文章目录
What is IoT?
IoT stands for interconnection of internet enabled devices or things unlike people only connectivity used in today’s internet. Due to huge growth in demand for IoT compliant devices chip makers are having great future ahead. IoT is the short form of Internet of Things. According to cisco and other organizations there will be about 50 billion devices connected using internet in the year 2020. Devices based on ethernet, zigbee, bluetooth and wifi will have huge requirements in consumer electronics segment. Cellular devices based on GSM and LTE also will be available to have connectivity with cellular wireless networks,
IoT Applications
IoT devices are used for following applications:
• In consumer market for smart home control(lighting,security,comfort),Optimized energy use maintenance.
• In Industrial market for smartmeters, Wear-out sensing devices, Manufacturing control, Climate control
• In Automotive industries for parking, traffic flow control, Anti-theft devices, Location tracking etc.
• In Environmental for species tracking, weather prediction and resource management.
• In agriculture market for crop management and soil analysis.
• In military for resource allocation, threat analysis, troop monitoring etc.
• In medical industry for wearable devices, implanted devices and telehealth services.
• In retail for product tracking, Inventory control, focused marketing, etc.
IoT Entities
There are two major subsystems involved in the IoT network viz. front end part and back end part. Front end is mainly consists of IoT sensors which are MEMS based. It includes optical sensors, light sensors, gesture and proximity sensors, touch and fingerprint sensors, pressure sensors and more.
Back end consists of cellular, wireless and wired networks which are interfaced with IoT devices. The devices will report to the central servers and also interact with databases in the backbone network. Routers and gateways are part of the wireless backbone networks.
IoT Protocol layers

As the standard has not been finalized for IoT but one can think of IoT having 4 protocol layers as shown in the figure-2. Sensing and Identification include various smart sensor devices based on GPS, RFID, WiFi etc. Network connectivity layer is based on wired and wireless network such as WLAN, WPAN, WMAN, ethernet, optical fiber and more.Other two layers are information Processing layer and application layer.
Cellular IoT

Wireless cellular companies are working towards providing collectivity and enhancement to existing wireless devices to support emerging IoT market.
IoT Device and components
The IoT device mainly consists of battery for providing power. It should have long life approx. about 10 years. The parts include interfacing with sensors and connectivity with wireless and wired network. Hence it include small part of physical layer and also upper protocol layers to interface with application layer. Devices should support both IPV4 and IPV6 based IP protocols. IoT devices must have receiver sensitivity atleast 20dB better than non-IoT devices. The IoT devices should be cheaper about less than $10.
IoT Wireless Technologies

THREAD
What is THREAD
Following wireless home network requirements for connected devices lead to the development of new technology known as thread.
• Low Power
• Resilient (mesh network)
• IP based
• Open protocol
• secure and user friendly
• Fast time to market
• Existing radio silicon
The thread technology is mainly targetted for M2M and IoT market. It is based on existing 802.15.4 standard. A software upgrade to existing 802.15.4 products can add thread features.
THREAD basics in M2M and IoT
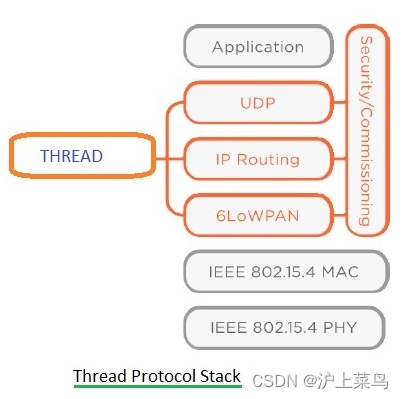
Following are the silent features of Thread.
• Uses 6LoWPAN and carries IPv6 packets
• Runs on existing 802.15.4 silicon
• New security architecture introduced to support easy addition and removal of security products.
Figure depicts thread protocol stack which mentions layers added for this technology to exist. It supports many application layers including low bandwidth ones which runs over Ipv6 protocol.
This Thread technology is designed and developed to support following products to be used in the home.
• Security products
• Safety products
• Lighting products
• Energy management products
• climate control products
• Access control products
• Home or household appliances
Some of products which uses thread technology are as follows:
• CoAP and Smart Objects
• ZigBee Smart Energy 2.0
• ECHONET Lite
WLAN
Introduction
Let us understand LAN first. LAN means Local Area Network. It is connection of more than one computer using some medium. For the case of LAN this medium will be wired which include Ethernet cable, fiber optic etc. As shown in figure on the left side LAN can be formed using either Ethernet switch or hub or router. All the computers are connected with this switch/Hub/router. This Switch/Hub/router is connected with cable modem provided by ISP(Internet Service Provider). Cable modem connects with ISP’s Web server i.e. Internet. The advantages of LAN are many such as speed of data communication (as Ethernet works at 10/100 Mbps), sharing of common resources such as printer, internet connection etc.
Basics of WLAN
WLAN is the short form of Wireless Local Area Network. Unlike LAN, WLAN will have Wireless medium which include radio wave, microwave etc. WLAN compatible Access points or routers are available which converts LAN to become WLAN. So that WLAN devices such as laptop, ipad, tablet can communicate any system in LAN. This wifi router is connected with cable modem on one side using cable. The other side of wifi router is wireless medium, by which it will connect with WLAN devices. There are various PC cards or USB dongles available with WLAN features so that they can be connected with WiFi network or WLAN network. The same is depicted in the figure on right hand side (laptop with wireless adapter card).
Wireless LAN works on radio frequency of usually around 2.5GHz or 5GHz. There are different flavors in WLAN for different data rates and distance coverage. They are 11a, 11b, 11g, 11n, 11ac, 11ad etc. developed and maintained by IEEE and popularly called as IEEE Standards. These IEEE standards define PHY and MAC layers of 11a/11b/11g/11n/11ac/11ad and upper layers are developed by IETF.
WLAN is the short form of Wireless Local Area Network. Unlike LAN, WLAN will have Wireless medium which include radio wave, microwave etc. WLAN compatible Access points or routers are available which converts LAN to become WLAN. So that WLAN devices such as laptop, ipad, tablet can communicate any system in LAN. This wifi router is connected with cable modem on one side using cable. The other side of wifi router is wireless medium, by which it will connect with WLAN devices. There are various PC cards or USB dongles available with WLAN features so that they can be connected with WiFi network or WLAN network. The same is depicted in the figure on right hand side (laptop with wireless adapter card).
Wireless LAN works on radio frequency of usually around 2.5GHz or 5GHz. There are different flavors in WLAN for different data rates and distance coverage. They are 11a, 11b, 11g, 11n, 11ac, 11ad etc. developed and maintained by IEEE and popularly called as IEEE Standards. These IEEE standards define PHY and MAC layers of 11a/11b/11g/11n/11ac/11ad and upper layers are developed by IETF.

WLAN Standards
WLAN devices are designed and developed as per IEEE standards. There are different versions based on RF frequency, data rate and coverage requirement. They are IEEE-802.11a, IEEE-802.11b, IEEE-802.11g, IEEE-802.11n, IEEE-802.11ac, IEEE-802.11ad etc. developed and mai








 本文详细介绍了物联网(IoT)的各种无线技术,包括THREAD的基本原理和在M2M、IoT中的应用,WLAN的标准和设备,LORA的技术特点,ZIGBEE的网络构成和协议栈,RFID的相关术语、应用和成本,NFC的操作模式和应用,以及EnOcean的无电池能量采集无线技术。物联网的应用广泛,涵盖消费电子、工业、农业、医疗等多个领域,而这些无线技术则为物联网的发展提供了基础支撑。
本文详细介绍了物联网(IoT)的各种无线技术,包括THREAD的基本原理和在M2M、IoT中的应用,WLAN的标准和设备,LORA的技术特点,ZIGBEE的网络构成和协议栈,RFID的相关术语、应用和成本,NFC的操作模式和应用,以及EnOcean的无电池能量采集无线技术。物联网的应用广泛,涵盖消费电子、工业、农业、医疗等多个领域,而这些无线技术则为物联网的发展提供了基础支撑。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








