1.环境搭建
1.1 anaconda环境配置
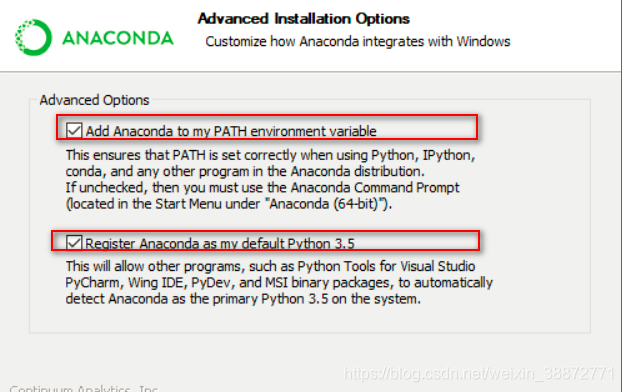
1st 选框 :将Anaconda设置添加到系统环境,如果没有勾选,需要使用Anaconda 命令行
2nd 选框 : 将Anaconda设置为系统默认的Python 3.5 环境
1.2解释器
解释器负责执行.py文件。
Python解释器类型包括:
CPython(C语言开发)、
IPython(功能与CPython相同,交互性增强)、
PyPy(动态编译;代码执行速度提高;和CPython存在差异,两者解释执行结果可能不同)
Jython(Java平台Python解释器)

IronPython(微软.NET平台解释器)

2.python初体验
2.1 print and input
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: latin-1 -*-
import os, sys
#print 'Hello World, Datawhale' #SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print('Hello World, Datawhale')?
print ('Hello World, Datawhale')
print('Good,Morning,Datawhale') # 对比逗号是否会出现空格效果,Geany编写不会?还是代码错误
print('Goood Morning, Datawhale')
#output:
#Hello World, Datawhale
#Good,Morning,Datawhale
#Goood Morning, Datawhale
###接上述问题,Python交互环境
>>> print('to be or not ','to be','is not a question')
to be or not to be is not a question #逗号效果出现,not与to之间有两空,be和is之间有一空格
print('100+100=',100+100) #单引号内为字符串
#output: 100+100=200
# input 支持交互式命令行;编译器仅能通过变量赋值,达到input 的效果?未解决!!!
###已解决,Python版本问题? 待查证
>>> name = raw_input()
Datawhale
>>> name
Datawhale
>>> name = input() #Python 3.7.2 测试成功
Datawhale
>>> name
'Datawhale'
>>>
>>> name = input('Please input your name ') # P372 测试成功
Please input your name Honey
>>> name
'Honey'
3.python基础讲解
3.1 python变量特性+命名规则
变量特性:存储信息并可调用,值可变化
命名规则; 变量是标识符的一种;标识符命名规则:
a.首字符为字母或下划线
b.其他部分:字母、数字、下划线
c.名称区分大小写
3.2 注释方法
“#”
print('100+100=',100+100) #单引号内为字符串
3.3 python中“:”作用
3.3.0 语句以冒号":"结尾时,缩进的语句视为代码块
3.3.1 数组中默认选择全部
3.3.2 数组中指定范围
3.3.3 列表中指定元素范围
#列表:
list[e:]即第e+1项到最后一项
list[:e]即第一项到第e项
list[e:f]即第e+1 项到f项
3.4 学会使用dir( )及和help( )
dir([object]) #返回模块的属性列表。
help() # 了解模块、类型、对象、方法、属性的详细信息
3.5 import使用
python中,每个.py文件被称之为模块,每个具有__init__.py文件的目录被称为包。只要模块或者包所在的目录在sys.path中,就可以使用import 模块或import 包来使用。
3.6 pep8介绍
Python代码编码规范基于Python主要发行版本的标准库。Python的C语言实现的C代码规范请查看相应的PEP指南。这篇文档以及PEP 257(文档字符串的规范)改编自Guido的原始文章《Python Style Guide》,同时添加了一些来自Barry的指南。
这篇规范指南随着时间的推移而逐渐演变,随着语言本身的变化,过去的约定也被废弃。 许多项目有自己的编码规范,规范之间出现冲突时,应该以项目自身的规范为主要参考。
4.python数值基本知识
4.1 python中数值类型,int,float,bool,e记法等
4.1.1整数:十六进制用0x前缀和0-9,a-f表示,
4.1.2浮点数:整数运算永远时精确的,浮点数运算可能会有四舍五入的误差
4.1.3字符串: ’ 或 " 括起来,
用反斜杠 \ 转义特殊字符:
\n 换行;、\t 制表符;
字符\本身也要转义,"\"表示的字符就是\
4.1.4布尔值:
两种值:True、False;
and/or/not 运算
4.1.5空值:None , 不能等同于0
4.1.6列表:元素类型可以不同;嵌套
4.1.7元组:元素不能修改、小括号 () ,逗号隔开
4.1.8集合:成员关系测试和删除重复元素
4.1.9字典:无序的对象集合
4.2 运算符
4.2.1 算数运算符:
+、-、*、/、%取模、**幂、//取整
4.2.2 逻辑运算符
and / or / not
4.2.3 成员运算符
in / not in
4.2.4 身份运算符
is / is not
4.2.5 运算符优先级
| 运算符 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| ** | 指数(最高) |
| ~+ - | 按位翻转、一元加号和减号 |
| * / % // | 乘、除、取模、取整数 |
| + - | 加、减 |
| >><< | 右移、左移运算符 |
| & | 位‘AND’ |
| ^ | 位运算符 |
| <= < > >= | 比较运算符 |
| <> == != | 等于运算符 |
| = %= /= //= -= += = **= | 赋值运算符 |
| is is not | 身份运算符 |
| in not in | 成员运算符 |
| not and or | 逻辑运算符 |
#code 身份运算符
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: latin-1 -*-
import os, sys
#身份运算符
a = 10
b = 100
if(a is b):
print ("1 - a and b same object")
else:
print ("1 - a and b different object")
if (a is not b):
print ("2 - a and b different object")
else:
print(" 2 - a and b same object")
#修改a值
a = 100
if(a is b):
print ("3 - a and b same object")
else:
print ("3 - a and b same object")
if (a is not b):
print ("4 - a and b different object")
else:
print(" 4 - a and b same object")
#output:
#1 - a and b different object
#2 - a and b different object
#3 - a and b same object
#4 - a and b same object








 本文从环境搭建开始,详细介绍Anaconda配置、Python解释器类型、基本语法如print与input的使用,变量命名规则,注释方法,以及核心概念如':'的作用。涵盖数值类型、列表、元组、集合、字典的基础知识,和运算符、身份运算符的使用,适合Python初学者。
本文从环境搭建开始,详细介绍Anaconda配置、Python解释器类型、基本语法如print与input的使用,变量命名规则,注释方法,以及核心概念如':'的作用。涵盖数值类型、列表、元组、集合、字典的基础知识,和运算符、身份运算符的使用,适合Python初学者。
















 6057
6057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








