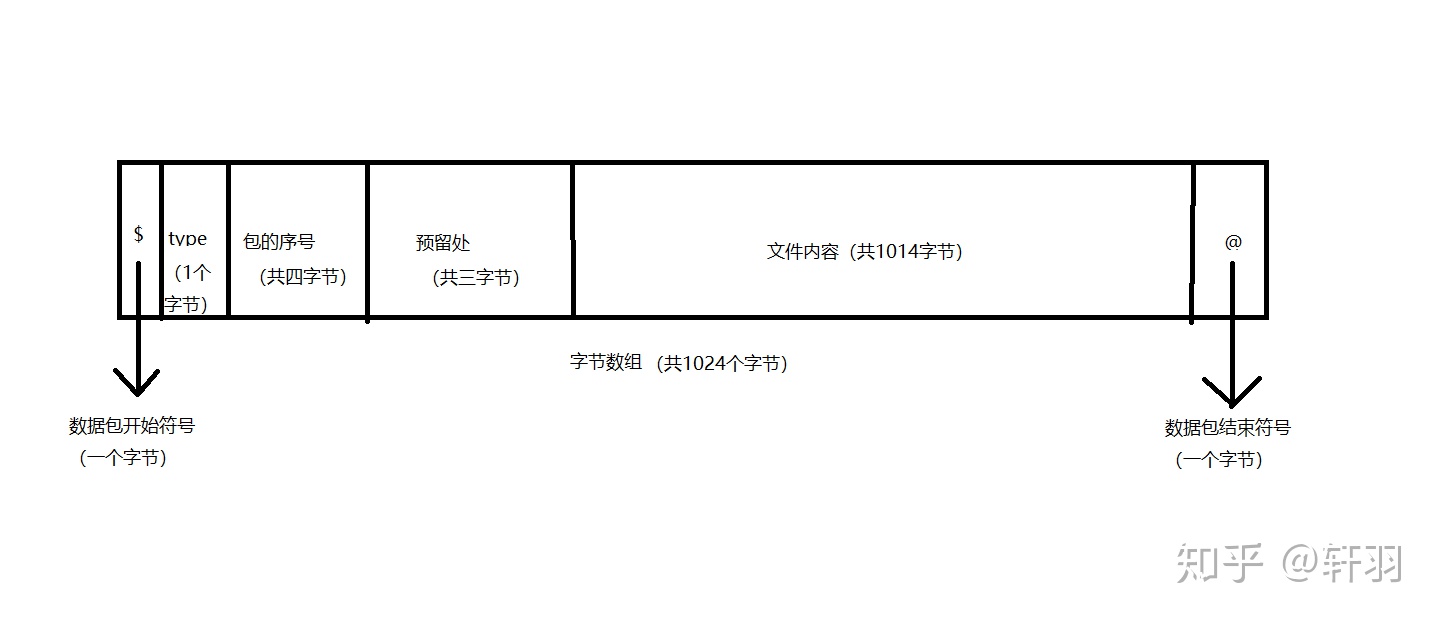
(1)在数据包开始和结束处,分别用$和@来做标记符,以此来处理网络拥挤情况而产生的分包问题
(2)type:用一个字节来做包类型判断,因为在整个文件的传输过程中,我们有三个环节,每个环节所用的包是不相同的,故对其进行分类,以示区分
(3)包的序号:这部分我们采用了四个字节,通过这四个字节,我们将其转换成int类型。因为在对文件进行分包的时候,必定会将文件的字节数组分成不同的包,为了让接收端能正确地将接收到的包进行整理,故对每一个包都进行序号排序
(4)预留处:这个当初是学长的建议,因为在实际的商业应用中,会存在文件的状态等考虑,故先预留一些字节,以实现数据包的扩展性。而在我们编写的UDP协议中,我们用其中的第一个字节来便是文件编号(考虑到多个发送端向服务器同时传输文件的情况)
(5)文件内容:这里是用1014个字节来对文件进行分包
2.建立连接
在传输文件开始时,我们采用了TCP中的三次握手来建立连接
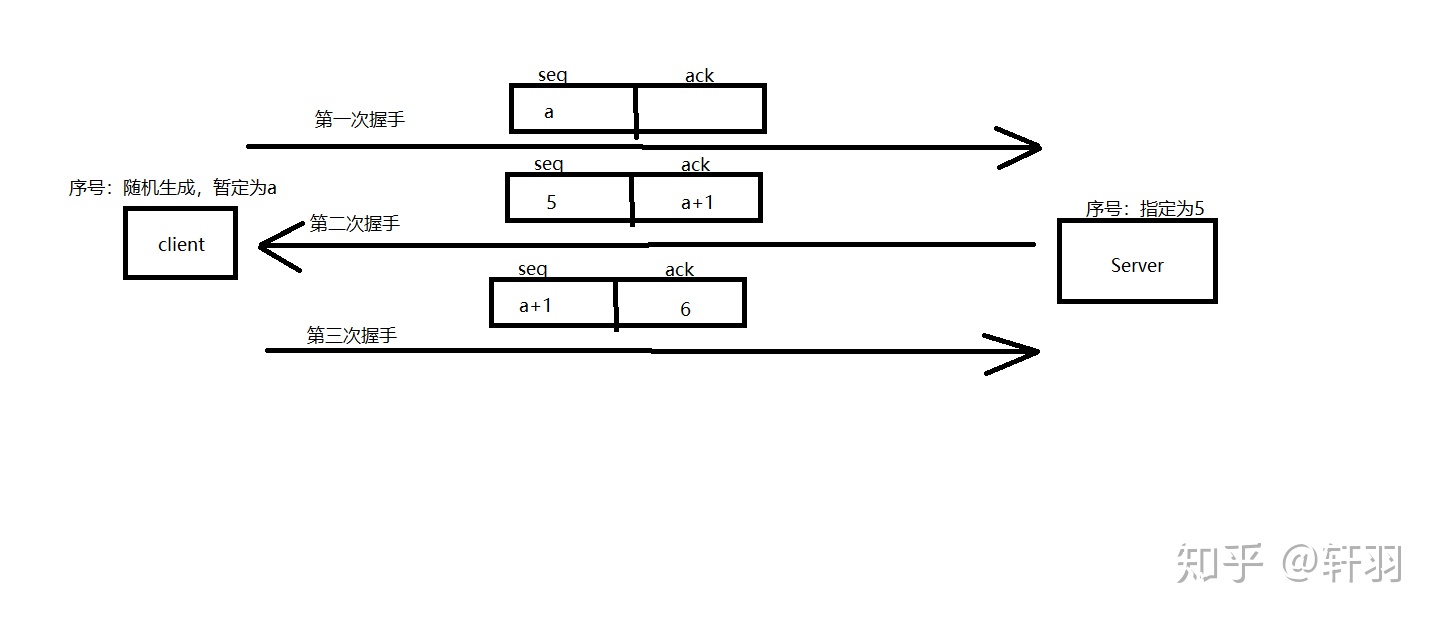
其中,我们规定Server的序号为5,而client的序号为随机生成,然后通过如图方式,进行握手。当然,在client向服务器进行第一次握手的时候,可能会造成丢包的情况,所以,在client出,会有一个重传机制。同样的,在进行第二次握手时,也需在Server中进行重传。如何重传,小编后面会讲到。在后面所讲的传输过程,均需要考虑重传。
当然了,这是传文件过程中的第一次传输,所以需对包进行分类,我们规定,建立连接时所用包的类型(type)为0。
而seq和ack这两个部分,我们在这里分别用一个字节来表示,其中均属于数据包中的文件内容部分
3.传输文件信息
当Server和client建立好连接之后,client首先需要向Server传输文件对应的信息,这样才好让Server对该文件创建空间
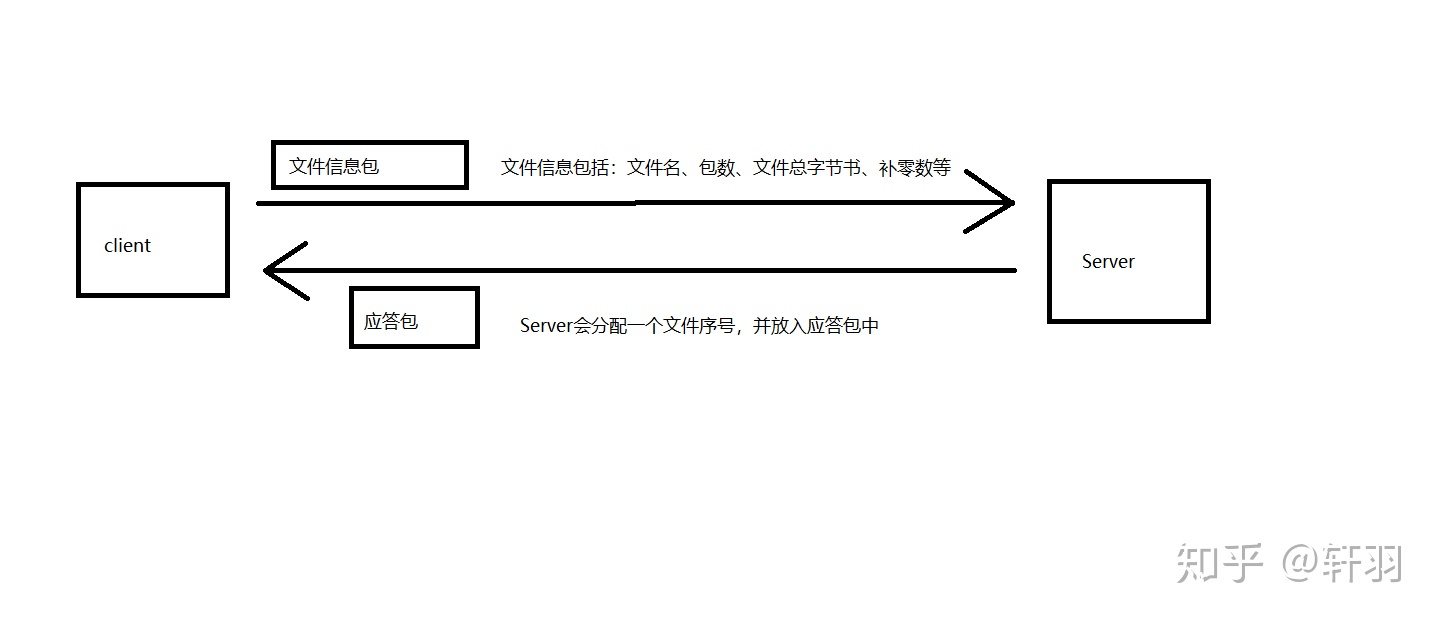
在第三次握手之后,client会将文件信息,转换成对应的字节数组,并放置于数据包中的文件内容部分,传给Server。
Server在接收到这个数据包之后,会解析其中的文件信息,然后生成对应的文件对象空间,来储存即将发过来的文件。并且Server会生成一个文件序号,放置于数据包中预留处部分。之后Server就会将该应答包返回给client
在这其中要考虑到重传,同时,这其中所用到的数据包类型(type),我们规定为1。
当然,文件信息不止小编所列的这些,还会有许多,应视情况而定,文件信息的放置方式有许多,可有设计者来定。在这里,小编和小伙伴是这样规定的:

4.文件具体内容传输
4.1 在进行文件信息传输成功后,就会开始进行文件内容的传输
(1)首先,client先将文件转换成字节数组,然后用1014个字节来对文件进行分包
(2)在分包之后,在类,在类型type(这里我们规定为2),包的序号,预留处中的文件编号处写好对应的信息,然后把文件内容写好,之后,将其发送给Server
(3)Server在接收到这个包之后,会发送一个类型3的数据包,同时也包含了文件编号,包的序号的信息,以告知client:不用再重发,Server已经接收到了
(4)当client传输完所有的包,并且均收到Server所有对应的应答包之后,就会发送一个类型4的数据包,其中附有文件编号,已告知Server:client已传完所有的数据包了。Server在接收到这个包之后,就会对包进行整合,生成对应的文件
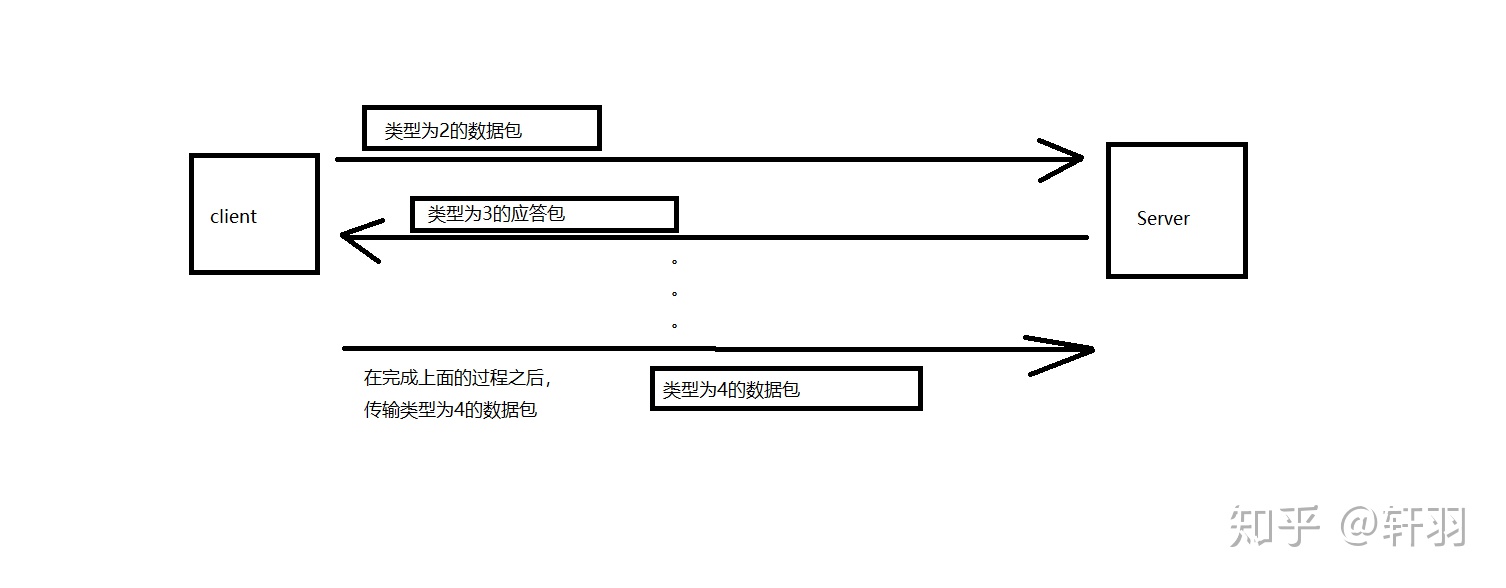
在这其中会涉及到重传机制
4.2 重传机制:
(1)在这里 小编先建立一个类,暂且称作user类,其中包括:包序号、发送次数、上次发送时间、1024字节数组三个属性。
(2)小编用HashMap来进行存储这个类的对象,其中包的序号作为 key,user对象作为value
(3)在对文件进行分包之后,就对每一个数据包创建一个user对象,并完善其中的信息,添加至HashMap中;在收到对应的应答包之后,就remove HashMap中对应的user对象
(4)新开一个线程,不断地循环,并判断是否需要重发:若当前发送时间距上次发送时间相差超过3000ms,则重发。当发现HashMap中已经没有存储对象时,则开始发送数据类型为4的 数据 包 ,并终止线程
5.文件编码
Server接收到类型为4的数据包之后,就开始通过文件名,合并每个数据包中的,文件内容部分的字节,然后通过文件 IO流生成对应的文件
当然了,在这里小编和小伙伴们也只是实现了把文件从手机端传送到了电脑端,而之后从电脑端传输文件到手机端这一环节,小编和小伙伴虽然写了,但是由于时间等原因,还没来得及演示,所以现在还只能说跟大家分享这些,之后,小编把后面部分完成了就会跟大家分享的。
以下便是小编负责Server部分,这部分只包含从client传文件到Server的过程
1.UDPserver代码:
package Server;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import Client.SendThread;
import Client.UserSend;
/ * 基站类,用于处理发过来的1024的包 /
public class UDPserver {
// 服务器端口号
private int port = 9999;
// 服务器序号,用于三次握手
private String no = "5";
int no1 = 5;
// 服务器IP地址
String serverIP = "";
// 目标地址
InetAddress destaddress = null;
int destport = 8888;
// 接收通道
DatagramSocket socket = null;
// 接收包
DatagramPacket request = null;
// 接收的字节数组
byte[] msg = null;
// 文件队列,采用HashMap方法,总共有255个
HashMap<Integer, User> filemap = new HashMap<Integer, User>();
// 缓存区队列
bufferstorage[] bstorage = new bufferstorage[255];
// 得到发过来的包
private void getPackage(byte[] msg, DatagramPacket request,
DatagramSocket socket) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.msg = msg;
this.request = request;
this.socket = socket;
destaddress = request.getAddress();
//destport = request.getPort();
//System.out.println("destaddress="+destaddress);
System.out.println("开始对包进行类别判断");
// 对包进行类别判断
Adjusttype();
}
// 字节数组类型判断
private void Adjusttype() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 获取类型的字节
byte[] b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1, b, 0, 1);
//System.out.println(msg);
// 转换成对应字符串
String type = b[0]+"";//new String(b);
System.out.println("包的类型type=" + type);
// 不同类型对应不同的处理方式
if ("0".equals(type)) {
solve0();
}
if ("1".equals(type)) {
solve1();
}
if ("2".equals(type)) {
solve2();
}
if ("3".equals(type)) {
}
if ("4".equals(type)) {
solve4();
}
}
// 分配文件序号
private int getfileno() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int i = 0;
for (; i < 255; i++) {
if (filemap.get(i) == null)
break;
}
return i;
}
/**
* 把一个int数值转为6个字节
*
* @param i
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intTo5Byte(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[5];
result[0] = (byte) ((i >> 32) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte) ((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte) ((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte) ((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[4] = (byte) (i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
/**
* 把一个int数值转为4个字节
*
* @param i
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intTo4Byte(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[4];
result[0] = (byte) ((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte) ((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte) ((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte) (i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
/**
* 把字符串的每个字符转化为两个字节 返回一个字节数组
*
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static byte[] get2Byte(String str) throws Exception {
int length = 0;// 字节数组的长度
byte[] buffer1 = new byte[1024];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char a = str.charAt(i);
byte[] bu = new byte[2];
if (a < 256) { // 英文字符
bu[0] = 0;
bu[1] = (byte) a;
} else { // 中文字符
bu = (a + "").getBytes("GBK");
}
buffer1[length++] = bu[0];
buffer1[length++] = bu[1];
}
byte[] buffer2 = new byte[length];
System.arraycopy(buffer1, 0, buffer2, 0, length);
return buffer2;
}
/**
* 把输入的字节数组还原为字符串的方法(每两位还原为一个字符)
*
* @return
*/
public static String getString(byte[] buffer) throws Exception {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i += 2) {
byte[] bu = new byte[2];
bu[0] = buffer[i];
bu[1] = buffer[i + 1];
if (bu[0] == 0) { // 高位为0,是英文字符
char a = (char) bu[1];
str += a;
}
if (bu[0] != 0) {
String a = new String(bu, "GBK");
str += a;
}
}
return str;
}
/**
* 把一个int数值转化为2个字节
*
* @param num
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intTo2Byte(int num) {
byte[] twoByte = new byte[2];
if (num > 255) {
twoByte[0] = (byte) (num / 256);
twoByte[1] = (byte) (num - (num / 256) * 256);
} else {
twoByte[0] = 0;
twoByte[1] = (byte) num;
}
return twoByte;
}
// 4个字节转换成int
public static int byteArray2Int(byte[] b) {
int num = b[3] & 0xFF;
num |= ((b[2] << 8) & 0xFF00);
num |= ((b[1] << 16) & 0xFF0000);
num |= ((b[0] << 24) & 0xFF0000);
return num;
}
// 两个字节转换成int类型
public static int tBytesToint(byte[] b) {
// int a =(((int) b[0]) << 8) + b[1];
// if (a < 0) {
// a = a + 256;
// }
// return a;
int num = b[1] & 0xFF;
num |= ((b[0] << 8) & 0xFF00);
// num |=((b[1] <<16)& 0xFF0000);
// num |=((b[0] <<24)& 0xFF0000);
return num;
}
// 6ge字节转换成int类型
public static int sBytesToint(byte[] b) {
int num = b[5] & 0xFF;
num |= ((b[4] << 8) & 0xFF00);
num |= ((b[3] << 16) & 0xFF0000);
num |= ((b[2] << 24) & 0xFF0000);
num |= ((b[1] << 32) & 0xFF0000);
num |= ((b[0] << 40) & 0xFF0000);
return num;
}
// 三次握手的处理方式
public void solve0() throws IOException {
// 存储对应的整数信息
int flag = 0;
String s = "";
// 获取ack的字节,并转出成字符串
byte[] b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1022, b, 0, 1);
flag = b[0];
//flag = Integer.valueOf(ack).intValue();
// 第三次握手的情况
if (flag == no1 + 1) {
// 获取对应的文件序号
b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 6, b, 0, 1);
int bnno = b[0];
//int bnno = Integer.valueOf(bno).intValue();
// 把之前的缓存区数组中的信息消除,与第一次握手判断重发的存储地方消除
this.bstorage[bnno] = null;
System.out.println("第三次握手:fileno=" + bnno);
}
// 第一次握手的情况
else {
// 判断是否为重发的消息
// 获取seq的字节,并转化成数字
b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1021, b, 0, 1);
int se = b[0];//new String(b);
//int se = Integer.valueOf(seq).intValue();
System.out.println("seq+++++++++++++++++++++++++===="+se);
se++;
msg[1022] = (byte)se;
msg[1021] = (byte)no1;
// 生成一个文件对象,同时存入文件队列中
//User user = new User();
// 分配文件的序号
int fileno = getfileno();
//user.fileno = fileno;
//filemap.put(fileno, user);
msg[6]=(byte)fileno;
// 发送给手机端消息
request = new DatagramPacket(msg, msg.length, destaddress, destport);
socket.send(request);
// 将此消息保存,以便未收到消息时,再次发送
bufferstorage bs = new bufferstorage();
bs.sendtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
bs.destaddress = this.destaddress;
bs.destport = this.destport;
bs.socket = this.socket;
System.arraycopy(msg, 0, bs.msg, 0, msg.length);
this.bstorage[fileno] = bs;
System.out.println("第一次握手:seq=" + (se - 1) + ";fileno=" + fileno);
}
}
// 得到文件信息
public void solve1() throws Exception {
/*
* 分解包的信息内容
*/
// 得到文件序号
byte[] b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 6, b, 0, b.length);
int fno = b[0]; // 获取文件序号
User user = new User();//filemap.get(fno);
// 获取补零数
b = new byte[2];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1021, b, 0, b.length);
int num0 = tBytesToint(b);
// 获取文件总字节数
b = new byte[6];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1015, b, 0, b.length);
int bytenum = sBytesToint(b);
// 获取文件包数
b = new byte[4];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1011, b, 0, b.length);
int packnum = byteArray2Int(b);
// 获取文件名
b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1010, b, 0, b.length);
int num = b[0];
b = new byte[num];
System.arraycopy(msg, 1010 - num, b, 0, b.length);
String filename = getString(b);
user.get(filename, packnum, bytenum, num0, fno);
filemap.remove(fno);
filemap.put(fno, user);
// 返回同样的包
request = new DatagramPacket(msg, msg.length, destaddress, destport);
socket.send(request);
// 将该包放入缓存区bstorage中,以便判断是否重发
bufferstorage bs = new bufferstorage();
bs.sendtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.arraycopy(msg, 0, bs.msg, 0, msg.length);
this.bstorage[fno] = bs;
bs.destaddress = this.destaddress;
bs.destport = this.destport;
bs.socket = this.socket;
System.out.println("获取到文件信息:fno=" + fno + "num0=" + num0 + "bytenum="
+ bytenum + "packnum=" + packnum + "filename=" + filename+"总字节数="+num);
}
// 得到文件内容
public void solve2() throws IOException {
// 得到当前包的序号
byte[] b = new byte[4];
System.arraycopy(msg, 2, b, 0, b.length); // 获取包序号的字节数组
int pno = byteArray2Int(b); // 包序号pno
// 得到文件序号
b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 6, b, 0, b.length);
//String s = new String(b);
int fno = b[0]; // 获取文件序号
System.out.println("获取到当前包序号:" + pno+";fno="+fno);
// 将solve1()中放入缓存区的包给消除
this.bstorage[fno] = null;
// 将对应的文件序号user中flist中的对应字节数组复制
User user = filemap.get(fno);
System.out.println("类型2的user"+user.toString());
System.out.println("类型2的user.filename:"+user.filename);
System.out.println("类型2的user.fileno:"+user.fileno);
//System.out.println("msg:"+msg.toString()+";");
// fcontent f= new fcontent(); //
user.filelist[pno-1] =f;
//System.out.println("user.filelist[pno-1].b:"+user.filelist[pno-1].b.toString()+";");
System.arraycopy(msg, 8, user.filelist[pno-1].b, 0, user.filelist[pno-1].b.length);
// 返回给手机端消息:服务器已收到该消息
b = new byte[1];
b[0] =3; //"3".getBytes();
System.arraycopy(b, 0, msg, 1, b.length);
request = new DatagramPacket(msg, msg.length, destaddress, destport);
socket.send(request);
}
// 得到客户端的消息:所有包已发完,则开始编码文件
public void solve4() throws IOException {
// 得到文件序号
byte[] b = new byte[1];
System.arraycopy(msg, 6, b, 0, b.length);
//String s = new String(b);
int fno = b[0]; // 获取文件序号
System.out.println("类型4的文件编号:"+fno);
// 将对应的文件序号user中flist中的对应字节数组复制
User user = filemap.get(fno);
System.out.println("类型4的user.filename:"+user.filename);
//System.out.println("user.getfilebyte():"+user.getfilebyte().toString());
user.getfilebyte();
//byte[] filebyte = user.filebyte;
// 将字节数组转换成对应的文件
File f = new File("D:" + user.filename);
FileOutputStream fileostr = new FileOutputStream(f);
fileostr.write(user.filebyte);
System.out.println("已生成对应的文件");
// 消除filemap中该文件的信息
//filemap.remove(fno);
fileostr.flush();
fileostr.close();
//开始传输文件给传输对象
SendThread sendthread = new SendThread(destaddress, user.filename, "D:");
sendthread.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 接收基站
final UDPserver Server = new UDPserver();
// 服务器端口号
int port = 9999;
// 接收通道
DatagramSocket socket = null;
// 三次握手所要字节数组
byte[] msg = new byte[1024];
// 接收包
DatagramPacket request = null;
System.out.println("Sever begins to contact");
// 创建对应的通道和传送包
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(port);
} catch (SocketException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
request = new DatagramPacket(msg, msg.length);
// 开启刷新缓存区的线程
new Thread() {
public void run() {
int i = 0;
bufferstorage bs;
while (true) {
i = i % 255;
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
bs = Server.bstorage[i];
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
if (bs != null && (time - bs.sendtime) > 3000) {
Server.request = new DatagramPacket(bs.msg,
bs.msg.length, bs.destaddress, bs.destport);
try {
bs.socket.send(Server.request);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("重发包一次");
Server.bstorage[i].sendtime = System
.currentTimeMillis();
}
i++;
}
}
}.start();
System.out.println("刷新缓存区的线程开启");
// 开启接收
while (true) {
System.out.println("在接收消息中");
try {
socket.receive(request);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("接收到消息,进入基站");
// 接收到后,进入基站
Server.getPackage(msg, request, socket);
// 开启三次握手线程
// UDPserver Server = new UDPserver(socket , request.getAddress());
// Server.start();
}
}
}2.User部分
package Server;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class User {
//文件名
String filename = null;
//包个数
int packnum;
//文件总字节数
int bytenum;
//补零数
int num0;
//文件序号
int fileno;
//文件内容字节数组
fcontent[] filelist ;
//ArrayList<fcontent> filelist = new ArrayList<fcontent>();
//文件总字节数组
byte[] filebyte;
//文件传输对象
//得到相应信息
public void get(String filename, int packnum, int bytenum, int num0, int fileno) {
this.filename = filename;
this.packnum = packnum;
this.bytenum = bytenum;
this.num0 = num0;
this.fileno = fileno;
filelist = new fcontent[packnum];
for(int i = 0; i<packnum ; i++){
fcontent f= new fcontent();
filelist[i] =f;
}
filebyte = new byte[bytenum];
}
//得到文件的总字节数组
public void getfilebyte() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int j = 0,i = 0;
for( i = 0;i<packnum-1;i++){
System.arraycopy(filelist[i].b, 0, filebyte, j*1014, filelist[i].b.length);
j++;
}
System.arraycopy(filelist[i].b, 0, filebyte, j*1014, filelist[i].b.length-num0);
}
}3.bufferstorage代码部分
package Server;
import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress;
public class bufferstorage {
public byte[] msg = new byte[1024];
//上次发送时间
public long sendtime = 0;
//对应的IP地址和port端口
// 目标地址
public InetAddress destaddress = null;
public int destport = 0;
// 接收通道
public DatagramSocket socket = null;
}
4.fcontent代码部分
Package Server;
/*
* 文件包字节数组
*/
public class fcontent {
public byte[] b = new byte[1014];
}





















 1204
1204

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








